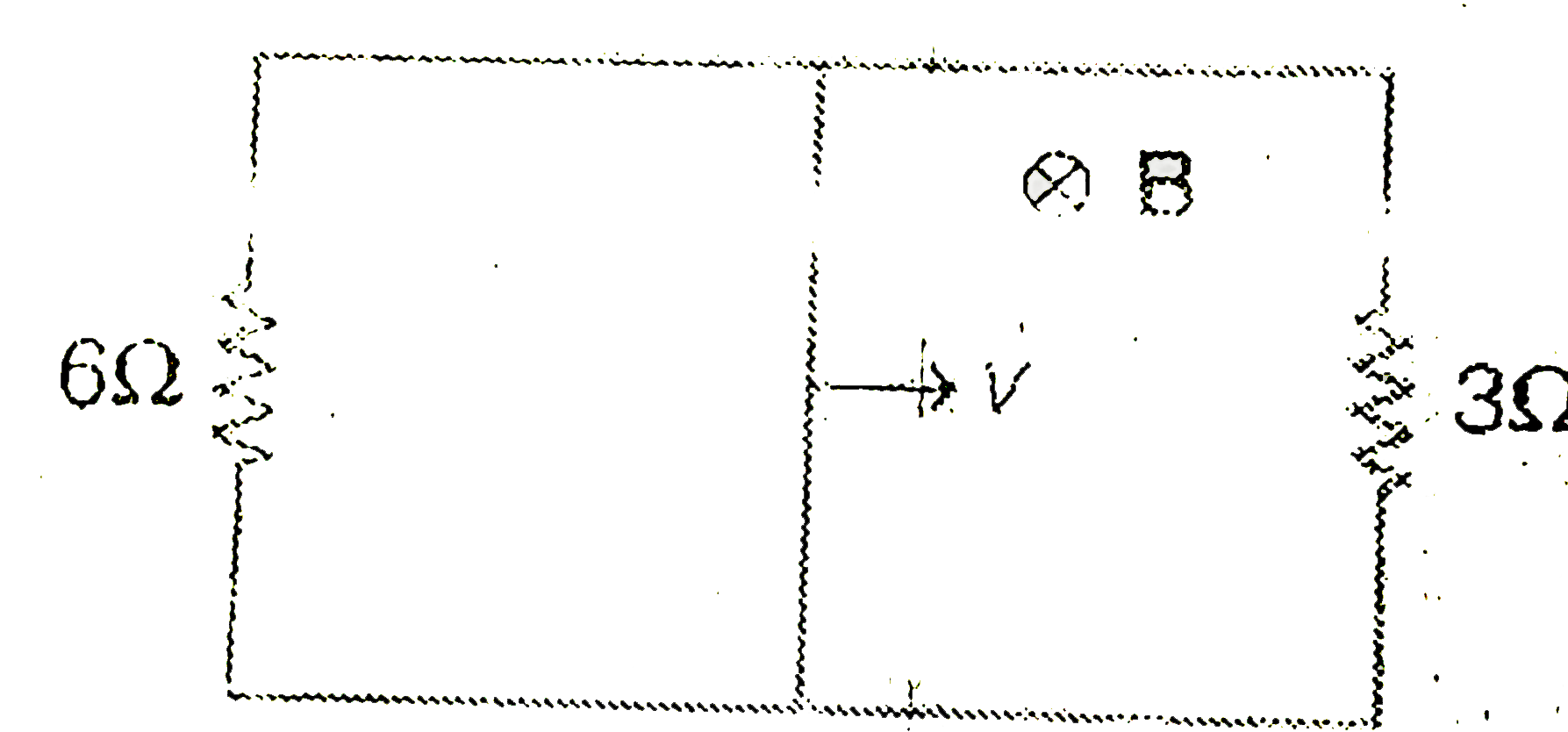
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise comprehensive type|7 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise single correct answer|3 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise comprehensive|5 VideosELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise M.C.Q|2 VideosELECTRON,PHONTS,PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT & X-RAYS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise dpp 3.3|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-single correct
- A copper rod of length l is rotated about one end perpendicular to the...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length 2l is rotating with constant angular speed ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod AC of length 4l is roated about a point O in a unifor...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum with bob of mass m and conducting wire of length L s...
Text Solution
|
- A square metal wire loop of side 10 cm and resistances 1Omega is moved...
Text Solution
|
- A conductivity rod PQ of length L=1.0m is moving with a uniform spped...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop with a sliding connector of length l=10m is the si...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of parallel conducting rails lie at right angle to a uniform ma...
Text Solution
|