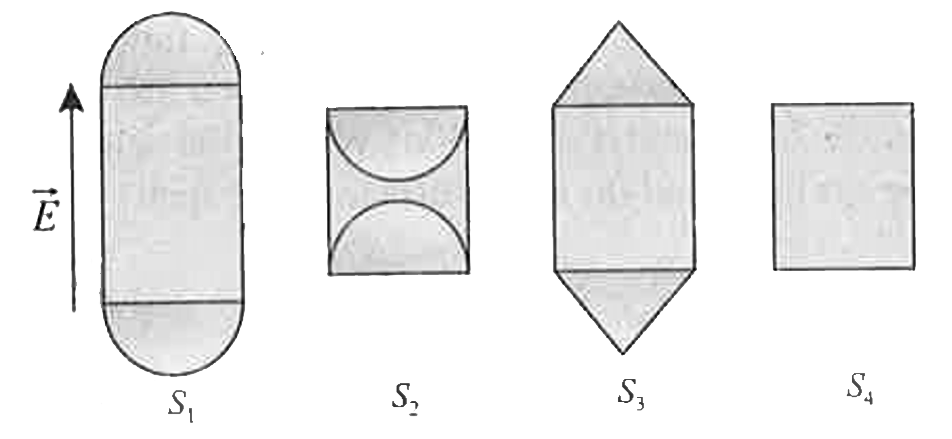
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS LAW-MCQ s
- In the figure a hemispherical bowl of bowl of radius R is shown Electr...
Text Solution
|
- figure shows, in cross section, two Gaussian spheres and two Gaussian ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows four Gaussion surfaces consisting of identical cylindrica...
Text Solution
|
- In figure , a solid sphere of radius a = 2.00cm is concentric with a s...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform charge density of 500 nC//m^(3) is distributed throughout a ...
Text Solution
|
- the net electric flux through each face of a die (singular of dice) ha...
Text Solution
|
- A Gaussian surface S encloses two charges q(1)= q and q(2) = -qthe fie...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field in a region is radially outward with magnitude E=A...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical ve...
Text Solution
|
- Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of...
Text Solution
|
- In a region of space having a spherical symmetic distribution of char...
Text Solution
|
- In a region of space the electric field in the x-direction and proport...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a closed dotted surface which intersects a conduccting un...
Text Solution
|
- figure shows a neutral metallic sphere with a point charge +Q placed n...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are semi - spherical surfaces of radius r(1)and r(2) (r(1) lt ...
Text Solution
|
- the electric field intensity at all points is space is given by vecE...
Text Solution
|
- the electric field intensity at all points is space is given by vecE...
Text Solution
|
- the electric field intensity at all points is space is given by vecE...
Text Solution
|
- Figure, shown above, shows three situations involving a charged partic...
Text Solution
|
- There are three concentric thin spheres of radius a,b,c (agtbgtc). The...
Text Solution
|