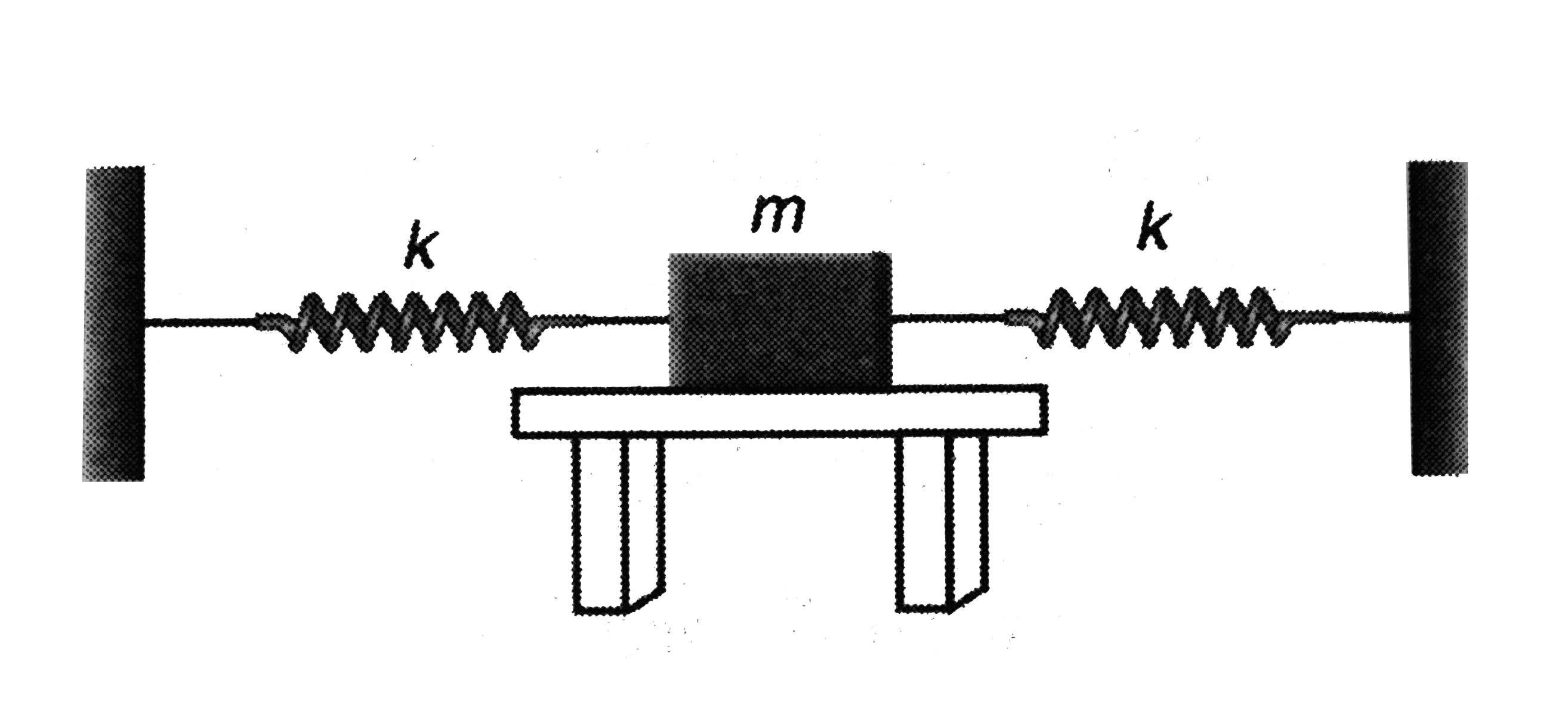
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRAVELLING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 5.1|9 VideosTRAVELLING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 5.2|23 VideosTRAVELLING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Integer|9 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct|9 VideosVECTORS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise Multiple Correct|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-TRAVELLING WAVES-Example
- A transverse mechanical harmonic wave is travellling on a string. Maxi...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a travelling plane sound wave has the form y=60 cos (1...
Text Solution
|
- One end of each of two identical springs, each of force constant 0.5N/...
Text Solution
|
- A wave pulse starts propagating in the +x-direction along a non-unifor...
Text Solution
|
- When a train of plane wave traverses a medium, individual particles ex...
Text Solution
|
- How long will it take sound waves to travel the distance l between the...
Text Solution
|
- A wave of frequency f =1000 Hz, propagates at a velocity v=700 m//s al...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a progressive wave is give by y=0.20 sin 2pi(60t-x//5)...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a snapshot of a sinusoidal travelling wave taken at t= 0...
Text Solution
|