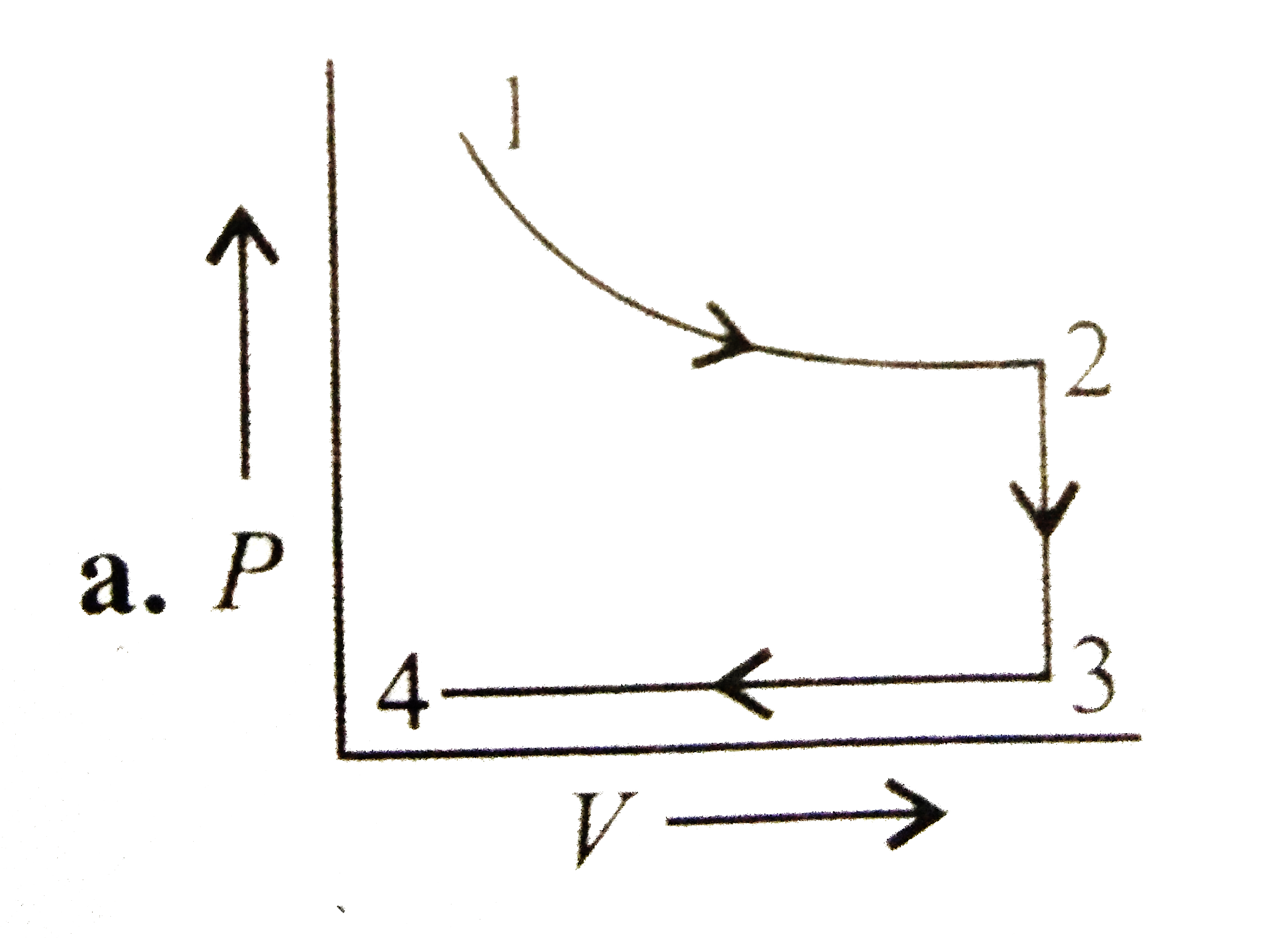
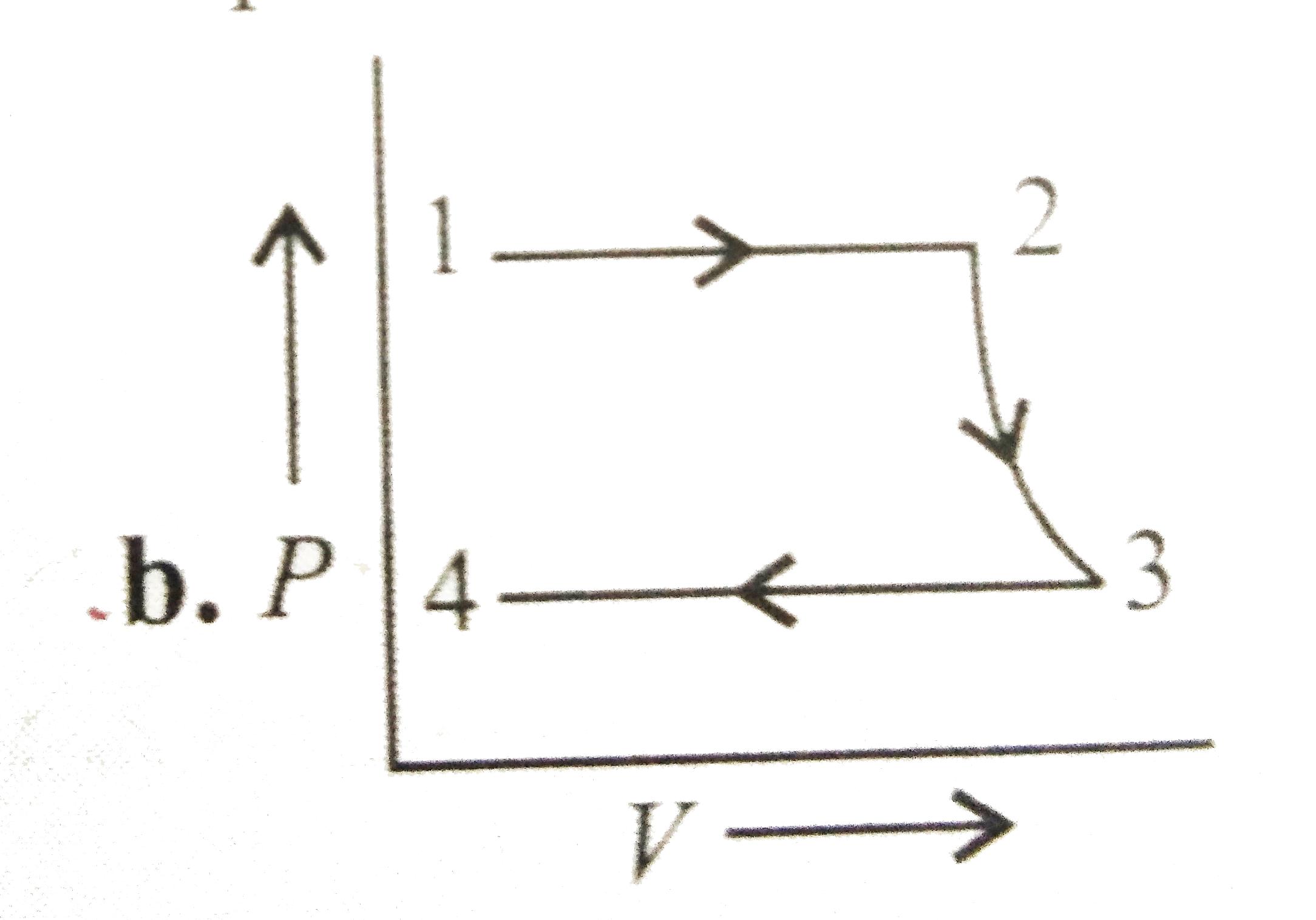
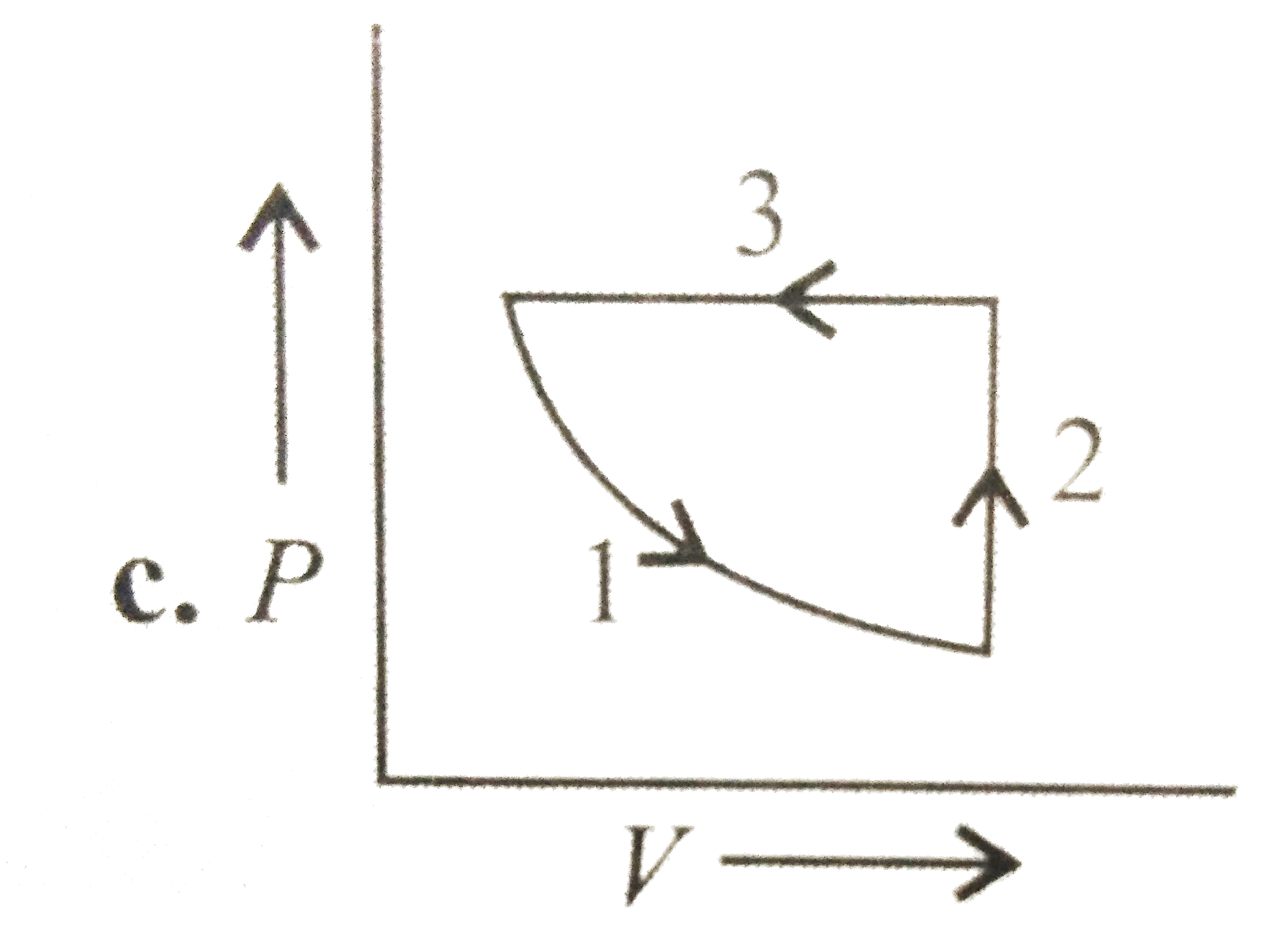
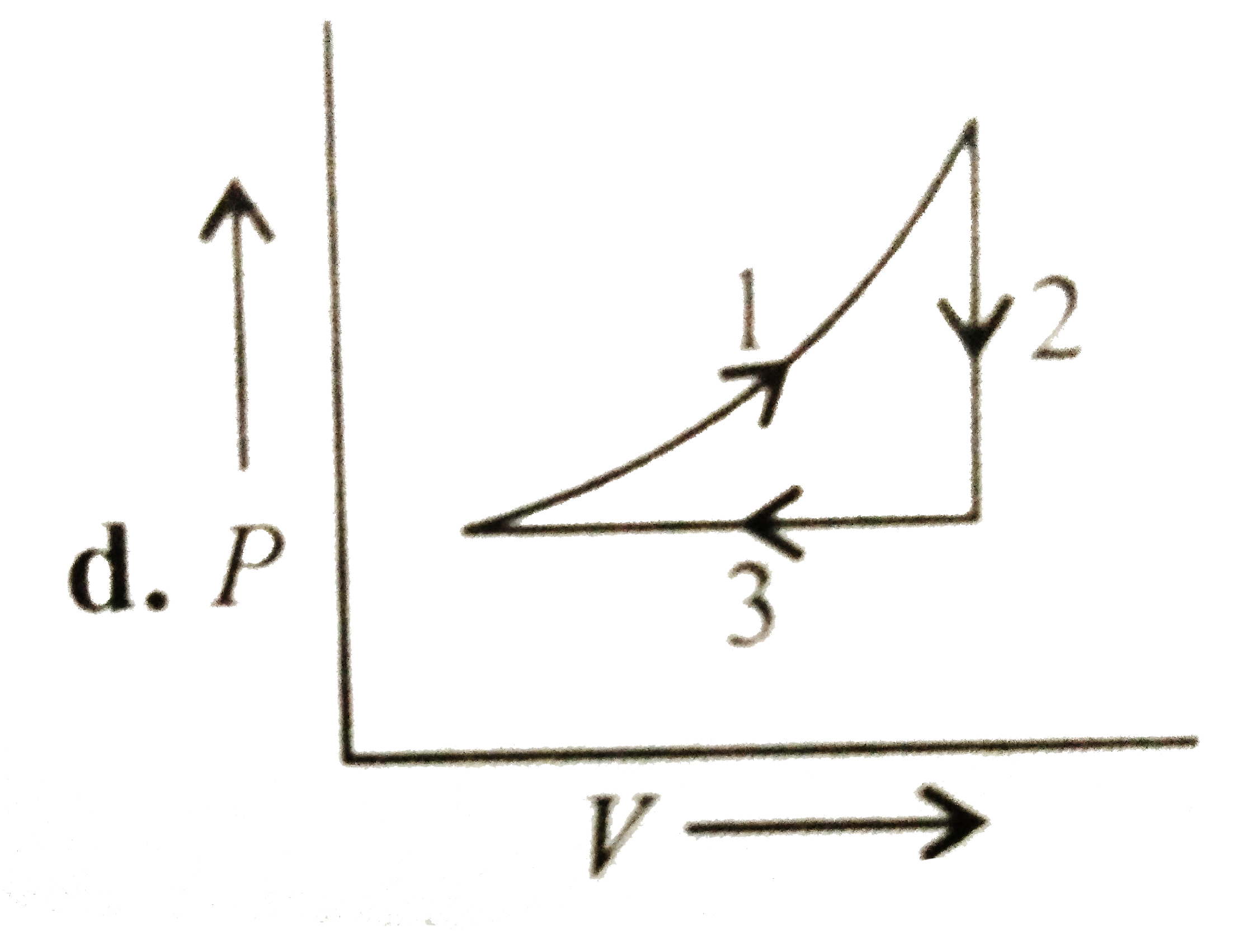A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMICS-Ex 6.2
- The bond enthalpies of H-H and Cl-Cl are 430 and 242 kJ mol^(-1), resp...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of a perfect gas undergo the following processes: a. A rev...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy change (DeltaH) for the reaction, N(2(g))+3H(2(g)) rarr 2...
Text Solution
|
- The difference between the heats of reaction at constant pressure and ...
Text Solution
|
- A gas present in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless pistion expands...
Text Solution
|
- Calcualte q, w, DeltaU, and DeltaH for the reversible isothermal expan...
Text Solution
|
- A swimmer coming out from a pool is covered with a film of water weig...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate q,w,DeltaU, and DeltaH for this isothermal reversible expans...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of argon gas at 1atm pressure and 27^(@)C expands reversibly ...
Text Solution
|
- An insulated contains 1mole of a liquid, molar volume 100mL at 1bar. W...
Text Solution
|
- 5mol of an ideal gas at 27^(@)C expands isothermally and reversibly fr...
Text Solution
|
- 10mol of an ideal gas confined to a volume of 10L is released into atm...
Text Solution
|
- A system absorbs 20kJ heat and also does 10kJ of work. The net interna...
Text Solution
|
- One moles of an ideal gas which C(V) = 3//2 R is heated at a constant ...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclic process ABCD is shown in the P-V diagram. Which of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- A thermodynamic process is shown in the following figure. The process ...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following indicator diagrams gives below do AB,BC, and...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure -temperature (P-T) phase diagram shown below corresponds ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion followed by heat removel a...
Text Solution
|
- Four curves A, B, C and D are drawn in the figure for a given amount o...
Text Solution
|