A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Integer|2 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Fill In The Blanks|4 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Multiple Correct|5 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|34 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Archives Single Correct
- The rate constant of a reaction depends upon
Text Solution
|
- A catalyst is a substance which :
Text Solution
|
- The specific rate constant of a first order reaction depends on the
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the reaction, 2N(2)O(5) to 4NO(2) + O(2) is 2 x...
Text Solution
|
- For an endothermic reaction, Delta H represents the enthalpy of the re...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant, activation energy, and Arrphenius parameter of a ch...
Text Solution
|
- If I is the intenisty of an absorbed light and c is the concentration ...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the chemical reaction N(2)(g) + 3H(2)(g) rarr 2NH(3)(g) T...
Text Solution
|
- In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant decreases...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction, (A) rarr products, the concentration of A ...
Text Solution
|
- What of the following statements for order of reaction is not correct?
Text Solution
|
- Conisder a reaction aG+bH rarr Products. When concentration of both th...
Text Solution
|
- Under the same reaction conditions, the intial concentration of 1.386 ...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A rarr P, the temperature (T) dependent rat...
Text Solution
|
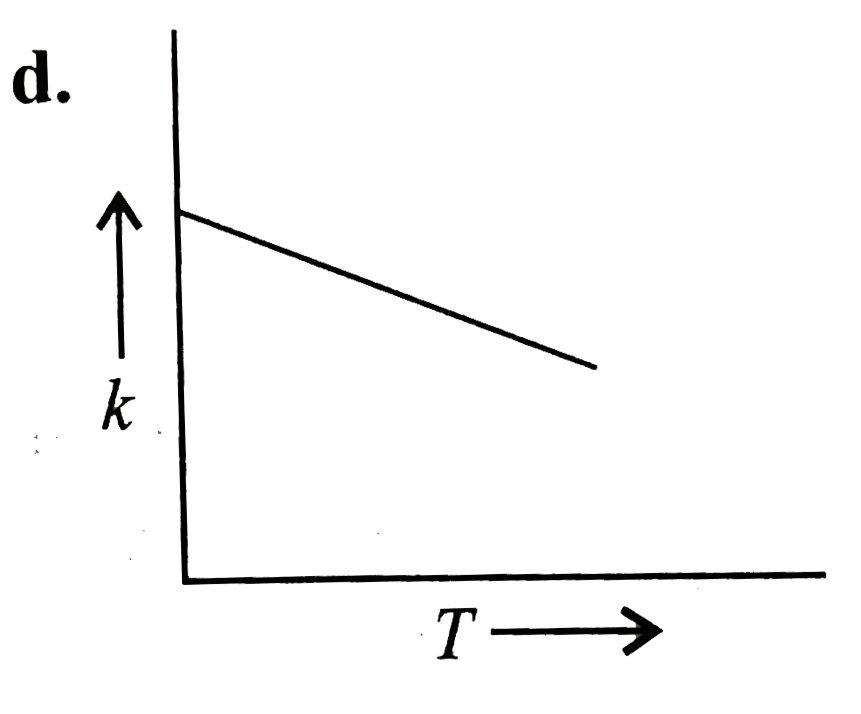
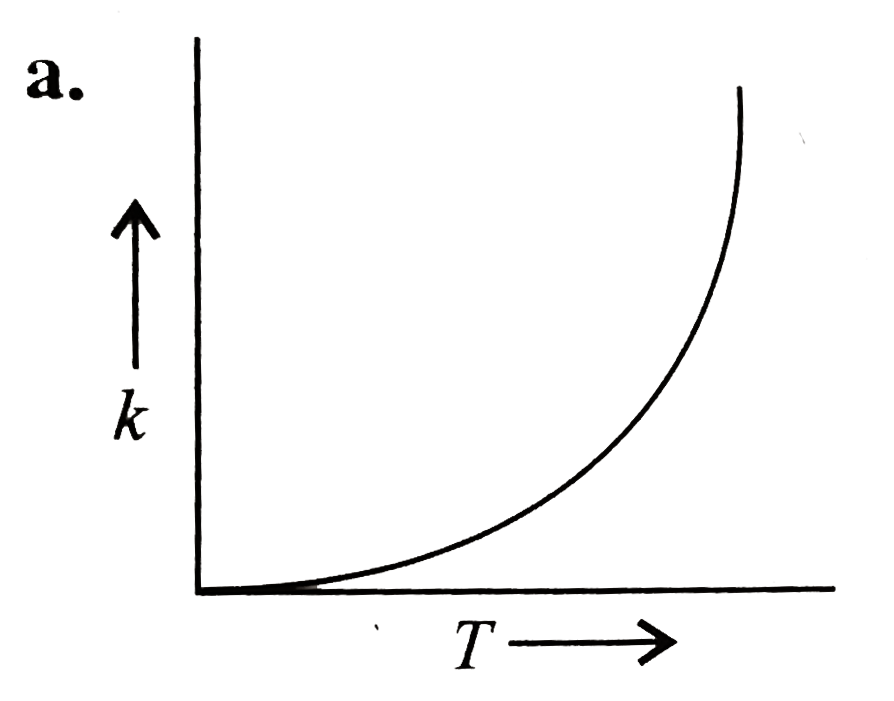
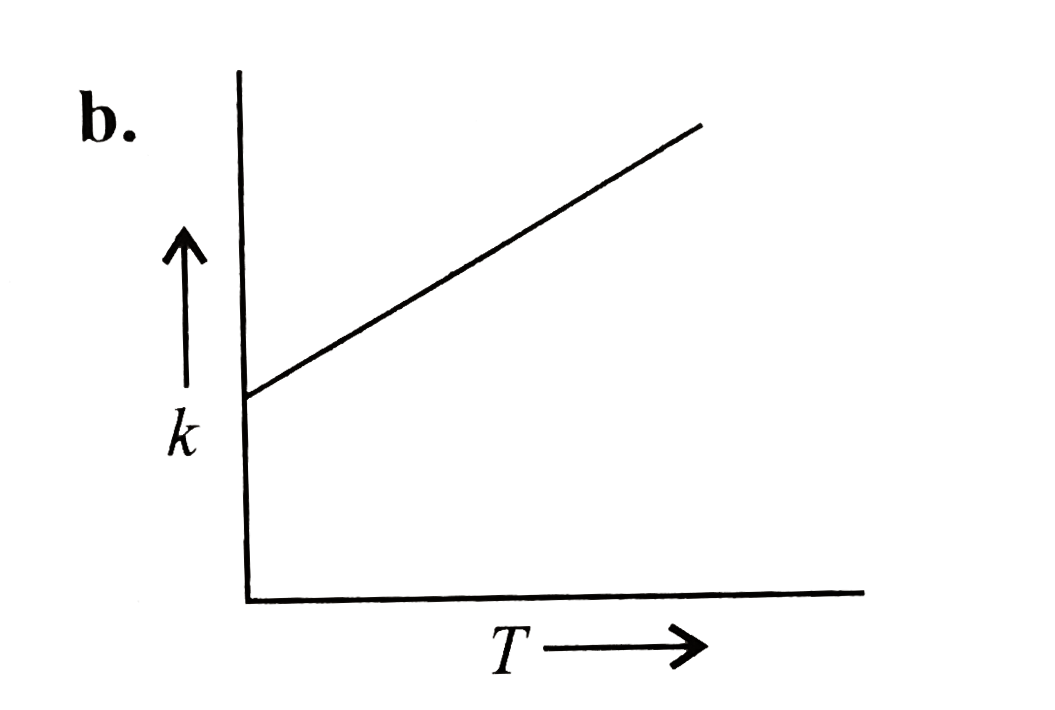
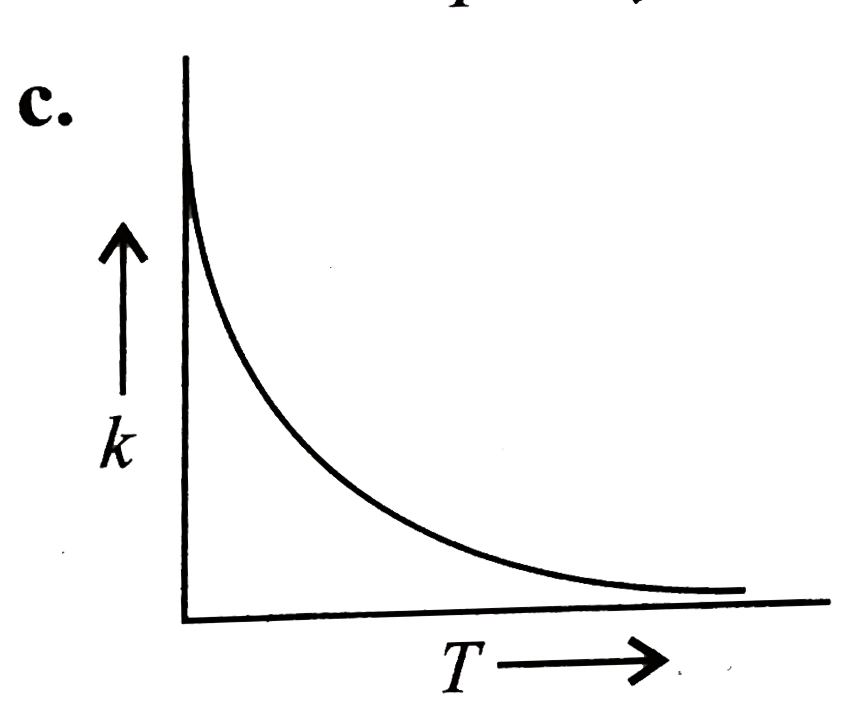
- Plots showing the variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of a reaction doubles when its temperature changes from 300 K...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction, P+Q rarr R+S the time taken for 75% reaction of P i...
Text Solution
|
- For the non-stoichiometric reaction 2A+BrarrC+D The following kineti...
Text Solution
|
- For the elementary reaction MrarrN, the rate of disappearance of M inc...
Text Solution
|