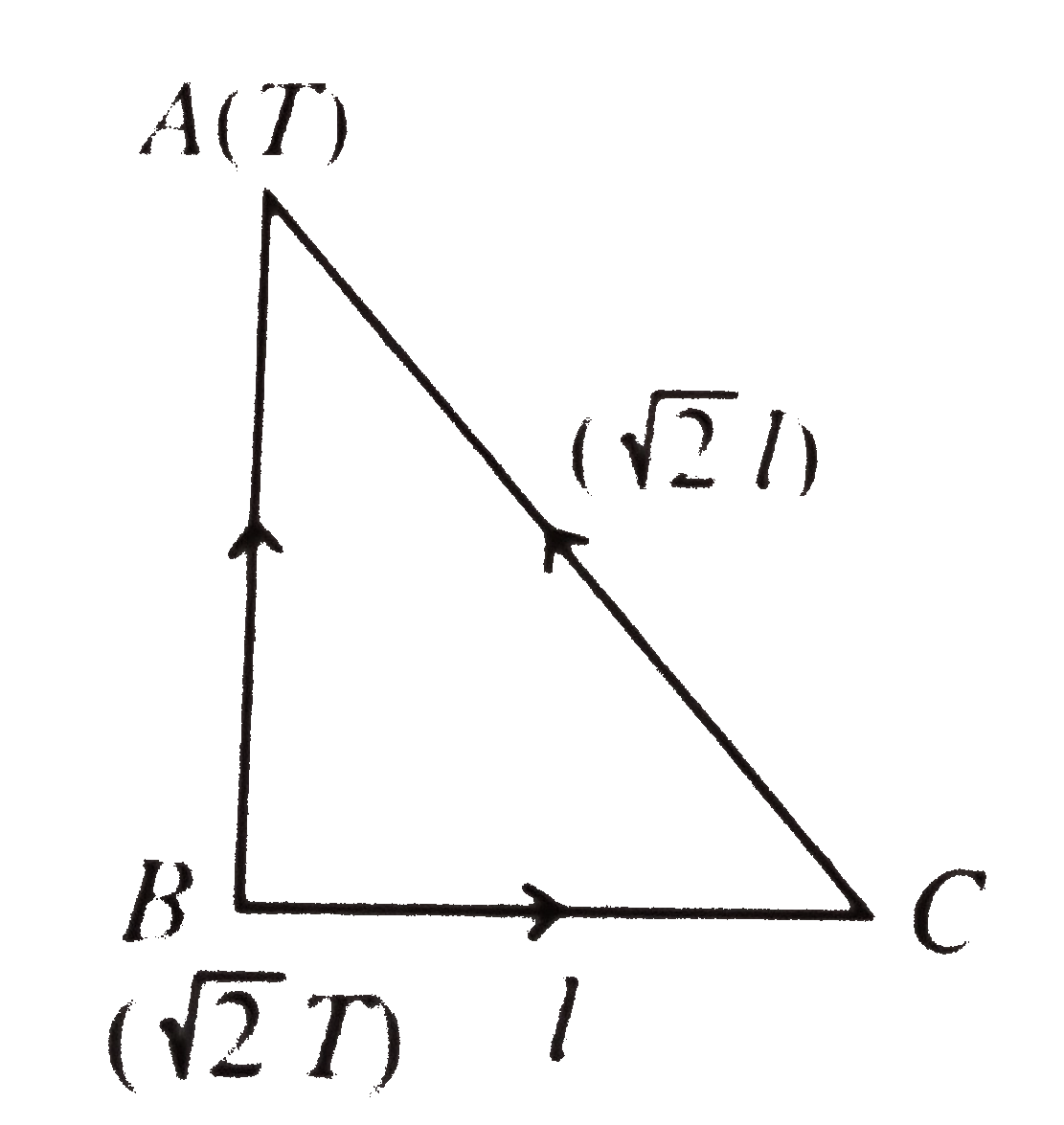A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|25 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|30 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|25 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 2.6|20 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CALORIMETRY-Single Correct
- A steel ball of mass 0.1 kg falls freely from a height of 10 m and bou...
Text Solution
|
- The earth receives its surface radiation from the sun at the rate of 1...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of identical cross-sectional area and made from the same me...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of linear expansion of crystal in one direction is alp...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform metal rod is used as a bar pendulum. If the room temperature...
Text Solution
|
- An iron rod of length 50 cm is joined at an end to aluminium rod of le...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of apparent expansion of mercury in a glass vessel is ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel is partly filled with a liquid. Coefficients of cubical expan...
Text Solution
|
- An electrically heated coil is immersed in a calorimeter containing 36...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following would raise the temperature of 20 g of wate...
Text Solution
|
- A kettle with 2 litre water at 27^@C is heated by operating coil heate...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains M grams of water at a certain temperature and water ...
Text Solution
|
- Two plates identical in size, one of black and rough surface (B1) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two spheres of different material one with double the radius and one f...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature across two different slabs A and B are shown I the ste...
Text Solution
|
- An earthenware vessel loses 1 g of water per second due to evaporation...
Text Solution
|
- 5g of water at 30^@C and 5 g of ice at -29^@C are mixed together in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A body cools in 7 min from 60^@C to 40^@C What will be its temperature...
Text Solution
|
- A room at 20^@C is heated by a heater of resistence 20 ohm connected t...
Text Solution
|
- A body cools from 50^@C to 49.9^@C in 5 s. How long will it take to co...
Text Solution
|