Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|17 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Subjective)|19 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|8 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES-Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)
- (a) Why do acyl chlorides undergo nucleophilic attack more readily tha...
Text Solution
|
- Write the chemical eqution to show what happens when 'Ethyl acetate is...
Text Solution
|
- State with balanced equation what happens when 'Acetic anhydride react...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following in one or two sentences. 'Acetic acid...
Text Solution
|
- Write down the reactions involved in the preparation of the following ...
Text Solution
|
- A certain hydrocarbon (A) was found to contain 85.7 % carbon and 14.3 ...
Text Solution
|
- Give reason in one or two sentences for the following : 'Formic acid i...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following in order of their increasing ease of hydrolysis ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following with appropriate structures : (CH(3) CO)(2) O...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid (X) having a molecular formula C(6) H(12) O(2) is hydrolysed ...
Text Solution
|
- Write the balanced equations for the following reaction : 'Acetamide...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound (A) on treatment with acetic acid in the presence ...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following : 'Carbon-oxygen bond lengths in form...
Text Solution
|
- Conversion of Ethanoic acid to mixture of methanoic acid and diphenyl ...
Text Solution
|
- The sodium salt of a carboxylic acid, A, was produced by passing a gas...
Text Solution
|
- In the following, identify the compounds/reaction conditions represent...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following as stated : 'Increasing order of acidic streng...
Text Solution
|
- In the following identify the compounds/reaction conditions represente...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following sequence of the reactions with approprite struc...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the major product in the following reactions : (i) (ii) ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following reactions, identify the compounds A, B, C and D. (i...
Text Solution
|
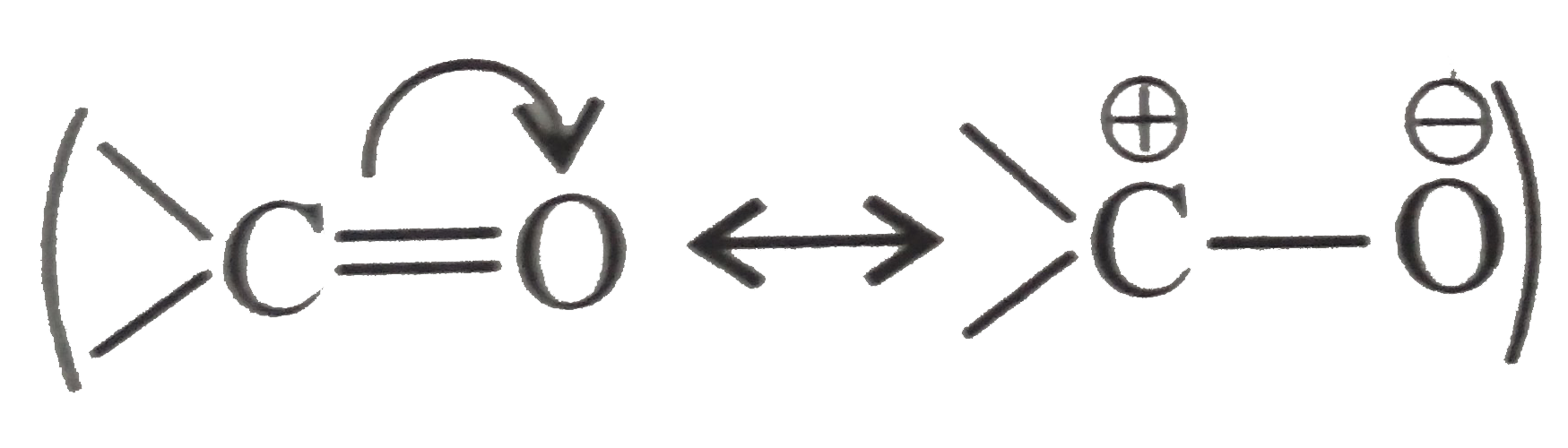 . `C` is more positive and more electrophilic than `C` in `(R-Cl)`.
. `C` is more positive and more electrophilic than `C` in `(R-Cl)`.