a. Gain of electron. When a neutral atom gains one electron to from an anion, its radius increase. Because the number of electrons in the anion increases while its nuclear charge remains the same as the parent atom. Since the same nuclear charge now attracts greater number of electons, therefore, force of attraction of the nucleus on the electrons of all the shells decreases (i.e. effective nuclear charge decreases) and hence the electron cloud expands. In other words, the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the last shelll that contains electrons increases thereby increasing the ionic radius, e.g.
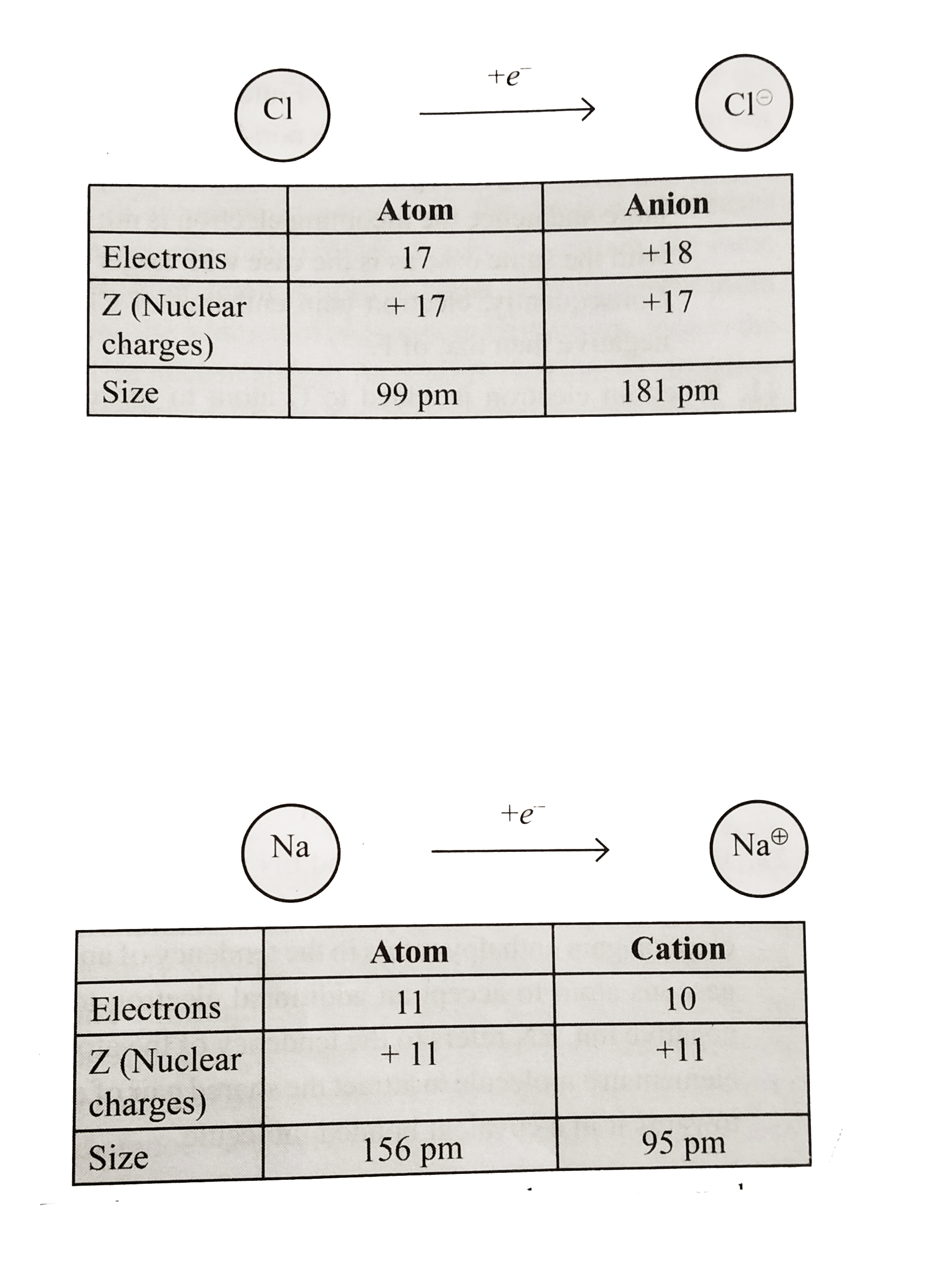
b. Loss of electrons. When a neutral atom loses one electron to form a cation, its atomic radius decreases. Because the number of electrons in the cation decreases while its nuclear charge remains the same as the parent atom. Since the same nuclear charge now attracts lesser number of electrons, therefore, the force of attraction of the nucleus on the electrons of all the shells increases (i.e. effective nuclear charges increase) and hence the size of cation decreases, e.g.
