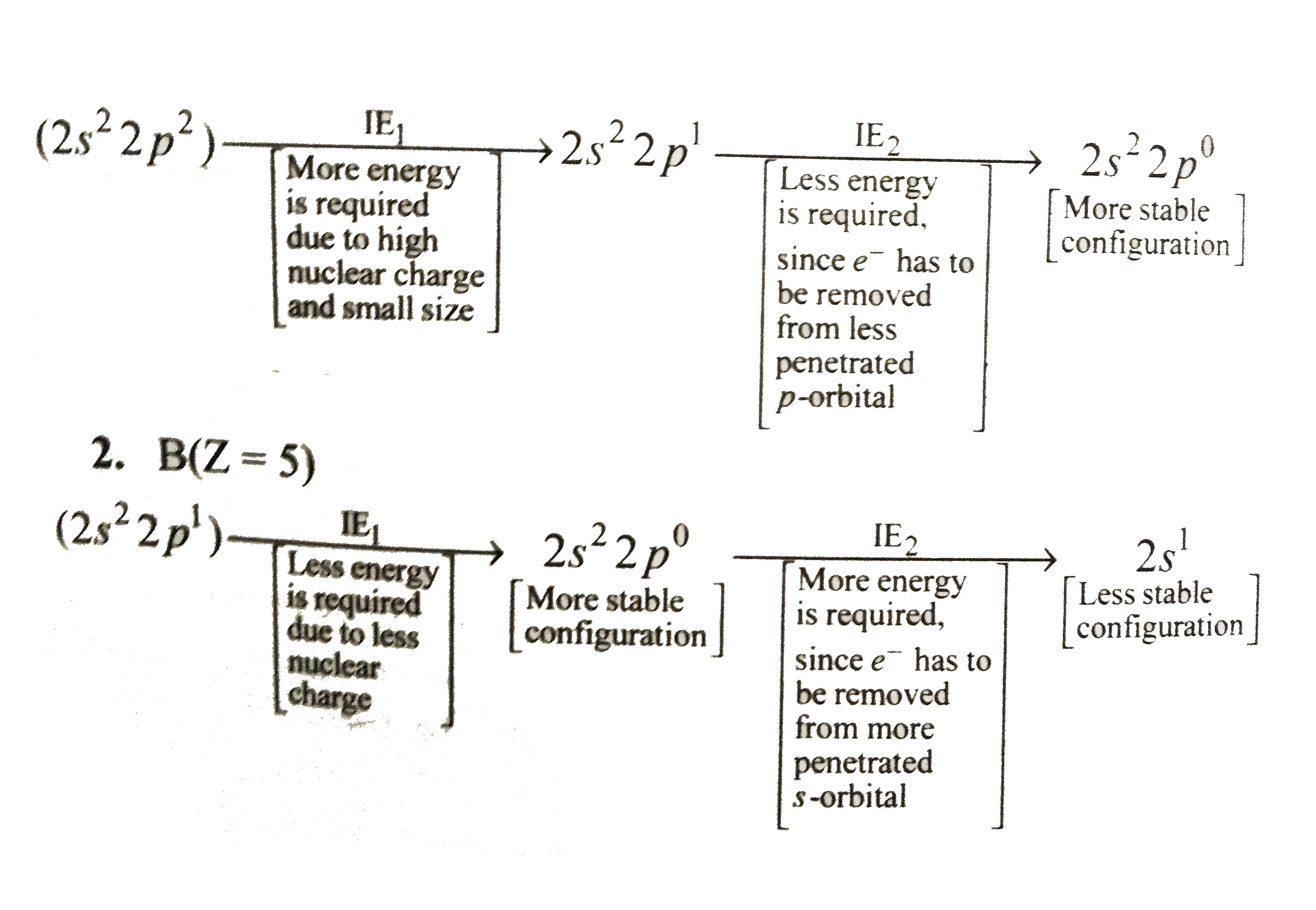
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
P-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|9 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex (Subjective)|21 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise Archives (Subjecive)|9 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Archives )Subjective|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-P-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY-Exercises Archives (Subjective)
- Give reason for the following : a. The first ioisation eathalpy of c...
Text Solution
|
- Write the chemical equations involved in the extraction of lead from g...
Text Solution
|
- State with balanced equations , what happens when NaoH is added to hcl
Text Solution
|
- Give reason for the following in one or two sentences : “Solid...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following in one or two sentences : 'Graphite is ...
Text Solution
|
- Write balanced equations for sodium hydroxide with Nitric acid
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction: Sn+2KOH+4H(2)Orarr……+…….
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structure of a cyclic silicate, (SiO(3)O(9))^(6-) with prope...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the reaction SnCl4 + C2 H5 Cl+ Na rarr
Text Solution
|
- Starting from SiCl4 prepare the following in steps not exceeding the n...
Text Solution
|