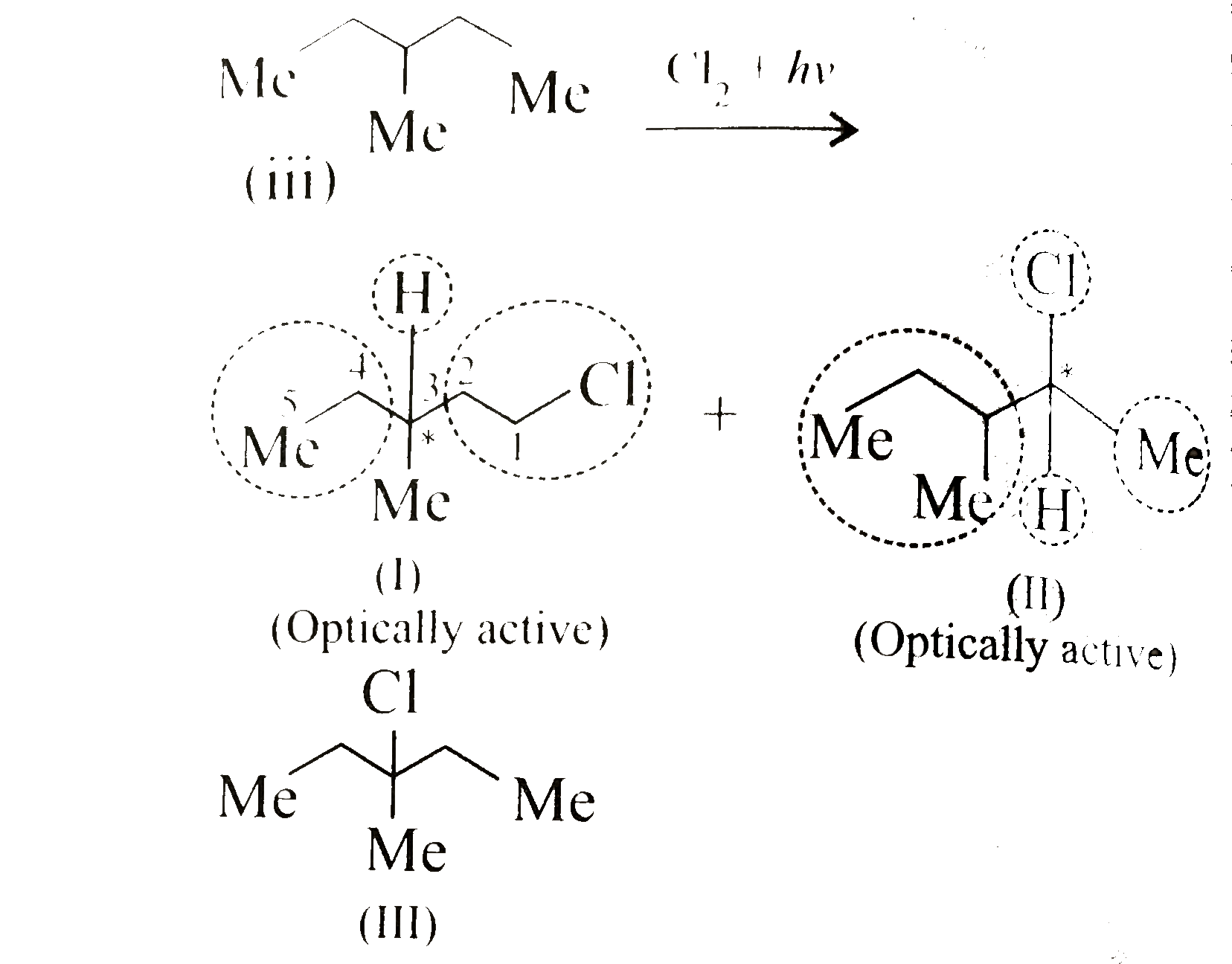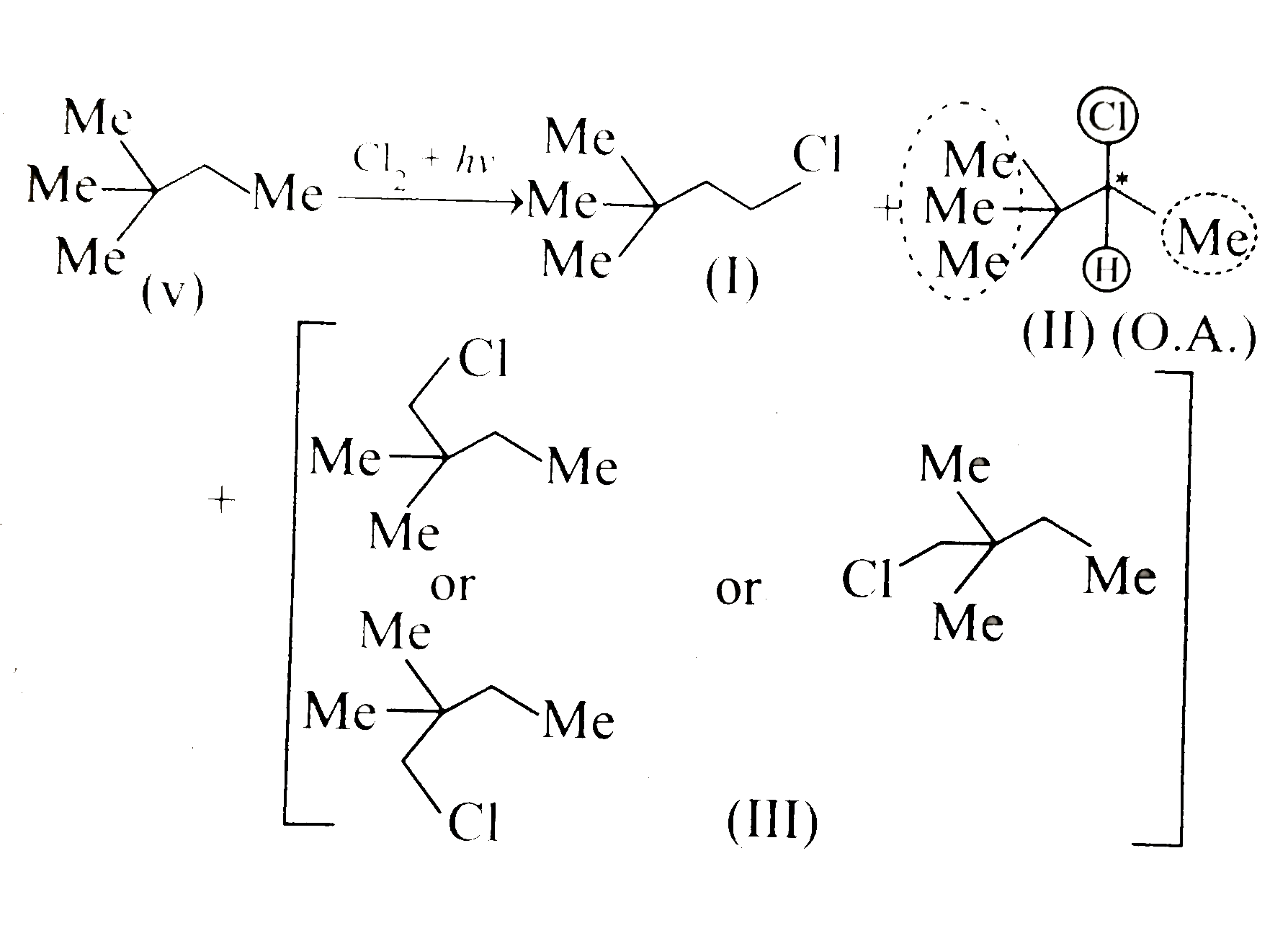Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISES|24 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Paragraph for problem|24 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES-SOLVED EXAMPLES
- Given the number of products obtained on inserting metjhylene in the f...
Text Solution
|
- Given the total number of isomers, including stereoisomers, obtained o...
Text Solution
|
- Given the total number of isomers, including stereoisomers, obtained o...
Text Solution
|
- a. Why are alkanes inert ? b. Why the (C----C) bond rather than (C...
Text Solution
|
- Write the name and structrue of the following optically active compoun...
Text Solution
|
- Synthesise the following compounds starting with CH(3)I.
Text Solution
|
- Convert the following: a. b.
Text Solution
|
- Give the decreasing order of stability at room temperature of the thre...
Text Solution
|
- a. Given the number of isomers including stereoisomers of alkane C(6)...
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of branching on melting and boiling points of alkan...
Text Solution
|
- Both hexane and CF(4) have the same molecular mass and are non-polar, ...
Text Solution
|
- Out of 2-methylhexane and 2,2-dimethyl butane, which one has higher me...
Text Solution
|
- Sulphuryl choride (SO(2)CI(2)) is also used as a chlorinating agent. W...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the difference in the melting point, boiling point, and densit...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds are isolable ? a.
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for the following? a. Deca...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following observation:
Text Solution
|
- Homologous series of alkanols have a general formula
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for the following ? a. 1,2-...
Text Solution
|
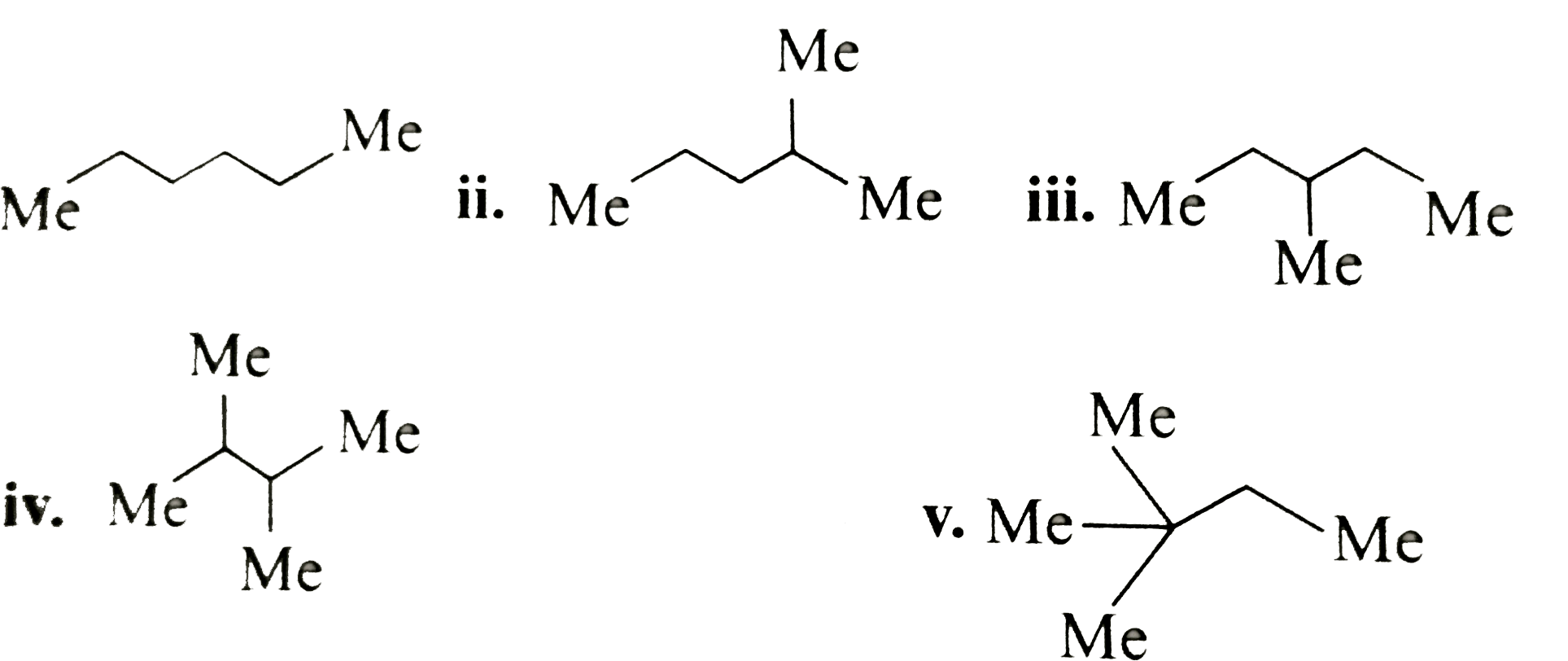 ii.
ii. 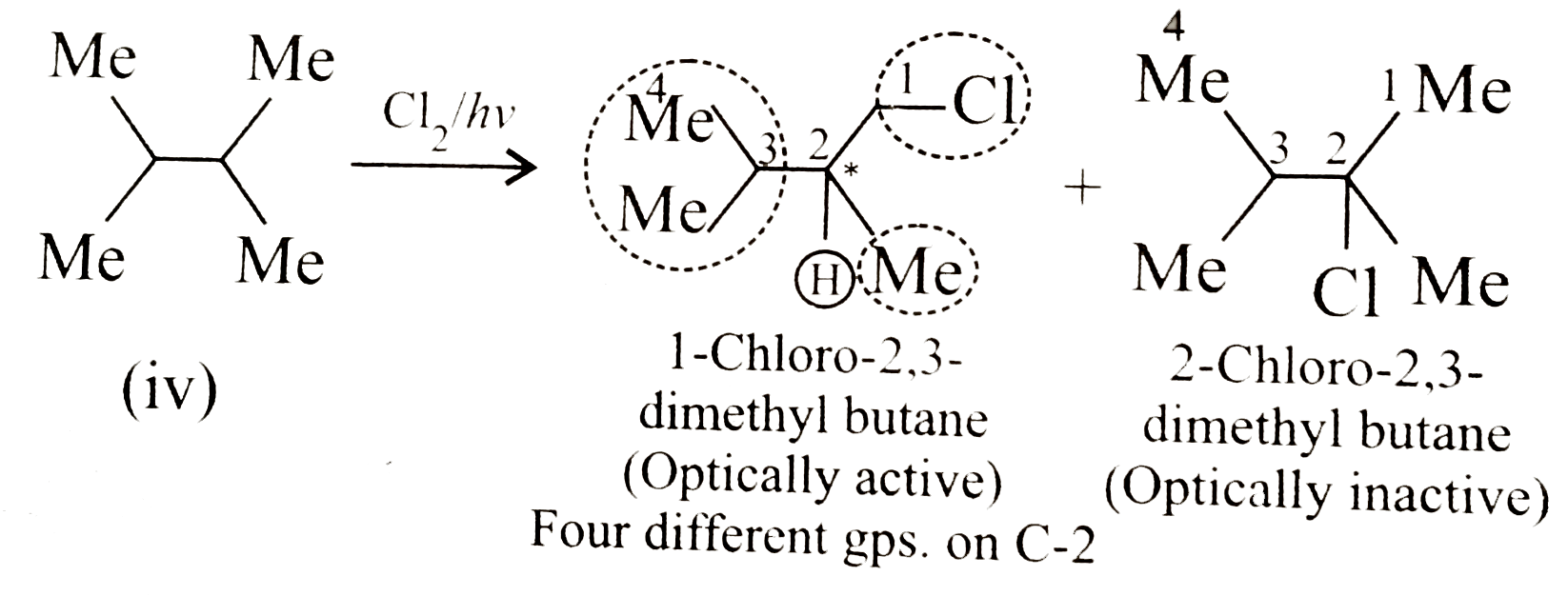 iii.
iii. 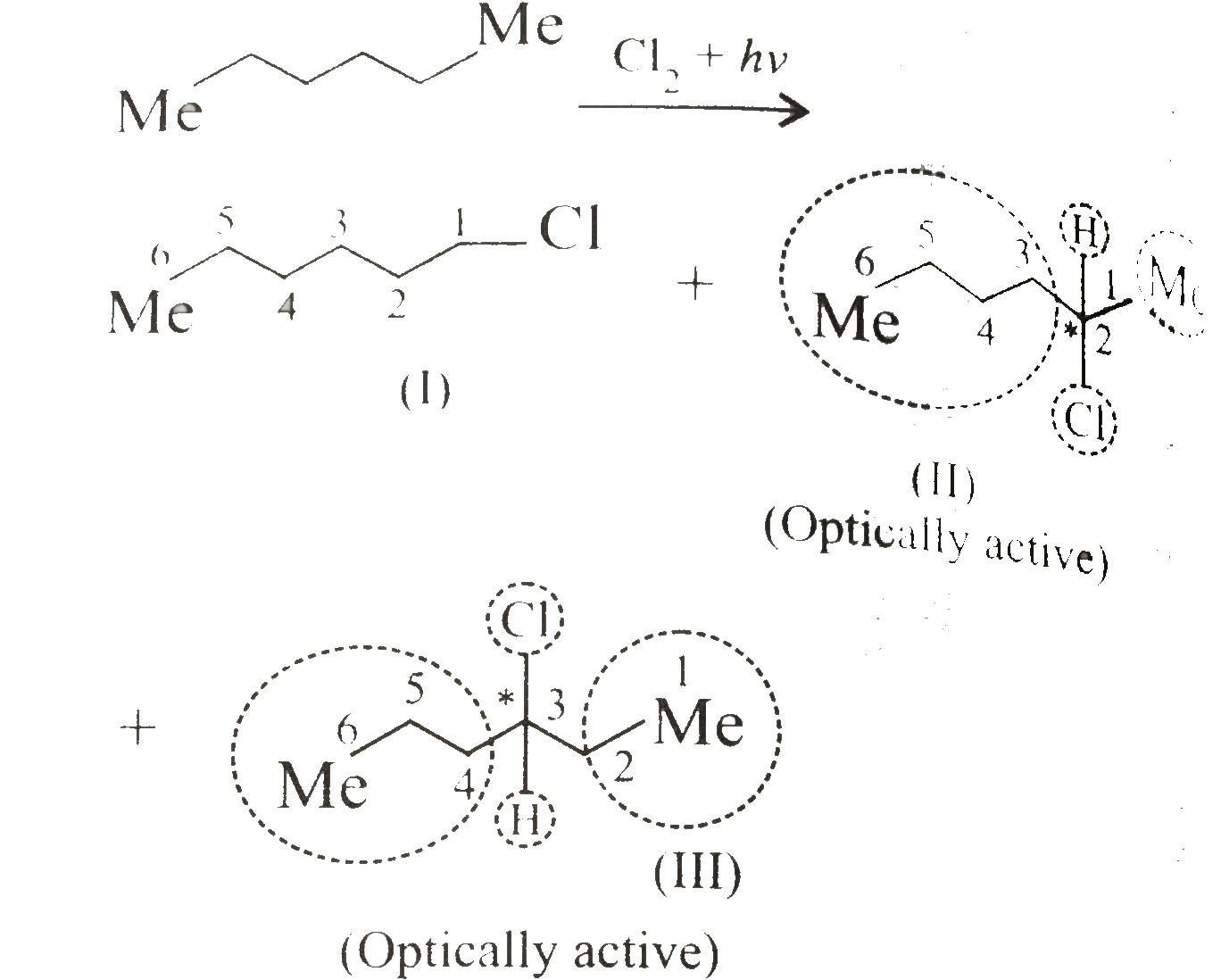
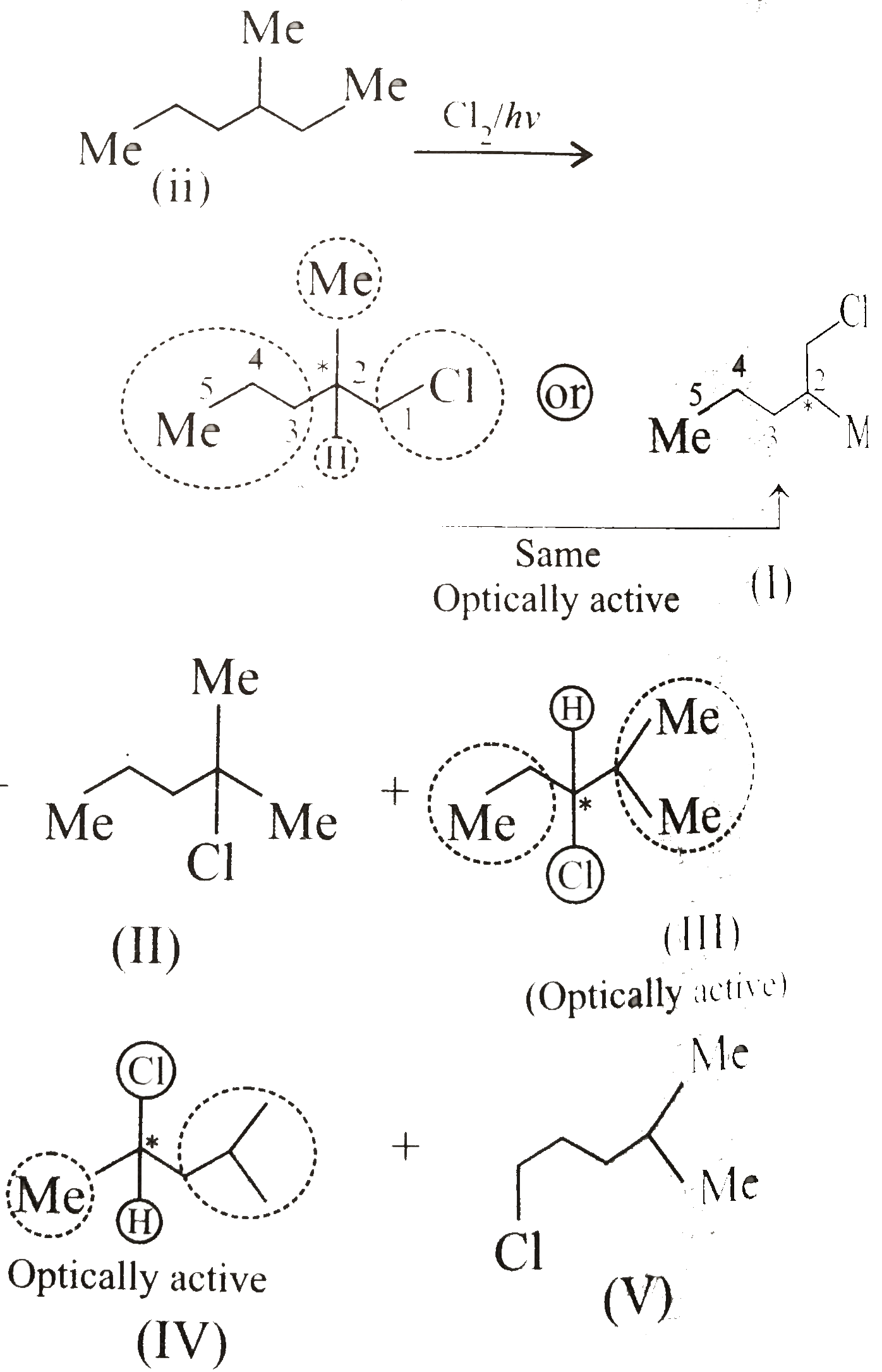 v.
v.