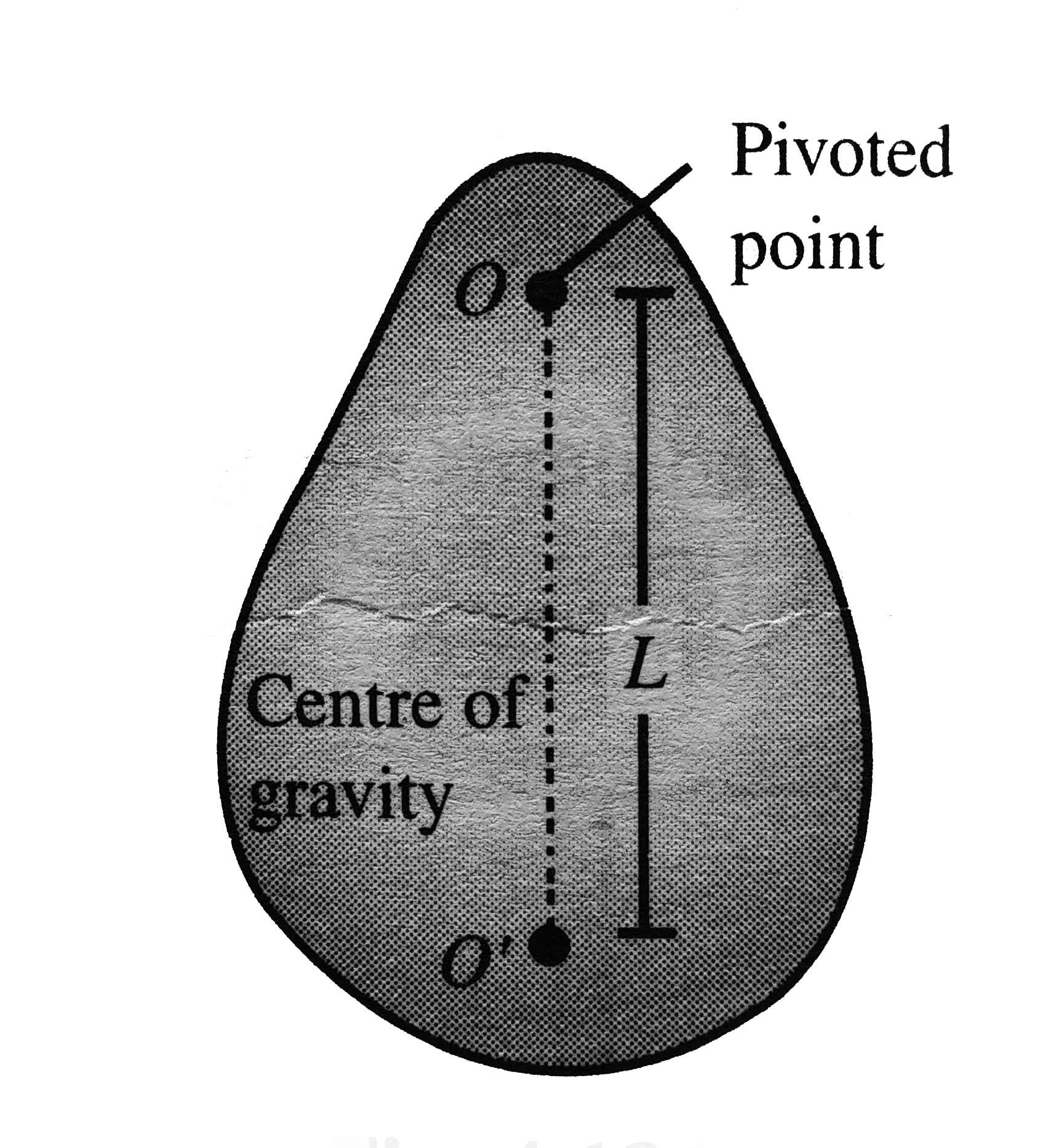
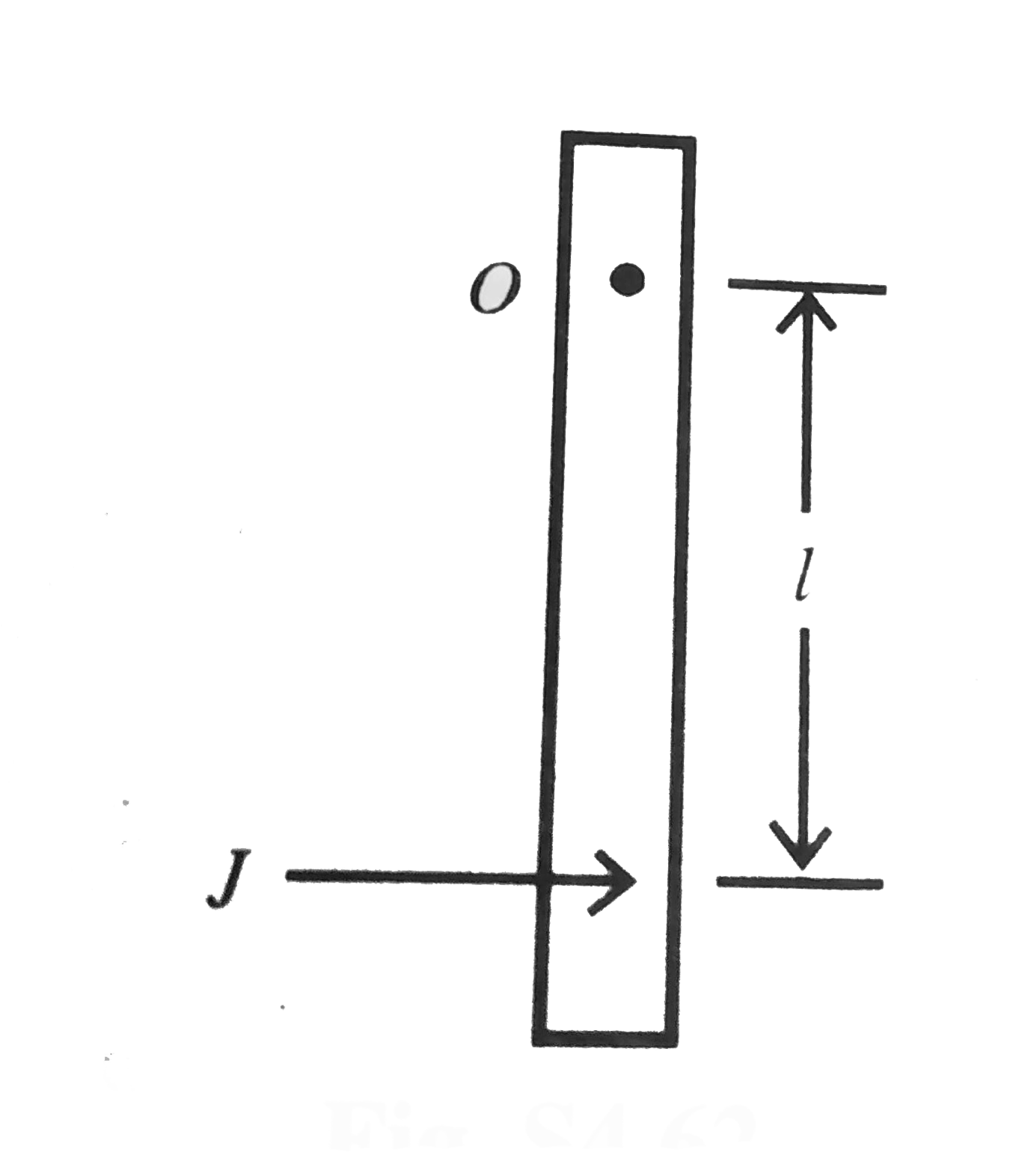
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|10 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective type|2 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion Reasoning|6 VideosKINETIC THEORY OF GASES AND FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger|11 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Interger type|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-LINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Comprehension
- In physical pendulum, the time period for small oscillation is given b...
Text Solution
|
- In physical pendulum, the time period for small oscillation is given b...
Text Solution
|
- In physical pendulum, the time period for small oscillation is given b...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is suspended from one end of a light spring as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is suspended from one end of a light spring as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is suspended from one end of a light spring as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m=3kg, are connected with t...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m=3kg, are connected with t...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m=3kg, are connected with t...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m is fixed at upper end of a massive vertical sp...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m is fixed at upper end of a massive vertical sp...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m is fixed at upper end of a massive vertical sp...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 g block is connected to a horizontal massless spring of force co...
Text Solution
|
- A spring having a spring constant k is fixed to a vertical wall as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A spring having a spring constant k is fixed to a vertical wall as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two fixed points at ta distance 3l apart. A particle of ma...
Text Solution
|