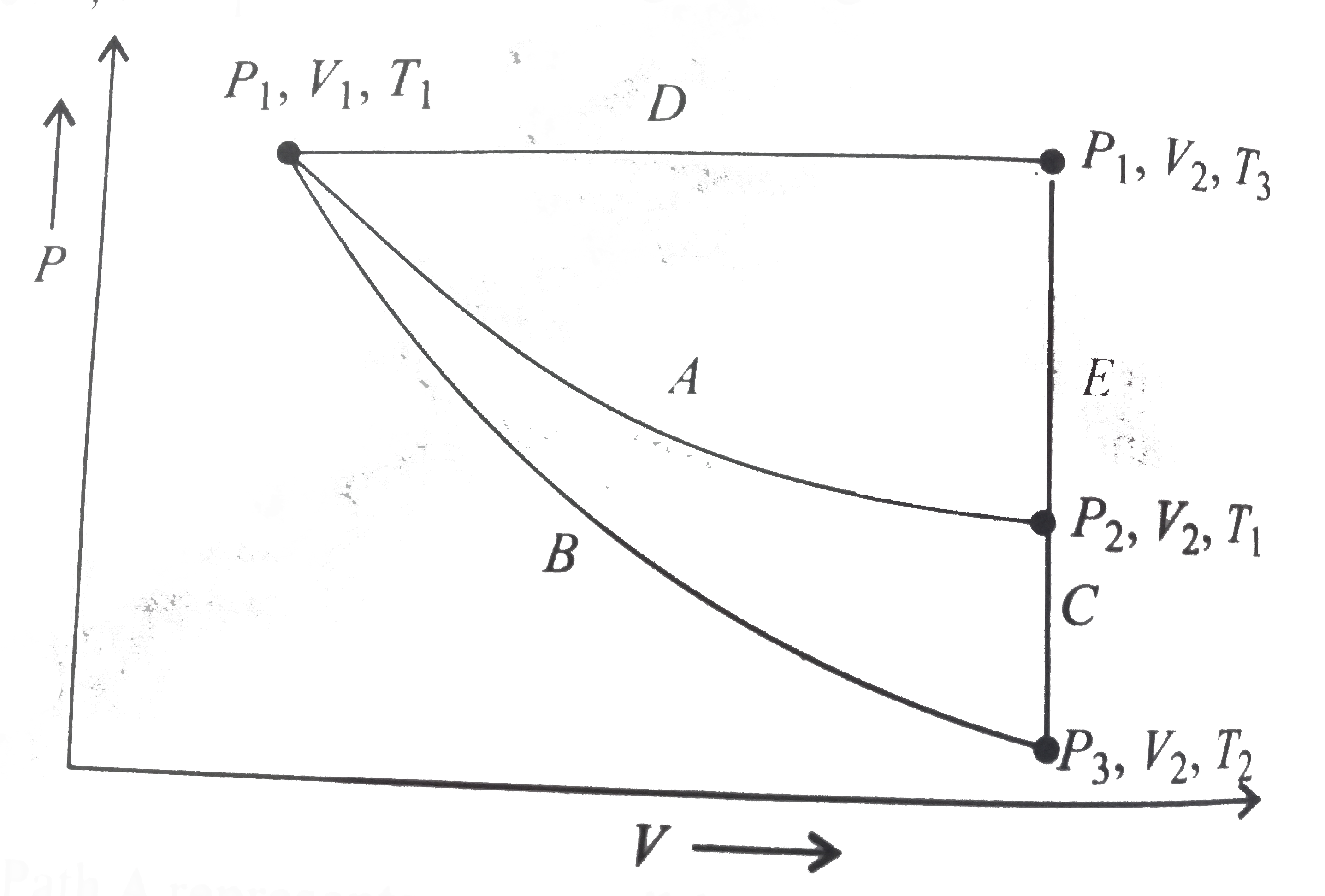
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct)|50 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple correct Answer Type|2 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Paragraph for Problem|1 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercises (Linked Comprehension)
- The enthalpy change for chemical reaction is denoted aas DeltaH^(Theta...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths A,(B+C) and...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, an illustratio of three different paths A(B+C) and (...
Text Solution
|
- Concrete is produced form a mixture of cement, water and small stones....
Text Solution
|
- Concrete is produced form a mixture of cement, water and small stones....
Text Solution
|
- Concrete is produced form a mixture of cement, water and small stones....
Text Solution
|
- Concrete is produced form a mixture of cement, water and small stones....
Text Solution
|
- Concrete is produced form a mixture of cement, water and small stones....
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion in a reversible m...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion in a reversible m...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion in a reversible m...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion in a reversible m...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of ideal gas undergoes isothermal expansion in a reversible m...
Text Solution
|
- Free enegry , G = H - TS, is state function that indicates whther a re...
Text Solution
|
- Free enegry , G = H - TS, is state function that indicates whther a re...
Text Solution
|
- Free enegry , G = H - TS, is state function that indicates whther a re...
Text Solution
|
- Free enegry , G = H - TS, is state function that indicates whther a re...
Text Solution
|