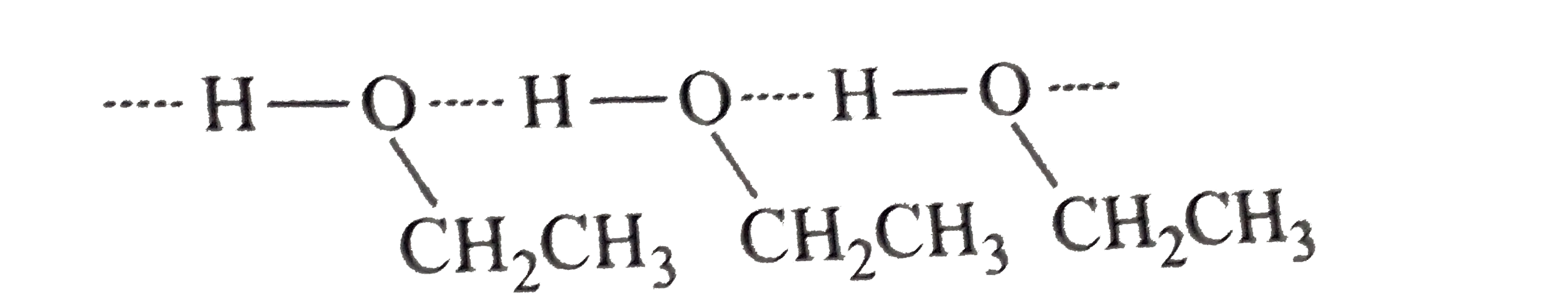Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Linked Comprehension|60 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|24 VideosALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Subjective|25 VideosALIPHATIC AND AROMATIC ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|26 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALCOHOL,PHENOL AND ETHERS-Exercises Concept Application
- Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare acid...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why is ortho nitrophenol more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring ac...
Text Solution
|
- Give equations of the following reactions: (i) Oxidation of propan-1...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following with an example: i. Kolbe's reaction ii. R...
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
Text Solution
|
- How are the following conversions carried out? (i) Propene rarr Pro...
Text Solution
|
- Name the reagents used in the following reactions: (i) Oxidation of ...
Text Solution
|
- Give reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to m...
Text Solution
|
- Give the IUPAC names of the following ethers: C(2)H(5)OCH(2)--overse...
Text Solution
|
- Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the f...
Text Solution
|
- Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson synthesis for t...
Text Solution
|
- How is 1-propoxypropane synthesised from propan-1-ol? Write mechanism ...
Text Solution
|
- Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alc...
Text Solution
|
- Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with: (i) 1-pro...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers (i) the alkoxy group activa...
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Text Solution
|
- Write equations of the following reactions: (i) Friedel-Crafts react...
Text Solution
|
- Show how would you synthesise the following alcohols from appropriate ...
Text Solution
|
- when 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction ta...
Text Solution
|