A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A long wire AB is placed on a table. Another wire PQ of mass 1.0 g and...
Text Solution
|
- A long, horizontal wire AB rests on the surface of a table and carries...
Text Solution
|
- A long wire AB is placed on a table. Another wire PQ of mass 1.0 g and...
Text Solution
|
- A long straight wire carrying current of 25A rests on a table as shown...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, a long wire AB is placed on a table. A wire CD 10cm long, i...
Text Solution
|
- A current carrying wire PQ is placed near an another long curre...
Text Solution
|
- A resistance of a metal wire of length AB is 2Omega. Another wire of l...
Text Solution
|
- एक तार AB से होकर 10A की स्थिर (अपरिवर्ती) विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित हो रह...
Text Solution
|
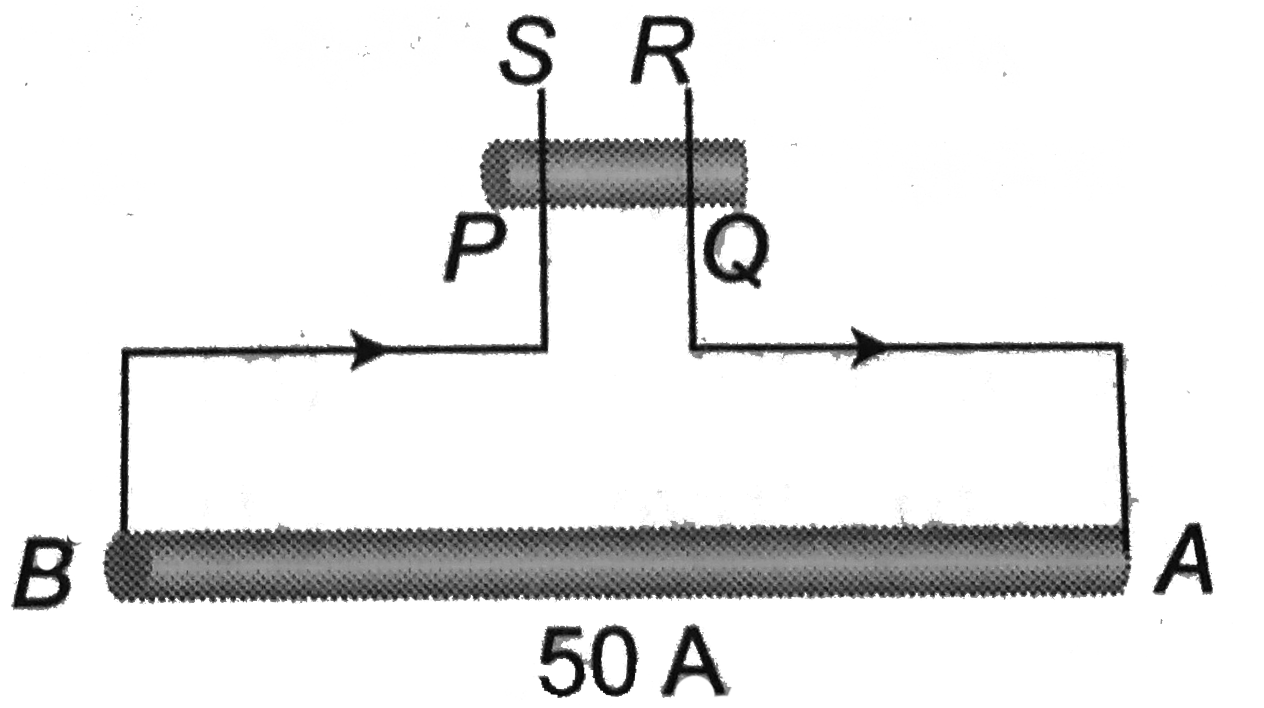
- A straight long wire carrying current 50 A is placed on a horizontal s...
Text Solution
|