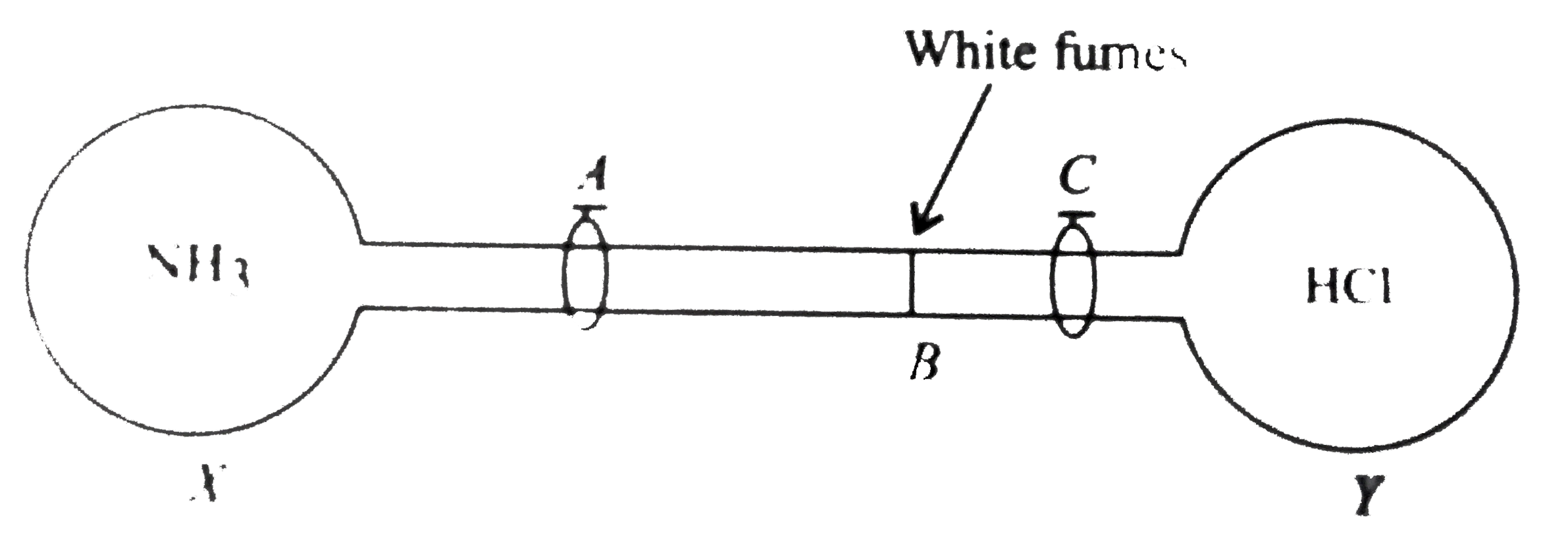
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correcttype)|32 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Single Correct)|85 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Linked Comprehensive|2 VideosSOME BASIC CONCEPTS AND MOLE CONCEPT
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|11 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-STATES OF MATTER-Exercises (Linked Comprehensive)
- Two gaseous molecules A and B are traveling towards each other. Let th...
Text Solution
|
- Two gaseous molecules A and B are traveling towards each other. Let th...
Text Solution
|
- Two gaseous molecules A and B are traveling towards each other. Let th...
Text Solution
|
- Two gaseous molecules A and B are traveling towards each other. Let th...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- X mL Hydrogen gas effuses through a hole in a container in 5 s. The ti...
Text Solution
|
- The constant motion and high velocities of gas particles lead to some ...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of ideal gas is goverened by various gas laws which are ...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of ideal gas is goverened by various gas laws which are ...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of ideal gas is goverened by various gas laws which are ...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of ideal gas is goverened by various gas laws which are ...
Text Solution
|
- The behaviour of ideal gas is goverened by various gas laws which are ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the adjacent diagram. Initially, flask A contained oxygen gas...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the adjacent diagram. Initially, flask A contained oxygen gas...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the adjacent diagram. Initially, flask A contained oxygen gas...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in the figure is in equilibrium, where A and B are is...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in the figure is in equilibrium, where A and B are is...
Text Solution
|
- The system shown in the figure is in equilibrium, where A and B are is...
Text Solution
|