Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-CENGAGE PHYSICS DPP-subjective type
- A boy throws a ball in air at 60^(@) to the horizontal along a road ...
Text Solution
|
- A girl riding a bicycle with a speed of 5 m//s to wards North directi...
Text Solution
|
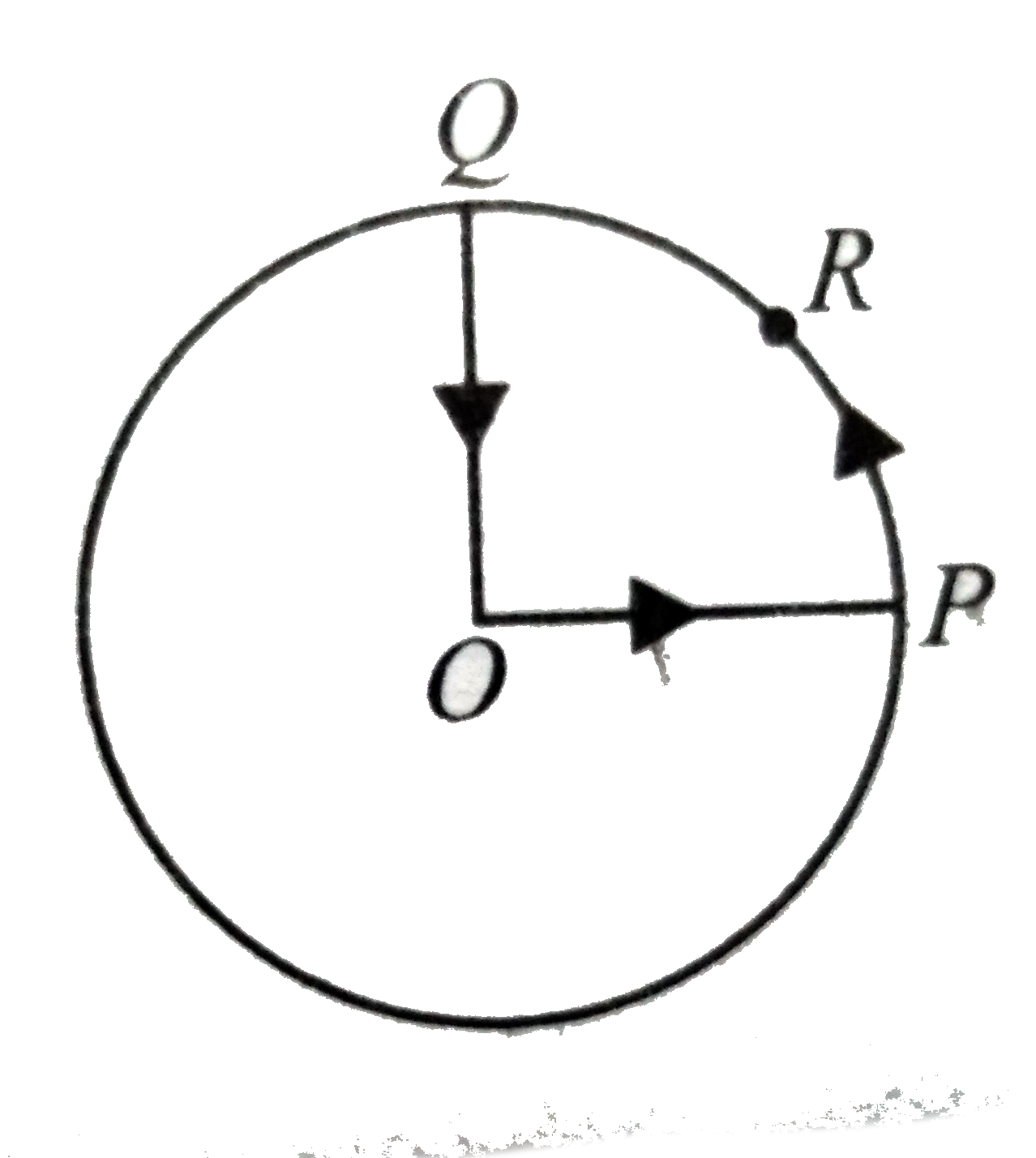
- A cyclist starts from the centre O of a circular park of radius 1 km a...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB is moving on a fixed circle of radius R with constant velocit...
Text Solution
|
- A helicopter of mass 2000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15m...
Text Solution
|
- Find all the normal reaction N(AG),N(BG),N(AB) and the acceleration of...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks are placed at rest on a smooth fixed inclined place. A forc...
Text Solution
|
- Find out the acceleration of the blocks and tensions in the strings.
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following cases the magnitude of acceleration of the b...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is being pulled by a horizontal force F=2mg applie...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose you are sitting on an accelrating trolley car. (i) Find the ...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m is standing on a lift which moves down with an upward ...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is in equilibrium relative to the smooth wedge of ...
Text Solution
|
- A force F is applied on block A of mass M so that the tension in light...
Text Solution
|
- In pulley system shown in figure, block C is going up at 2(m)/(s) and ...
Text Solution
|
- System is shown in the figure and man is pulling the rope from both si...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal speing, with a pointer attached to its end, hangs next to a s...
Text Solution
|
- In an elevator a system is arranged as shown in figure. Initially elev...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shoen calculate the angle of friction . The block dows n...
Text Solution
|
- A block of 7 kg is placed on a rough horizontal surface and is pulled ...
Text Solution
|