Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|36 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex 2 .2 Subjective (Intermolecular Forces And H-Bonding)|7 VideosATOMIC STRUCTURE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Concept Applicationexercise(4.3)|19 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective type|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE-Archives Subjective
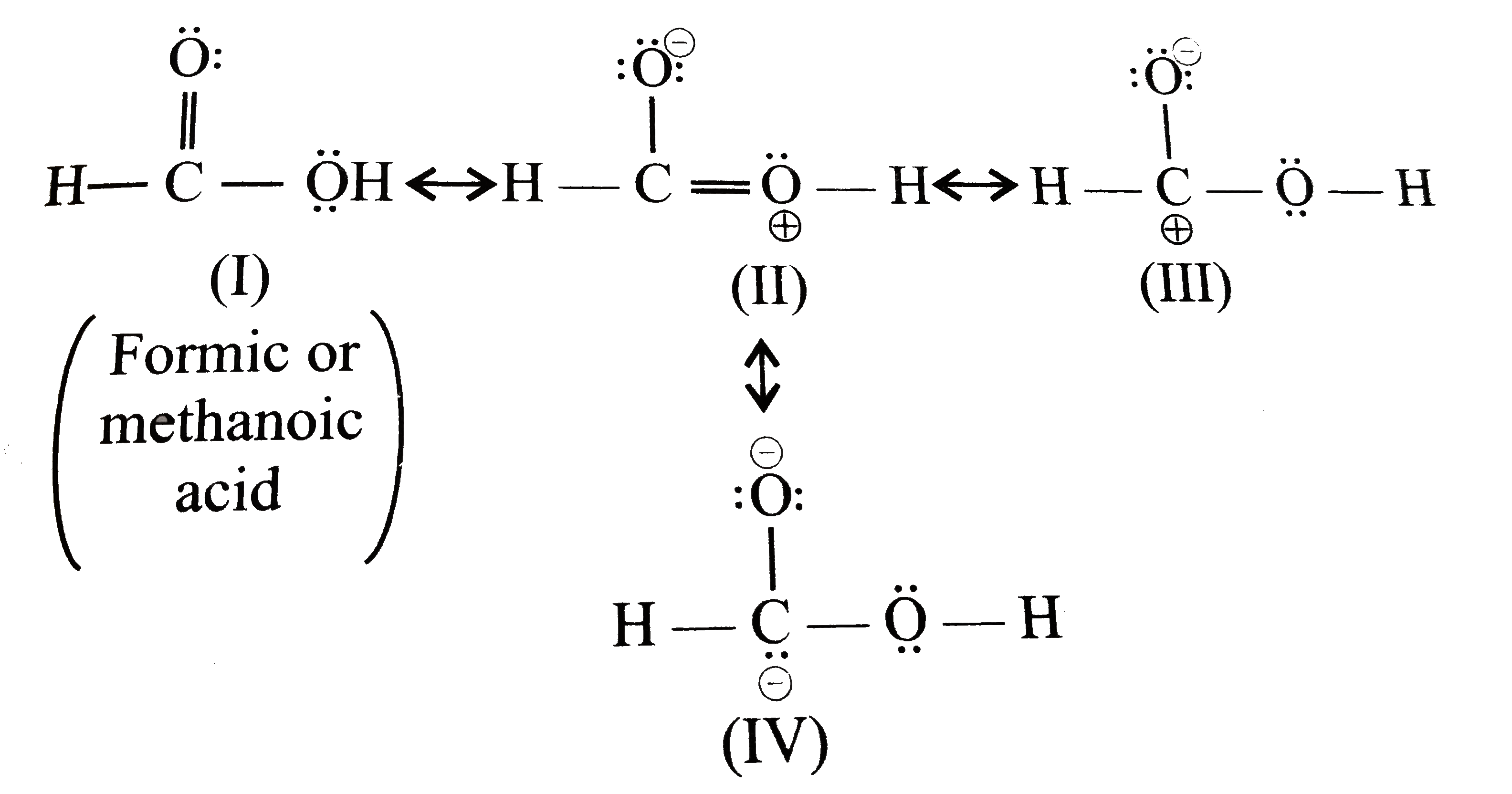
- A arrange the following resonating structures in the order of decreasi...
Text Solution
|
- State four major physical properties that can be used to distinguish b...
Text Solution
|
- Write the Lewis dot structural formula for each of the following Also ...
Text Solution
|
- The sigma and pi-bonds present in benzene ring are
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following as stated Increasing strength of hydrogen bond...
Text Solution
|
- Given reasons in two or there sentences only for the following Hydroge...
Text Solution
|
- The dipole moment of KCI is 3.36 xx 10^(-29)Cm The interatomic distanc...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the difference in the nature of bonding in LiF and LiI .
Text Solution
|
- Using the VSEPR theory, identify the type of hybridization and draw th...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the non-linear shape of H(2)S and non-planar shape of PCl(3) u...
Text Solution
|
- Write the molecular orbital electron distribution of oxygen (O(2)) Spe...
Text Solution
|
- Which one is more soluble in diethyl ether : anhydrous AlCl(3) or hydr...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the shape of BrF(5)
Text Solution
|
- Draw the shape of XeF(4) and OSF(4) according to VSEPR theory Show the...
Text Solution
|
- One the basic of ground electronic configuration, arrange the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Predict whether the following molecules are isostructural or not Justi...
Text Solution
|
 .
.