Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|20 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|22 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|11 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive Type|3 VideosHYDROGEN, WATER AND HYDROGEN PEROXIDE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Archive (Subjective)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Concept
- Using curved-arrow notation, show the formation of reactive intermedi...
Text Solution
|
- Giving justification, categorise the following molecules/ions as nucle...
Text Solution
|
- Identify electrophilic centre in the following: CH(3)CH=O, CH(3)CN, CH...
Text Solution
|
- Which bond is more polar in the following pairs of molecules: (a) H(...
Text Solution
|
- In which C–C bond of CH(3)CH(2)CH(2)Br , the inductive effect is expec...
Text Solution
|
- Write resonance structures of CH(2)=CH–CHO . Indicate relative stabili...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why the following two structures, I and II cannot be the major...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why (CH(3))(3)overset(+)Cis more stable than CH(3)overset(+)CH...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the complete structures of bromomethane
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs of structures do not constitude resonance...
Text Solution
|
- Which is expected to be more stable, (I) O2NCH2CH2O^- or (II) CH3C...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the el...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a n s...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the reagents shown in bonds in the following equations as nuc...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied i...
Text Solution
|
- What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of str...
Text Solution
|
- For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electr...
Text Solution
|
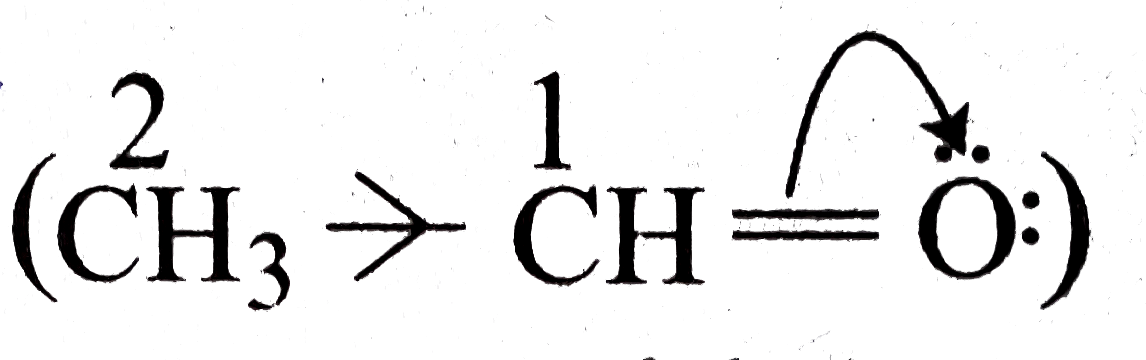 due to greater `EN` of `O` than `C,pi overline e^, s` are withdrawn by oxygen through electromeric effect and `C-1` aquires a positive change and oxygen atom acquires a negative charge
due to greater `EN` of `O` than `C,pi overline e^, s` are withdrawn by oxygen through electromeric effect and `C-1` aquires a positive change and oxygen atom acquires a negative charge  . So to overcome the deficiency of `overline e` on `C-1, (CH_3)` group attached to it gives `sigma overline e^, s` to `C-1` and thus `(CH_3)` group acts as an `overline e` donar via inductive effect.
. So to overcome the deficiency of `overline e` on `C-1, (CH_3)` group attached to it gives `sigma overline e^, s` to `C-1` and thus `(CH_3)` group acts as an `overline e` donar via inductive effect.  .
.