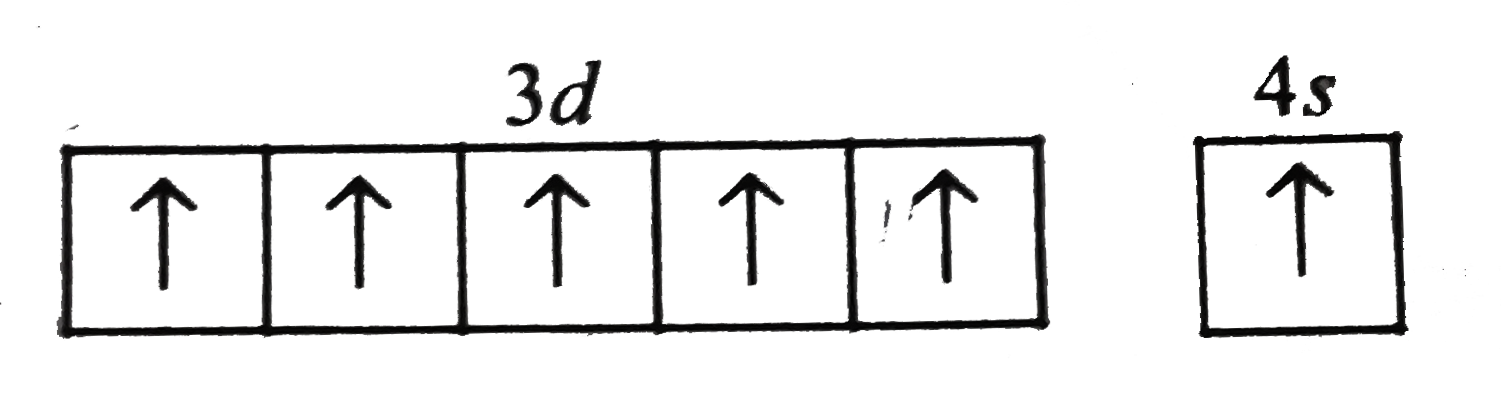
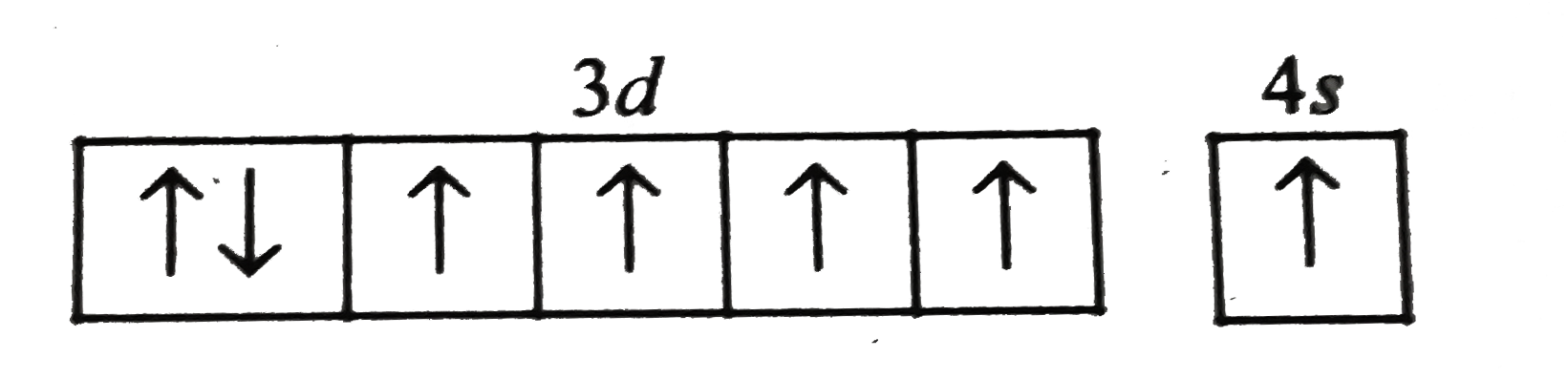
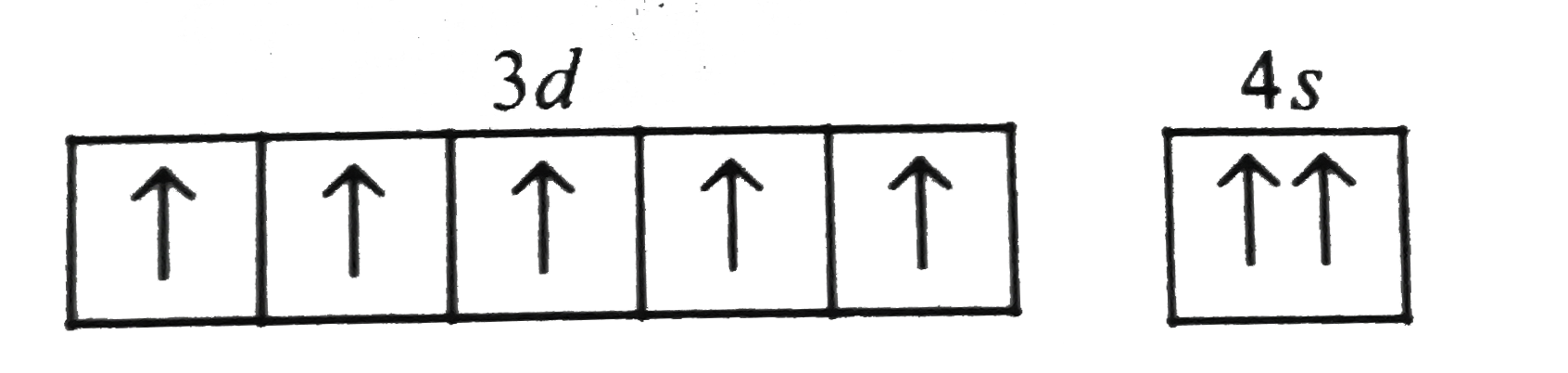
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Assertion And Reason|21 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Integer|11 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|45 VideosAPPENDIX - INORGANIC VOLUME 1
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise chapter-7 Single correct answer|1 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ATOMIC STRUCTURE-Exercises Single Correct
- The ratio of kinetic energy to the total energy of an electron in a Bo...
Text Solution
|
- The ratio of potential energy and total energy of an electron in a Boh...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following arrangements of electron is mostly likely to th...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of electron moving in 3rd orbit of He^(+) is v. The veloc...
Text Solution
|
- The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of H atom is -13.6 e...
Text Solution
|
- The spectral line obtained when an electron jumps from n = 6 to n = 2 ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following species will produce the shortest wavelength fo...
Text Solution
|
- The ionisation potential of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV The energy requir...
Text Solution
|
- If the wavelength of the first line of the Blamer series of hydrogen a...
Text Solution
|
- The energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of H atom is -13.6 e...
Text Solution
|
- The ground state electronic configeration of nitrogen atom can be re...
Text Solution
|
- The electronic configuration of an element is 1s^(2)2s^(2)2p^(6)3s^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The de Broglie wavelength associated with a ball of mass 200 g and mov...
Text Solution
|
- Rutherford's experiment , which established the nuclear model of atom...
Text Solution
|
- Amongst the following elements (whose electronic configuration an gi...
Text Solution
|
- The correct state electronic configuration of chromium atom is
Text Solution
|
- The correct set of quantum numbers for the unpaired electron of chlori...
Text Solution
|
- The orbital diagram in which the Aufbau principle is violated is
Text Solution
|
- The first loinsatisation in electron volts of nitrogen and oxygen ato...
Text Solution
|
- Atomic radii of fluorine and neon in Angstrom units are respectively g...
Text Solution
|