Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS-Archives Analytical And Descriptive
- Which has higher boiling point ? (I) Phenol (II) Benzenethiol
Text Solution
|
- An alcohol A, when heated with conc. H(2)SO(4) gives an alkene B. When...
Text Solution
|
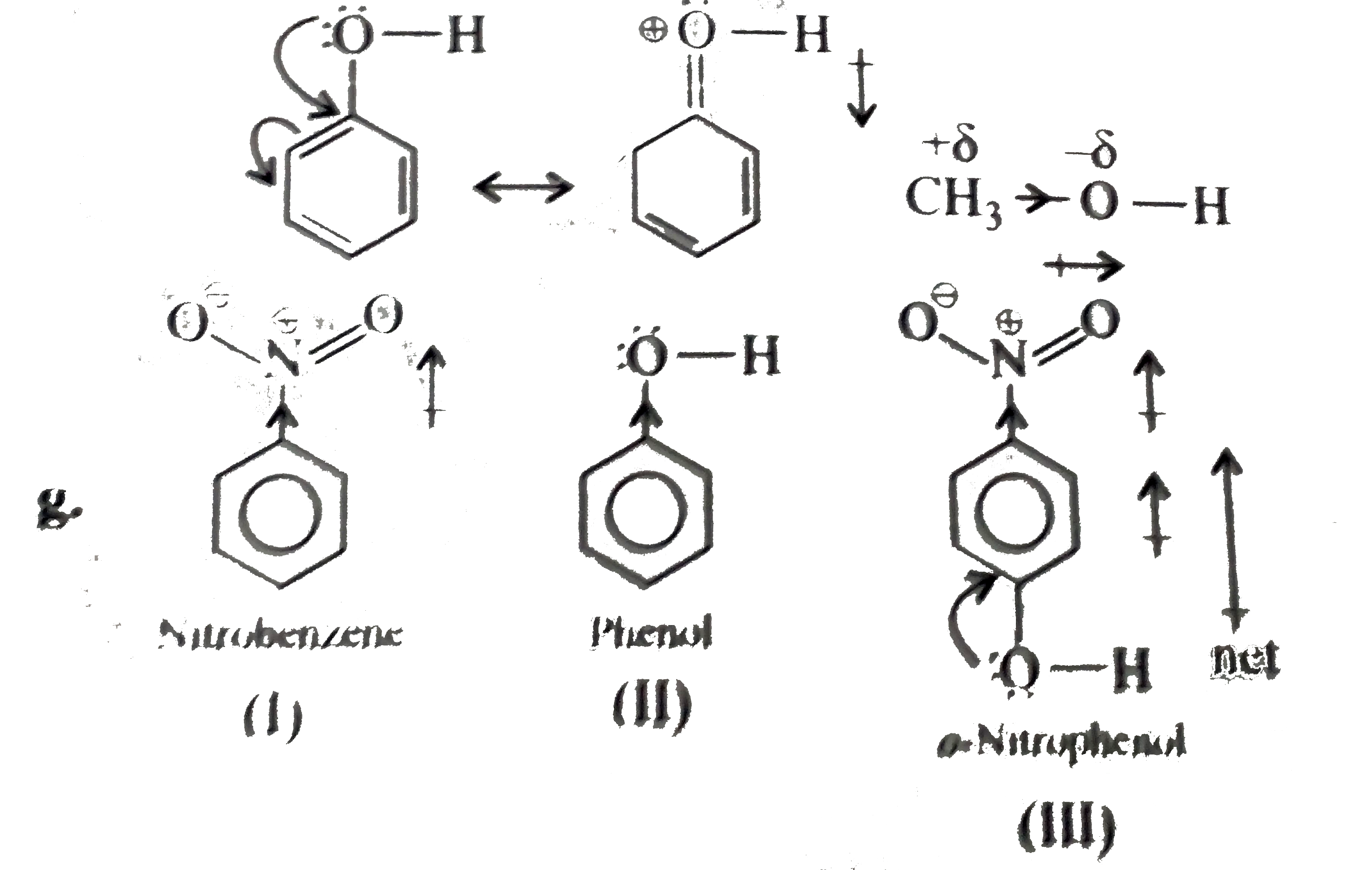
- Give reason in one or two sentences form the following: 'o-nitrophenol...
Text Solution
|
- Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and b...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following with apporopriate reagent:
Text Solution
|
- Phenol is an acid but does not react with sodium bicarbonate solution...
Text Solution
|
- Indicate steps which would convert: a. Phenol to acetopenone b. ...
Text Solution
|
- An optically active alcohol A (C(6)H(10)O) absorbs 2 mol of hydrogen p...
Text Solution
|
- 2,2-Dimethyloxirane can be cleaved by acid (H^(o+)). Write the mechani...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following two methods : "Method 1 : "(CH(3))(3)CBr +NaO...
Text Solution
|
- Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than c...
Text Solution
|
- Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butan...
Text Solution
|
- Explain briefly the formation of the product giving structures of the ...
Text Solution
|
- What would be that major product in each of the following reactions ? ...
Text Solution
|
- How would you synthesis 4-methoxyphenol form bromobenzene in NOT more ...
Text Solution
|
- Convert
Text Solution
|
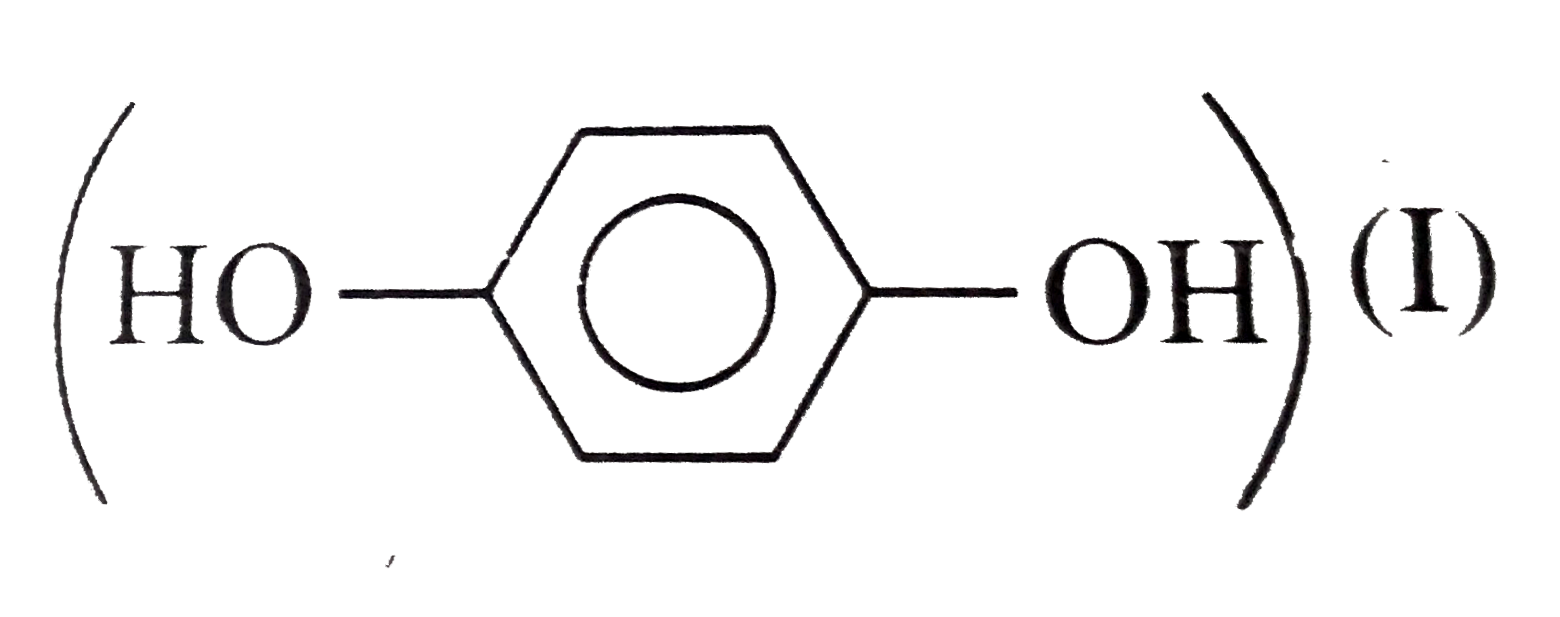 (I) has high melting point than catechol
(I) has high melting point than catechol 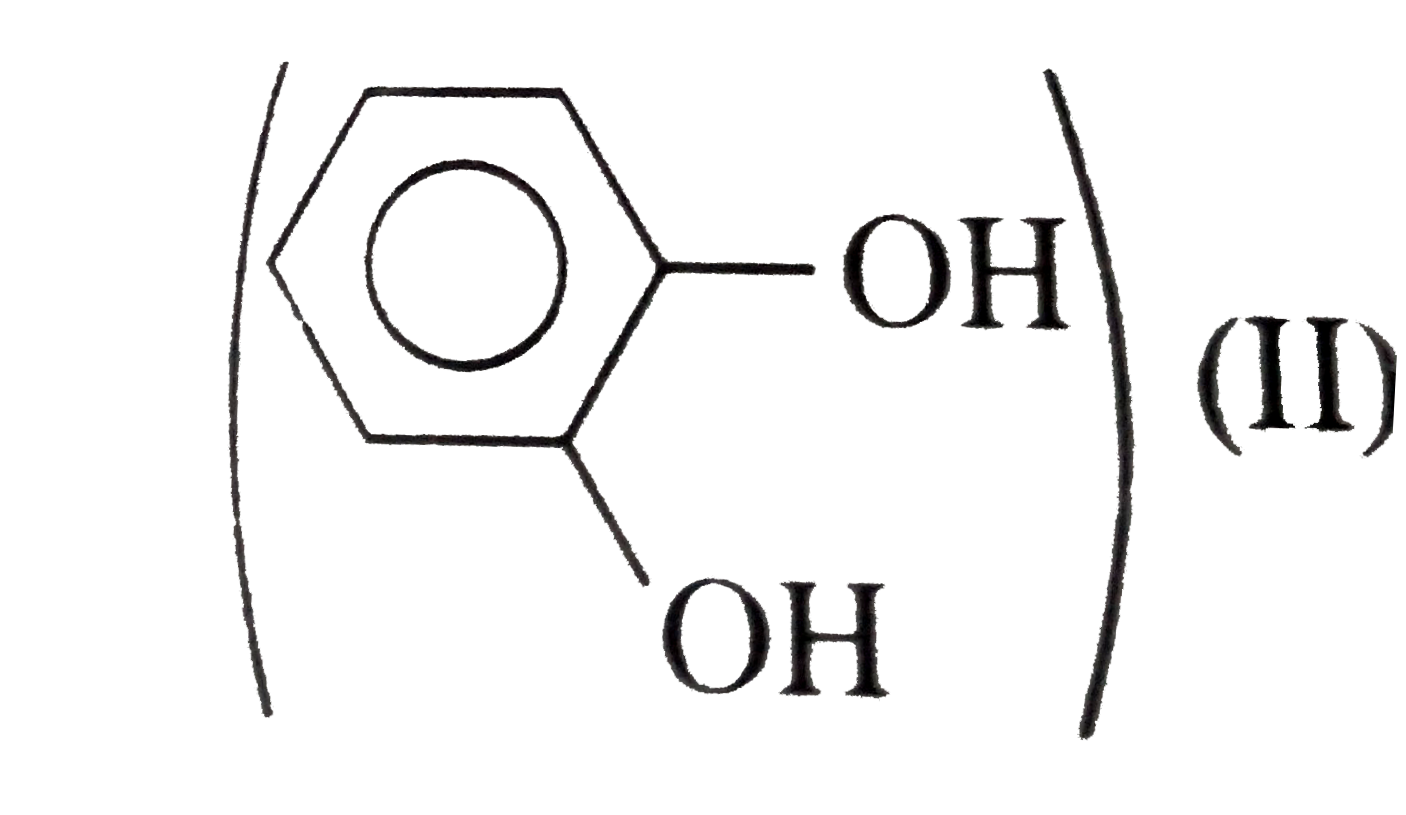 (II), because of the symmetrical packing of p-isomers of (I), (II), and (III), intramolecular H-bonding (chelation) occurs which inhibits the intermolecular attraction between these molecules and thus lowers the boiling point and also reduces H-bonding of tehes molecules with `H_(2)O`, thereby, decreases water solubility. Intramolecular chelation does not occur in p- and m- isomers.
(II), because of the symmetrical packing of p-isomers of (I), (II), and (III), intramolecular H-bonding (chelation) occurs which inhibits the intermolecular attraction between these molecules and thus lowers the boiling point and also reduces H-bonding of tehes molecules with `H_(2)O`, thereby, decreases water solubility. Intramolecular chelation does not occur in p- and m- isomers. 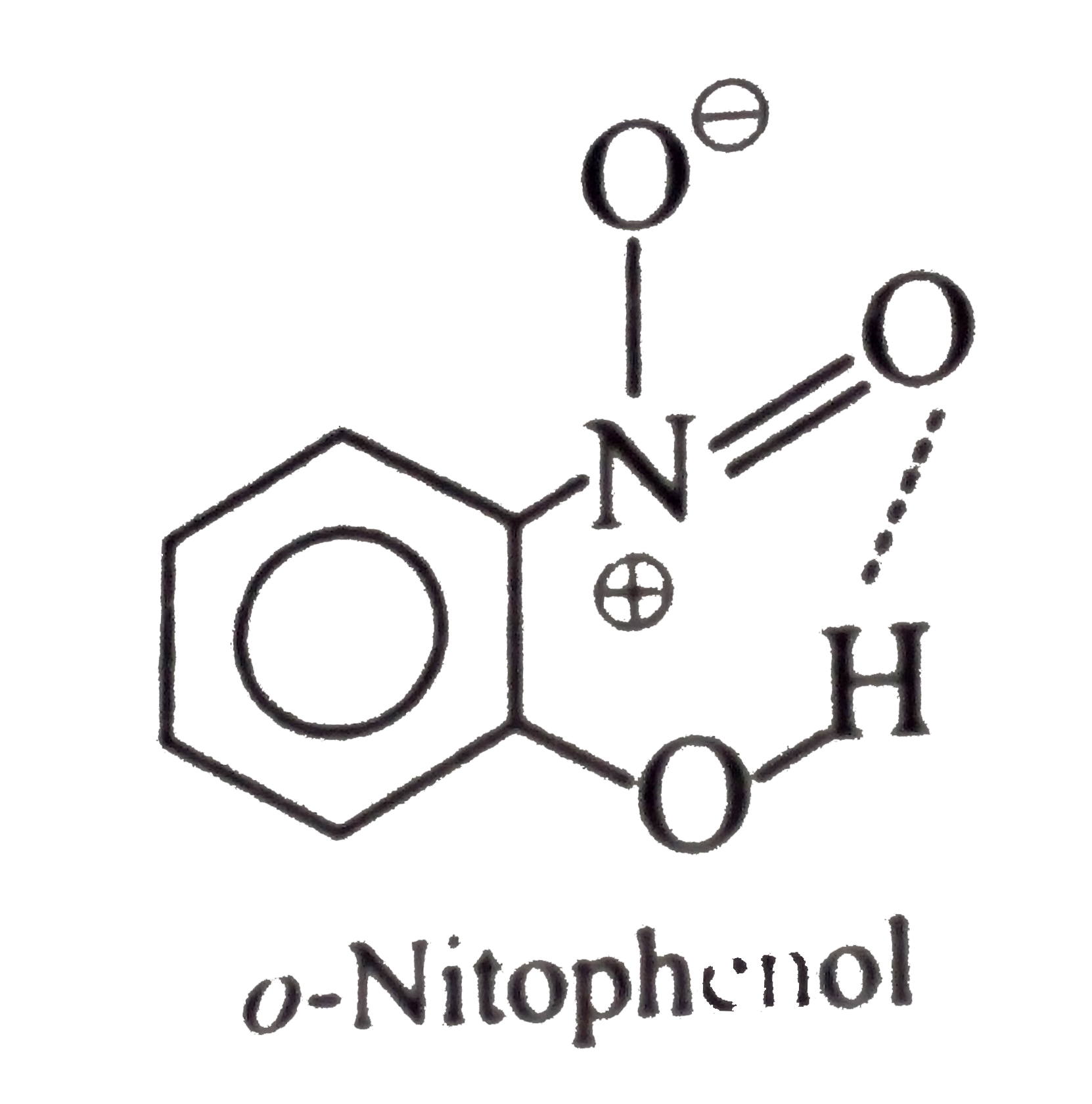
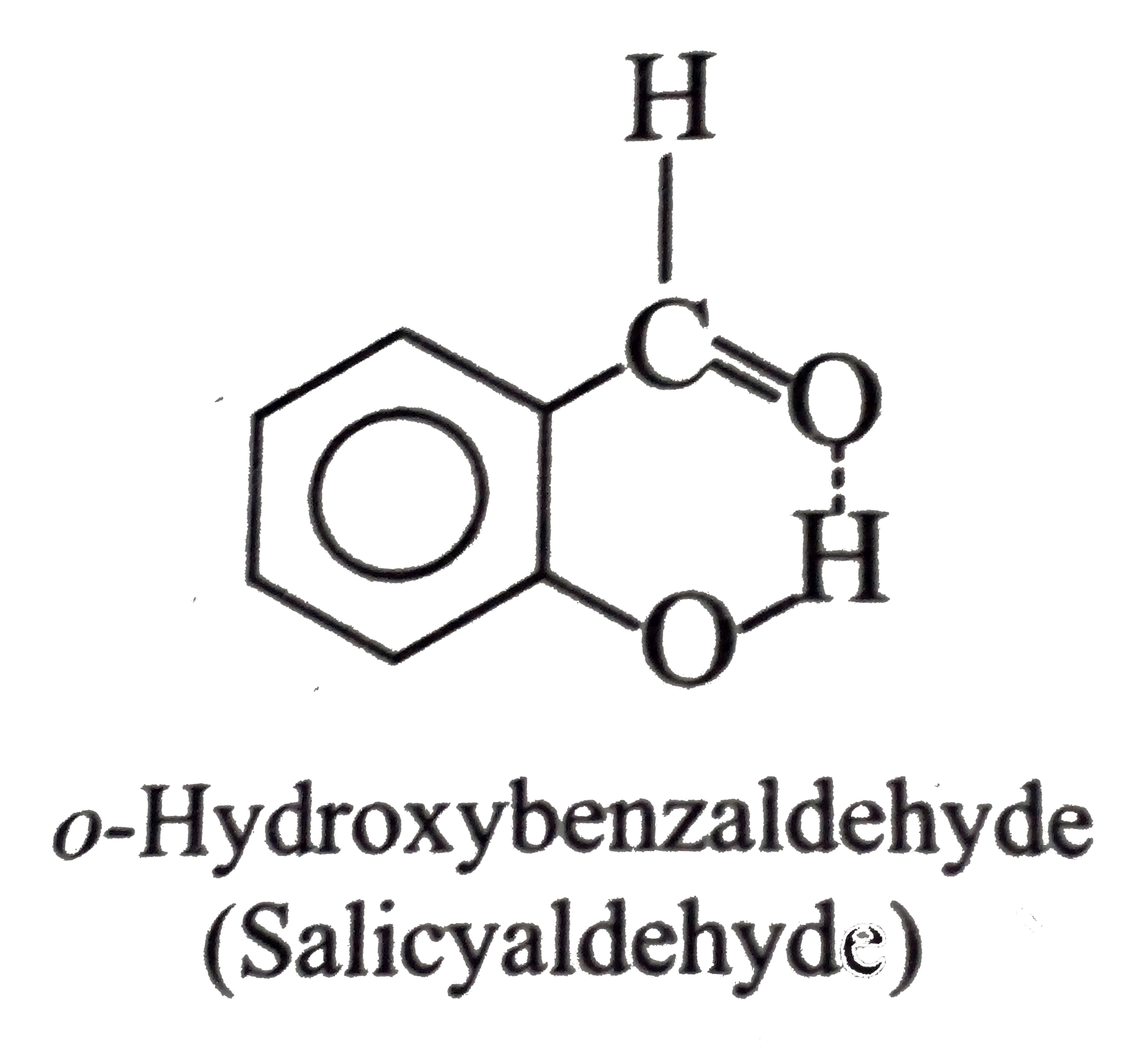
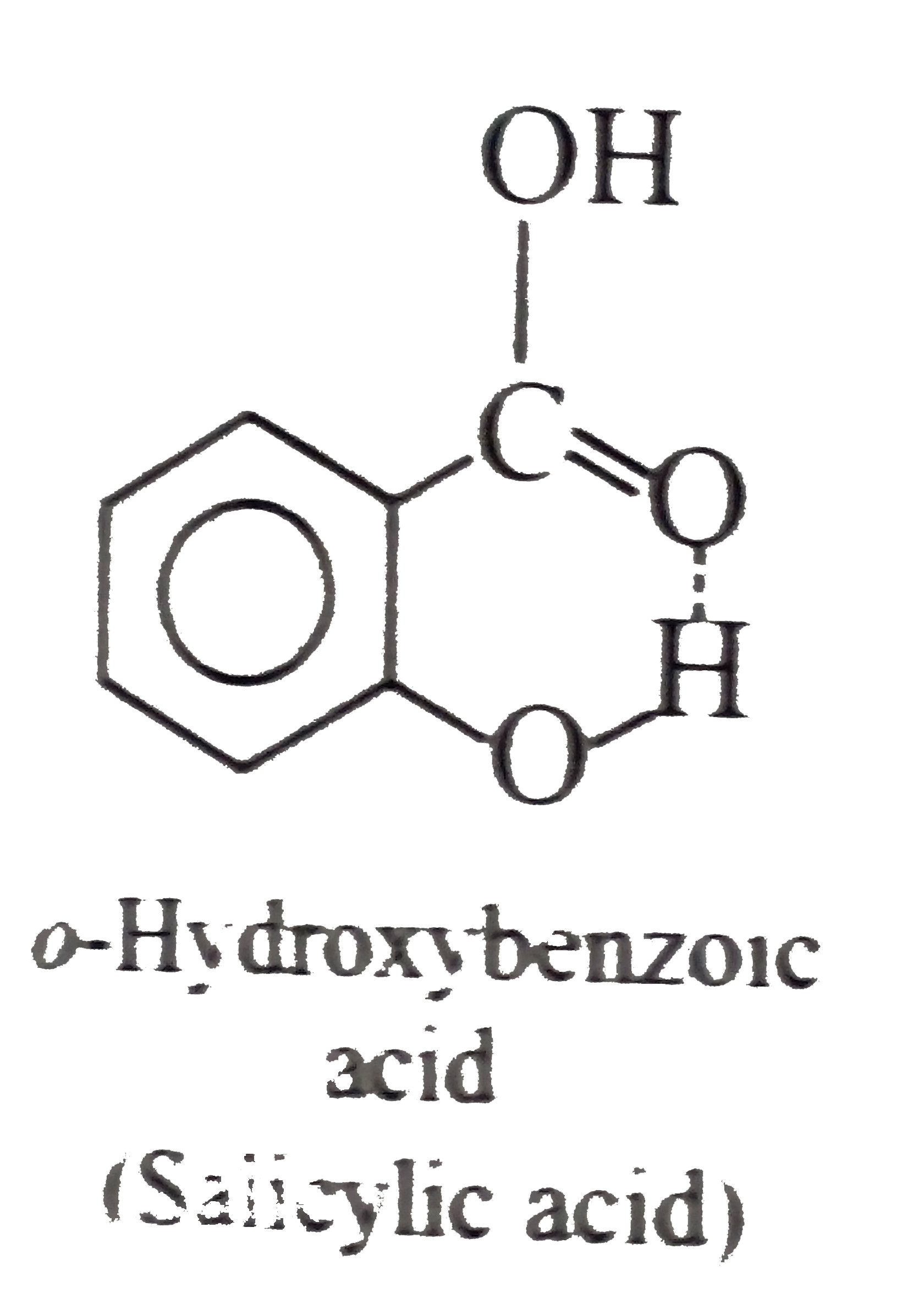
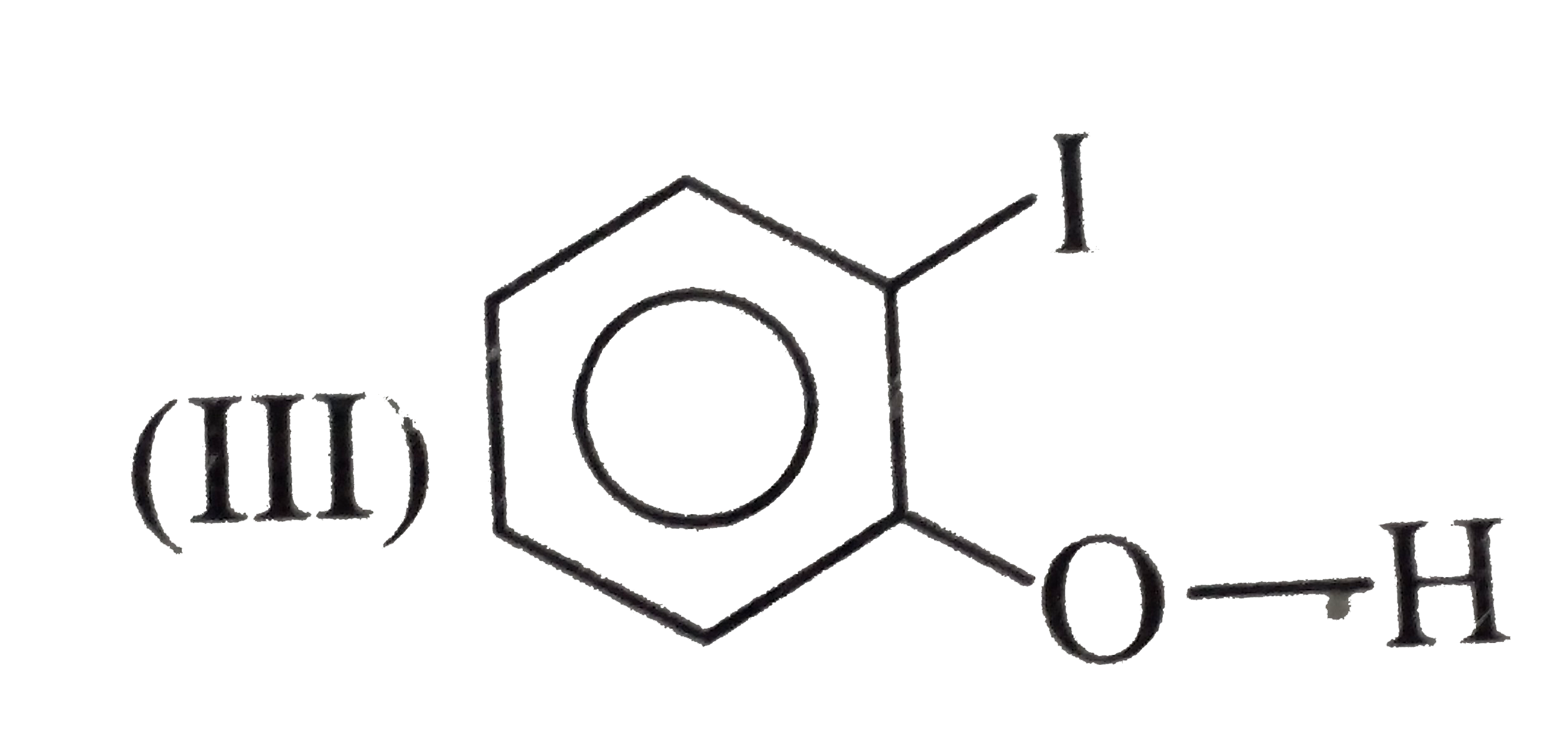
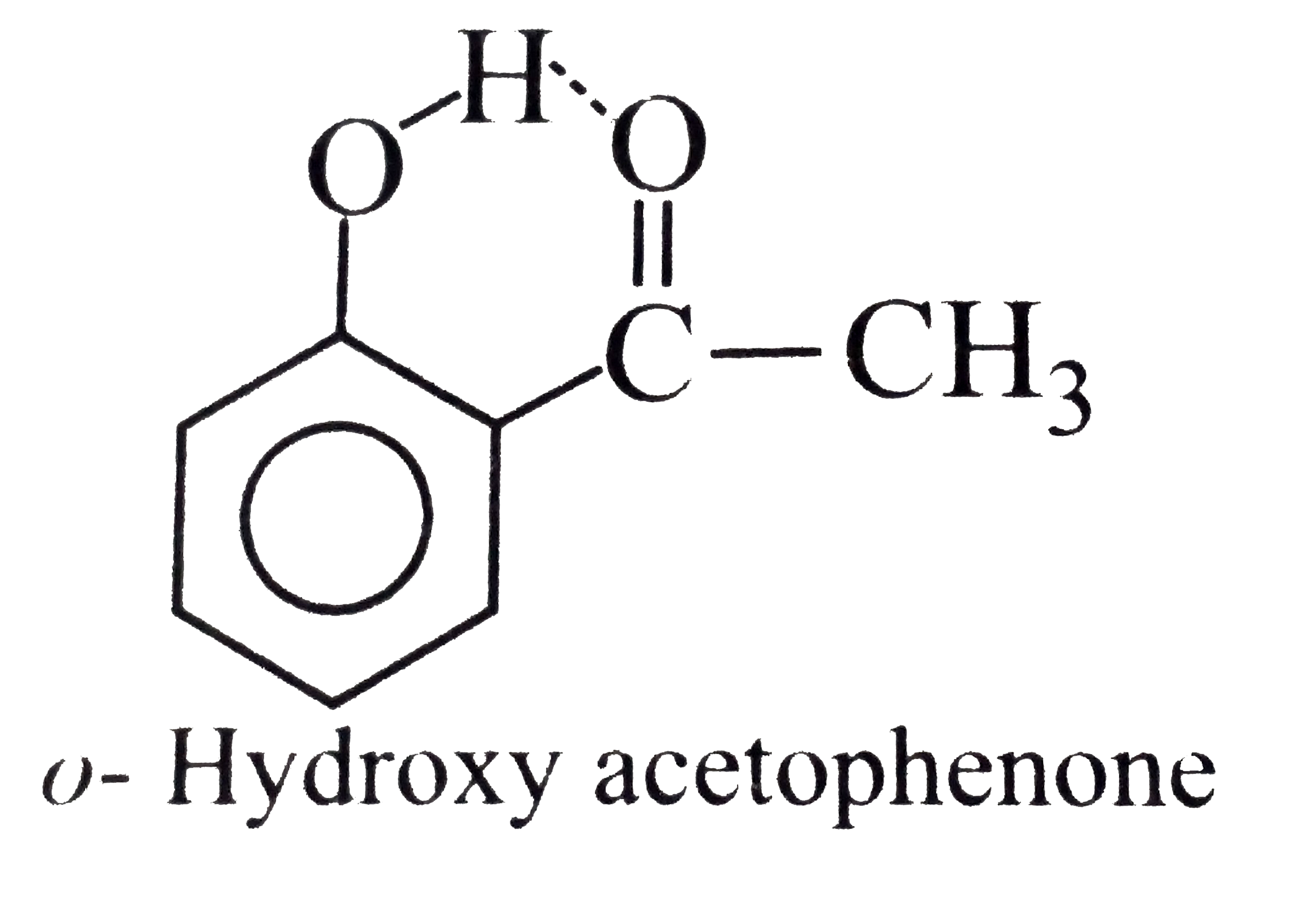 (Not possible.) H-bonding is formed
(Not possible.) H-bonding is formed 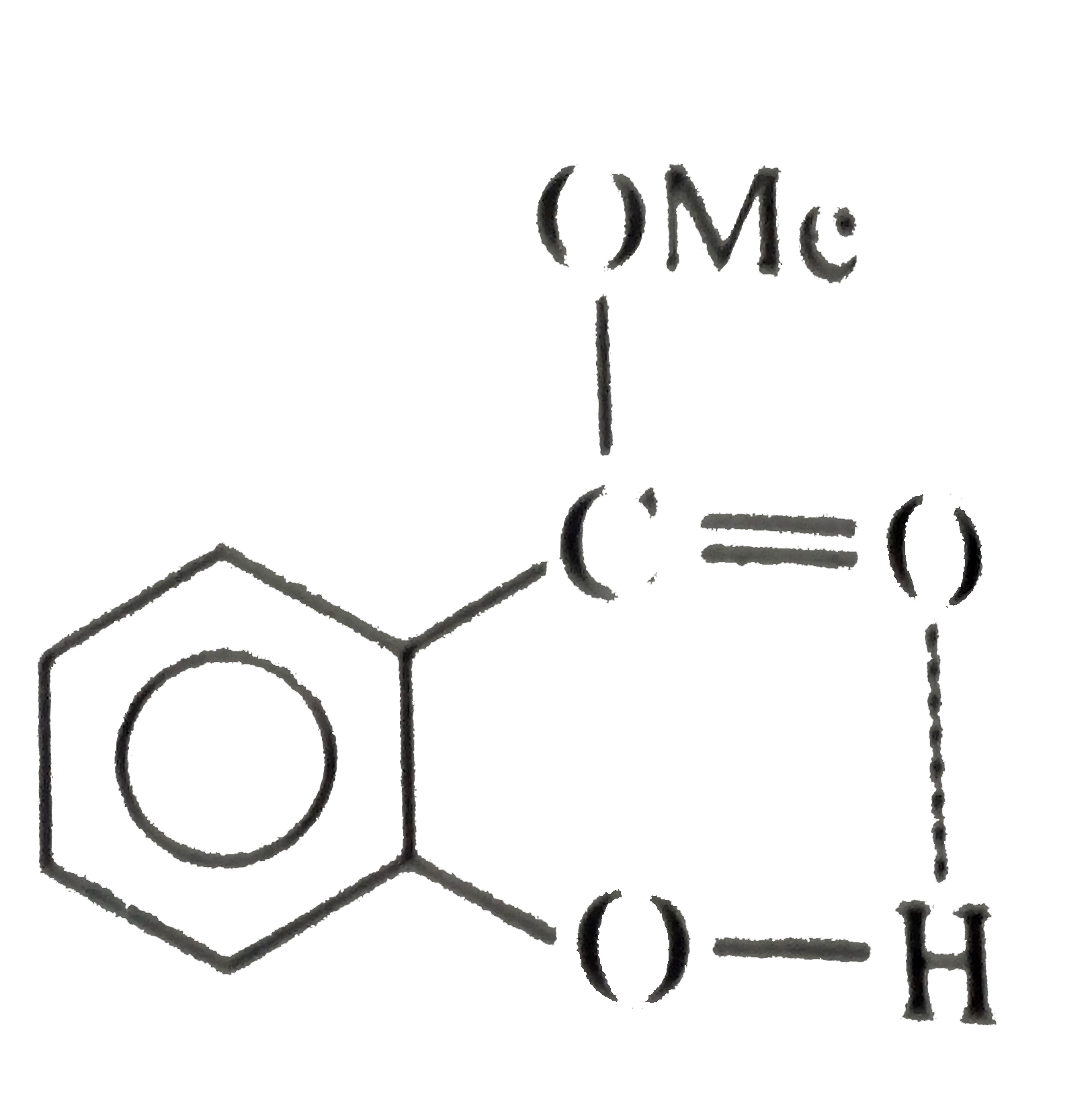 with EN elements such as F, O, N, and sometimes with CI, but not with C. of `CH_(3)` group.
with EN elements such as F, O, N, and sometimes with CI, but not with C. of `CH_(3)` group. 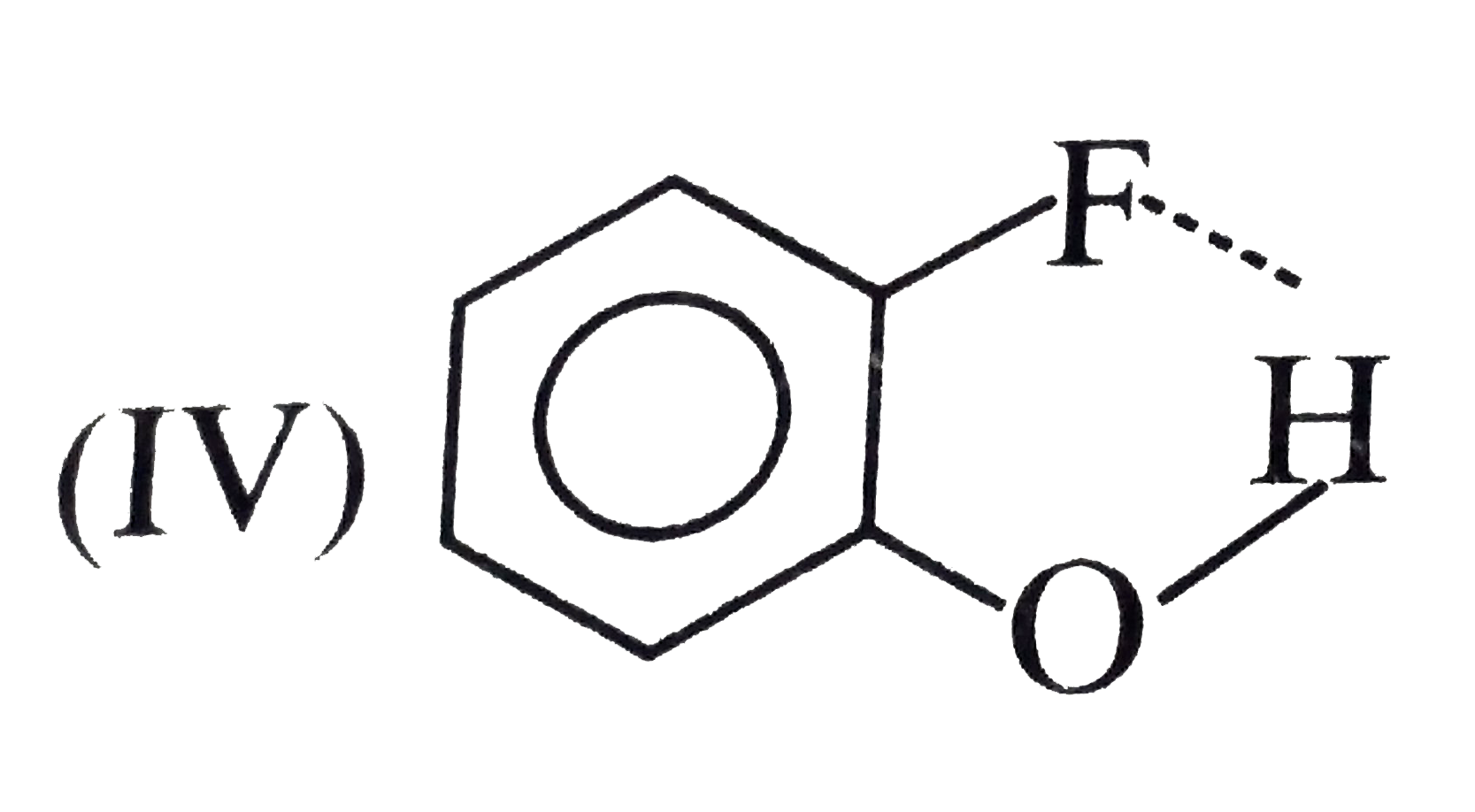 (Not possible.) EN of I not sufficient to form H-bonding.
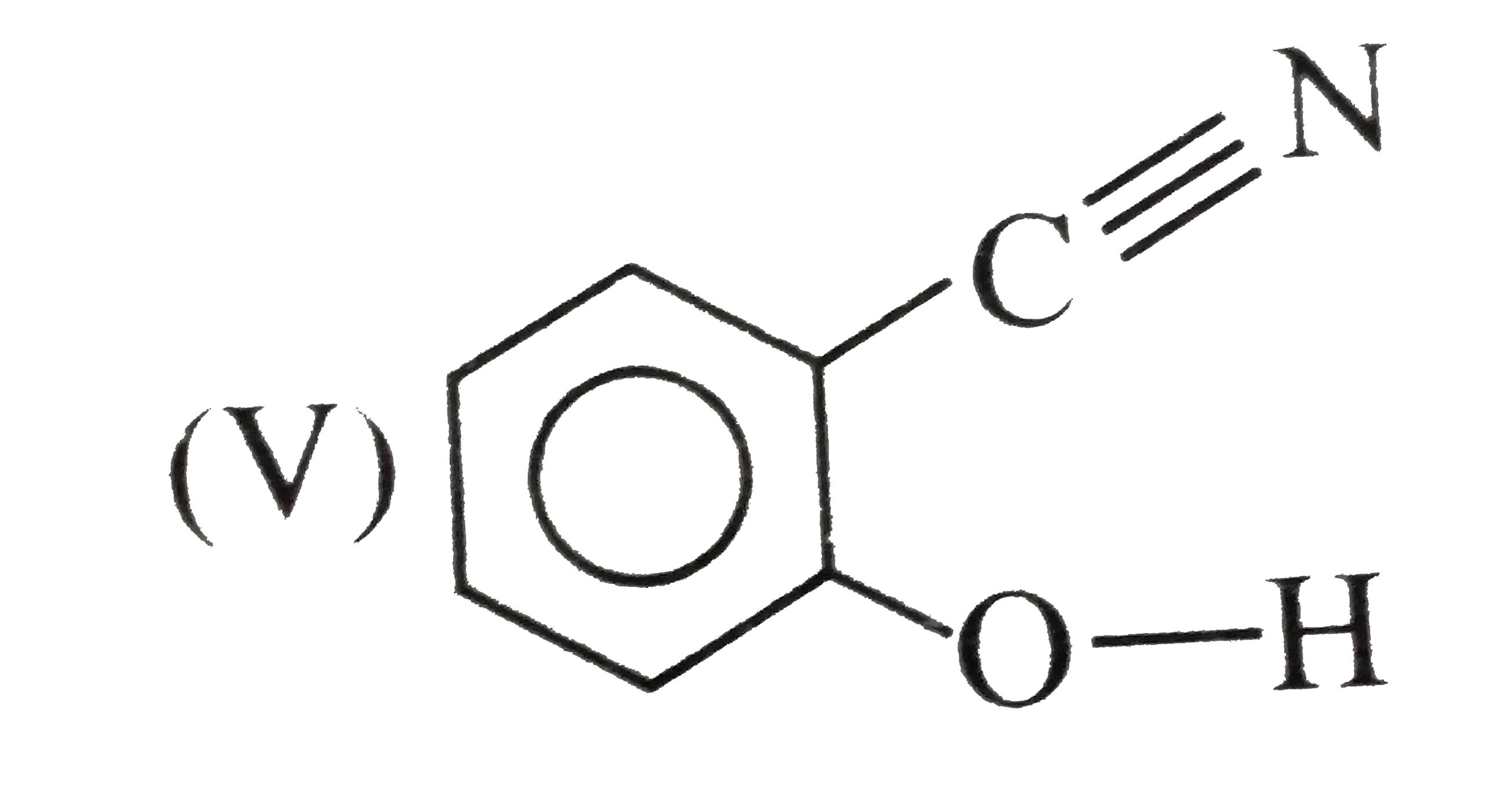
(Not possible.) EN of I not sufficient to form H-bonding. 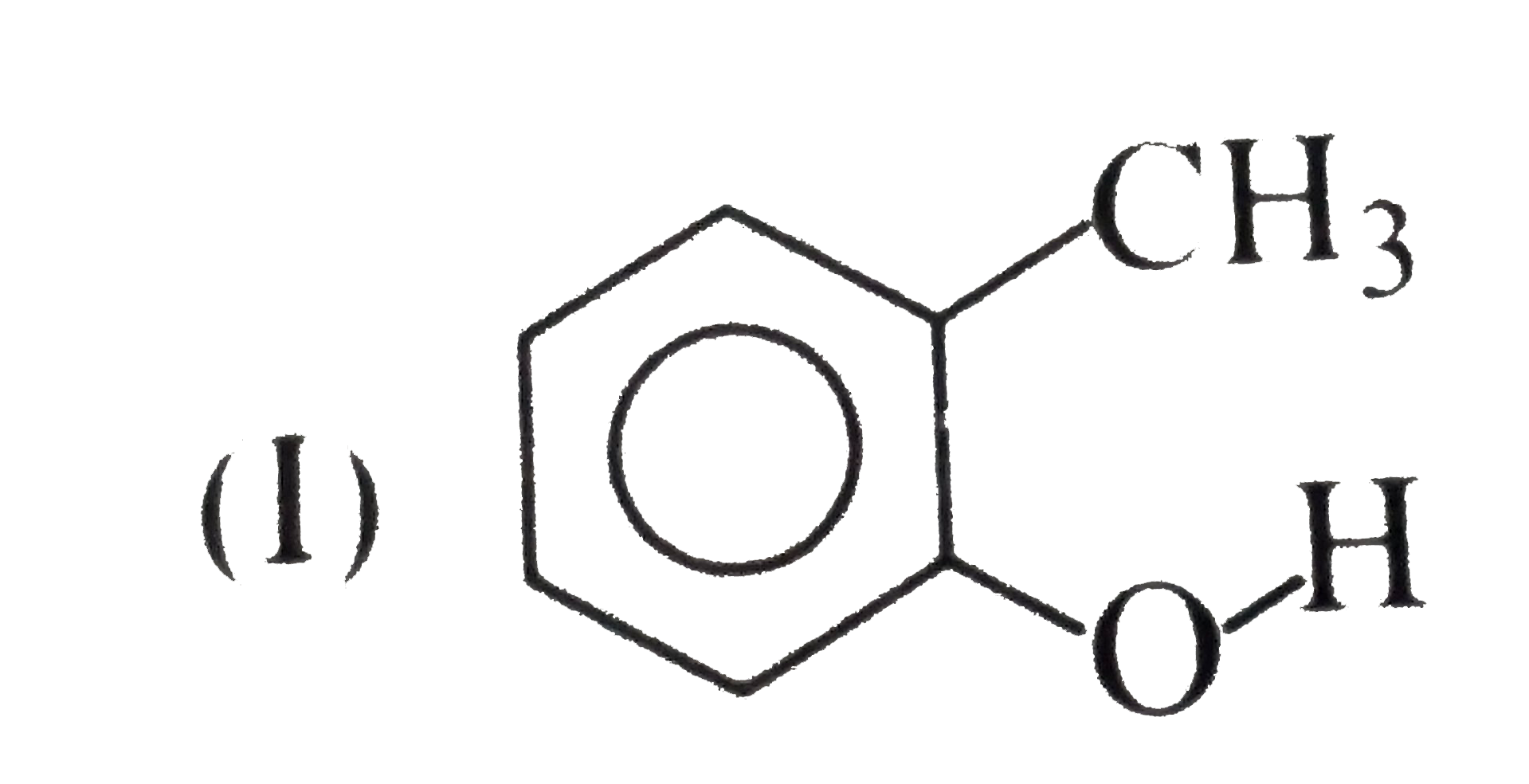 (Not possible.) Although EN of N is high for the formation of H-bonds, but the `(C-=N)` group is linear and is far away form the (OH) group.
(Not possible.) Although EN of N is high for the formation of H-bonds, but the `(C-=N)` group is linear and is far away form the (OH) group.