Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex 5.1|15 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex 5.2|16 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives (Integer)|1 VideosSOME BASIC CONCEPTS AND MOLE CONCEPT
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|11 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-STATES OF MATTER-Archives (Subjective)
- Calculate the root mean square velocity of ozone kept in a closed vess...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon of 21 cm diameter is to be filled with hydrogen gas at S.T.P...
Text Solution
|
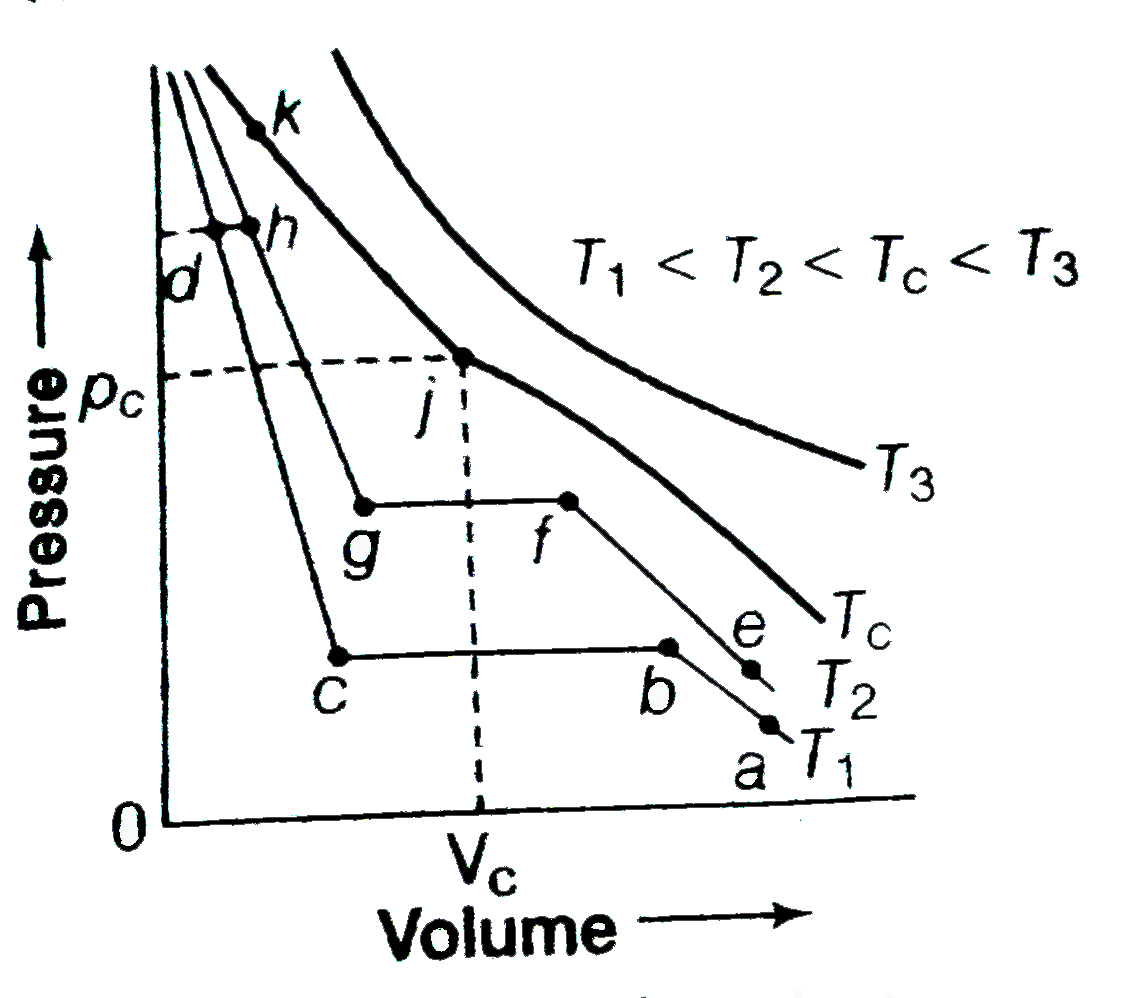
- Isotherms of carbon dioxide at various temperatures are repersented in...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the volume occupied by 5.0 g of acetylene gas at 50^(@)C and...
Text Solution
|
- At room temperature, the following reaction proceeds nearly to complet...
Text Solution
|
- At 27^(@)C, hydrogen is leaked through a tiny hole into a vessel for 2...
Text Solution
|
- A gas bulb of 1 L capacity contains 2.0xx10^(11) molecules of nitrogen...
Text Solution
|
- An LPG cylinder weighs 14.8 kg when empty. When full it weighs 29.0 kg...
Text Solution
|
- A 4: 1 molar mixture of He and CH4 is contained in a vessel at 20 bar ...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of ethane and ethene occupies 40 mL at 1.0 atm, and 400 K. T...
Text Solution
|
- The composition of the equilibrium mixture (Cl(2) 2Cl) , which is att...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of ideal gases is cooled up to liquid helium temperature 4.2...
Text Solution
|
- One way of writing the equation of state for real gases is PV=RT[1+(...
Text Solution
|
- An evacuated glass vessel weighs 50.0 g when empty, 148.0 g when fille...
Text Solution
|
- For the equation N(2)O(5)(g)=2NO(2)(g)+(1//2)O(2)(g), calculate the ...
Text Solution
|
- Using van der Waals' equation, find the constant 'a' (in atm L^(2)mol^...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of nitrogen gas at 0.8atm takes 38s to diffuse through a pinh...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure exerted by 12 g of an ideal gas at temperature t^(@)C in ...
Text Solution
|
- The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der...
Text Solution
|
- The density of the vapour of a substance at 1 atm pressure and 500 K i...
Text Solution
|