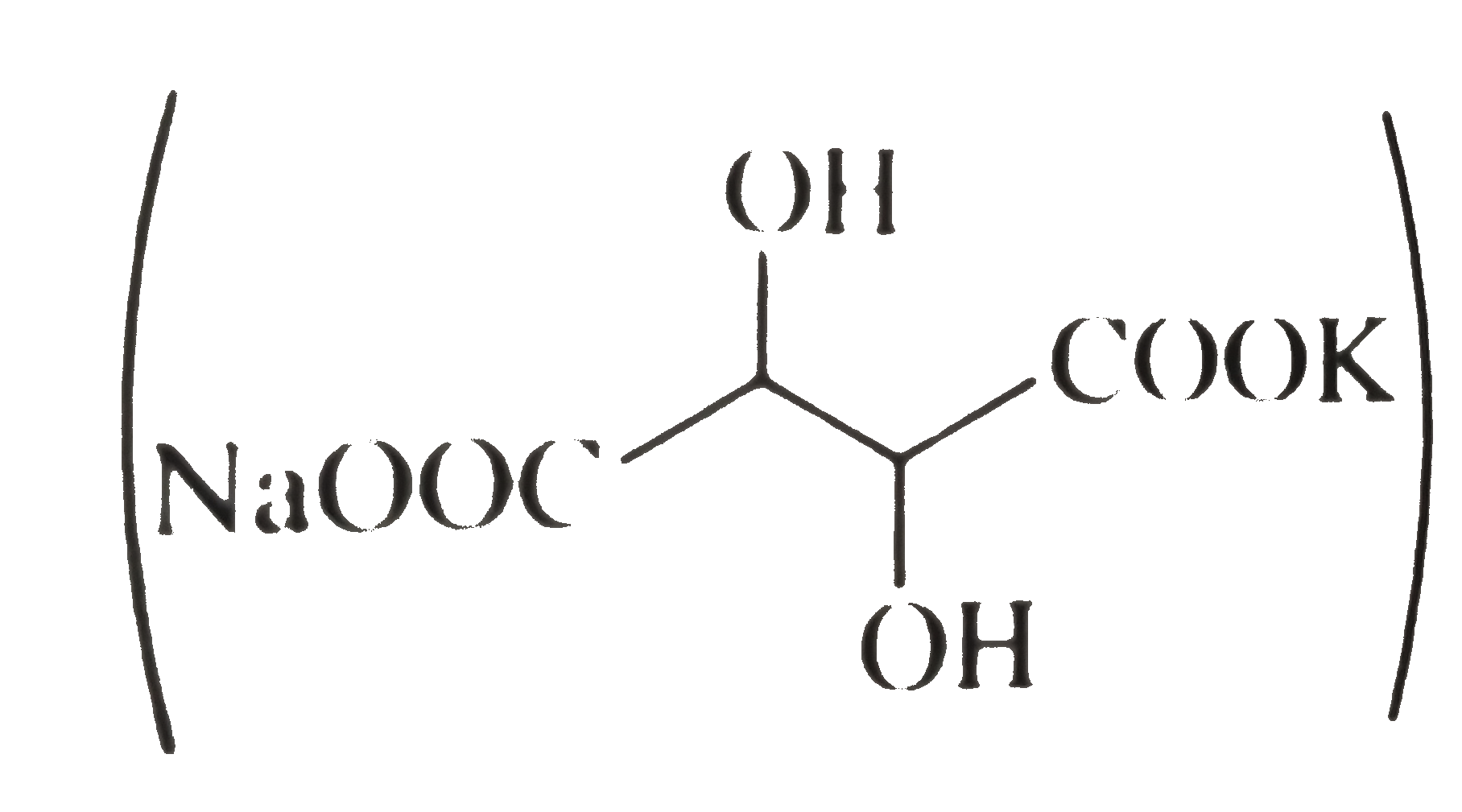
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Fill in the Blanks Type|5 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive Type|3 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct Answer Type|44 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective type|1 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS-Assertion-Reasoning Type
- Assertion (A) : Pentane and 2-methy1 pentane are homolo-gues. Reason...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : All the C atoms of but-2-ene lie in one plane Reason...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : The IUPAC name of the citric acid is 2-hydroxy-propane...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : Rochelle's salt is used as a complexing agent in Tolle...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A): The IUPAC name of isoprene is 2-methy1 buta-1,3-diene. ...
Text Solution
|