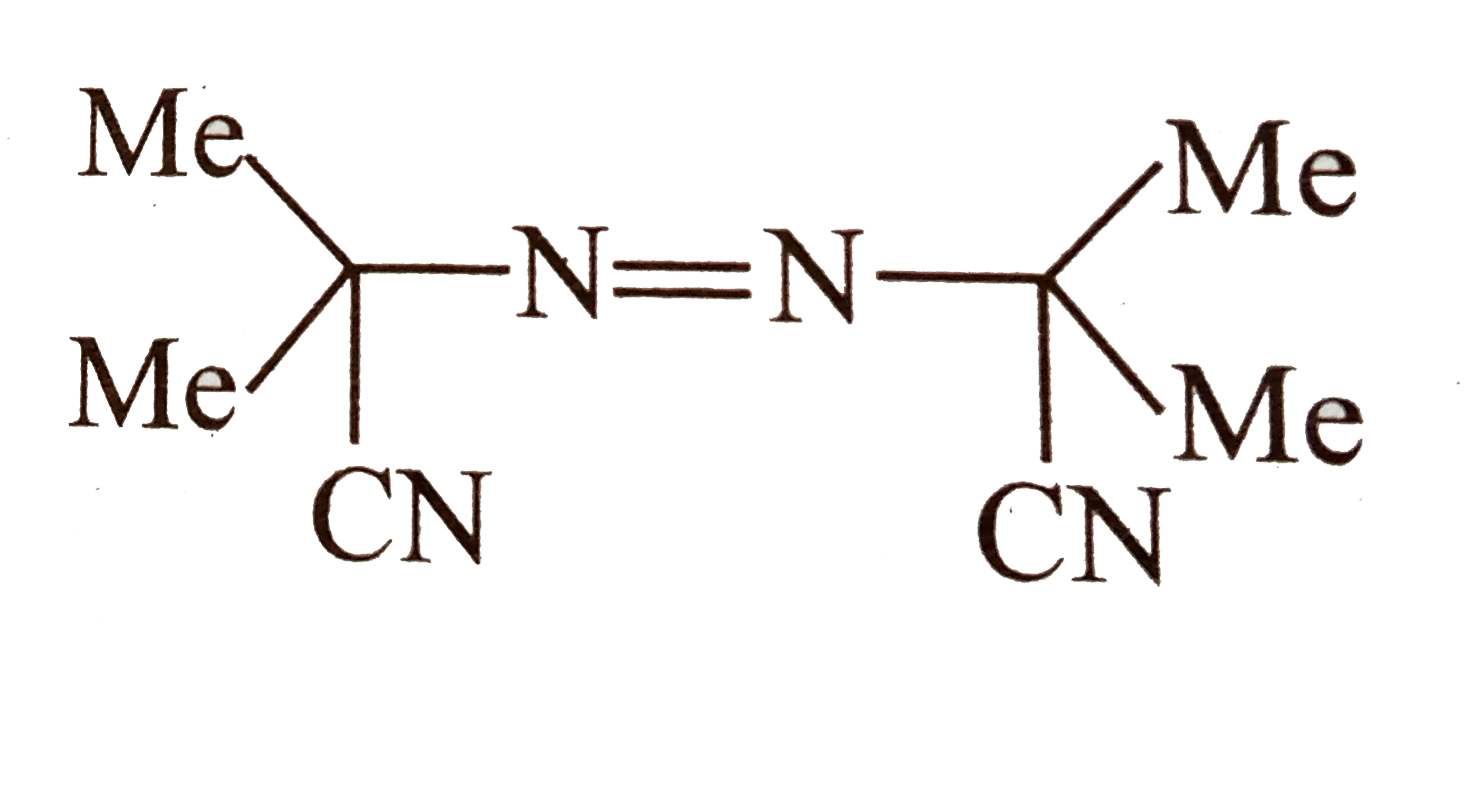Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Paragraph for problem|24 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise True and False|1 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLES|19 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES-EXERCISES
- A compound (A) with molecular formula C(5) H(10) gives one monochlorin...
Text Solution
|
- Why dose a fuel with high ocatane number has less tendency to knock, w...
Text Solution
|
- a. What is the relative abstraction of H and D ? b. Why free-ra...
Text Solution
|
- There are six isomeric alkenes (A, B, C, D, E, and F) that require 1 m...
Text Solution
|
- There are five isomeric alkenes (A, B, C, D, and E) that require 1 mol...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure of all the alkenes that can be hydrogenated to fro...
Text Solution
|
- Write the reaction of benzyl magnesium obmide with CH(3)OD and also id...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the percentage of compounds obtained by monobromination of i...
Text Solution
|
- Which factors determine the reactivity of halogens in the subsitution ...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the percentage of ismoers formed during monobromination of 2,3...
Text Solution
|
- In the study of chlorination of propane, four prouducts A, B, C, and D...
Text Solution
|
- Chloro derivative of an organic compound 'X' on reduction with zinc-co...
Text Solution
|
- An alkyl halide is reduced to the corresponding alkane by tributyl sta...
Text Solution
|
- When a mixture of 2-merthyl propane and C C1(4) is reacted at 403-413 ...
Text Solution
|
- Alkanes are monochlorinate with t-butyl hypochlorite as a radical ...
Text Solution
|
- Delta Hc^(-) (the standard enthalpy of combustion) of butane and 2-met...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following compounds according to the decreasing order of h...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following has the highest boiling point ? i. 2-Methyl ...
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for 1,2,4-Trimethyl cyclohex...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reaction: i. ii.
Text Solution
|