Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Example|15 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 4.1|23 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger type|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Single correct anwer type
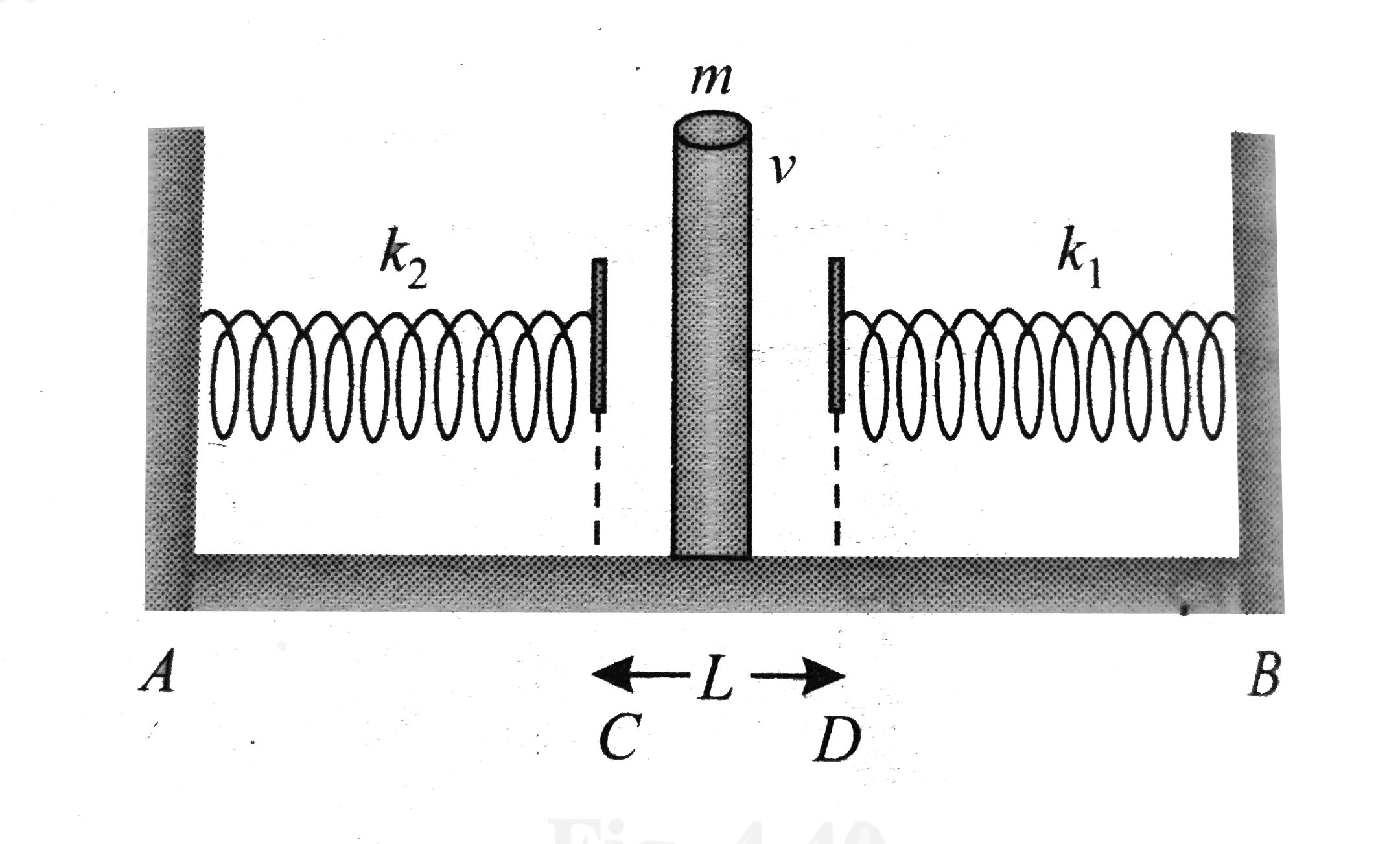
- Two light spring of force constants k(1) and k(2) and a block of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- The period of a simple pendulum whose bob is hollow metallic sphere is...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum has time period T in air when it is made to oscillate in wa...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius r is kept on a concave mirror of radius of curation...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple pendulums of length 0.5 m and 0.2 m respectively are given ...
Text Solution
|
- The bob of a simple pendulum is displaced from its equilibrium positio...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple pendulum whose lengths are 100cm and 121cm are suspended si...
Text Solution
|
- Two pendulum have time period T and 5T/4 . They starts SHM at the same...
Text Solution
|
- Two simple pendulum first of bob mass M(1) and length L(1) second of b...
Text Solution
|
- The case of a simple pendulum, time period verus length is depicted by
Text Solution
|
- A U tube pf uniform born of cross sectional area A has been set up ver...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal platform with an object placed on it is executing S.H.M. ...
Text Solution
|
- The matallic bob of a simple pendulum has the relative density rho. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A brass cube of side a and density sigmais floating in mercury of dens...
Text Solution
|
- A man weighing 60kg stands on the horizontal platform of a spring bala...
Text Solution
|