A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct)|34 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Singlecorrect)|64 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Subjective)|19 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|8 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives Subjective|23 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES-Exercises (Linked Comprehension)
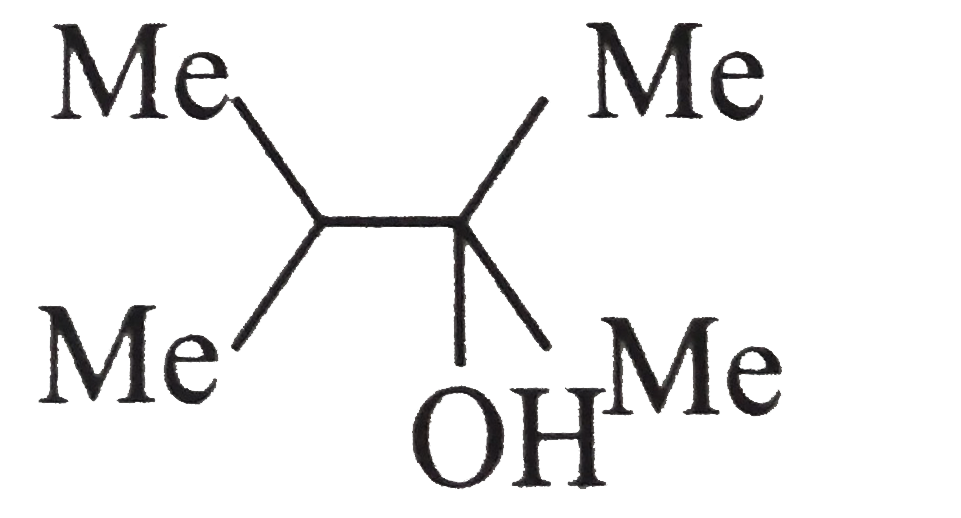
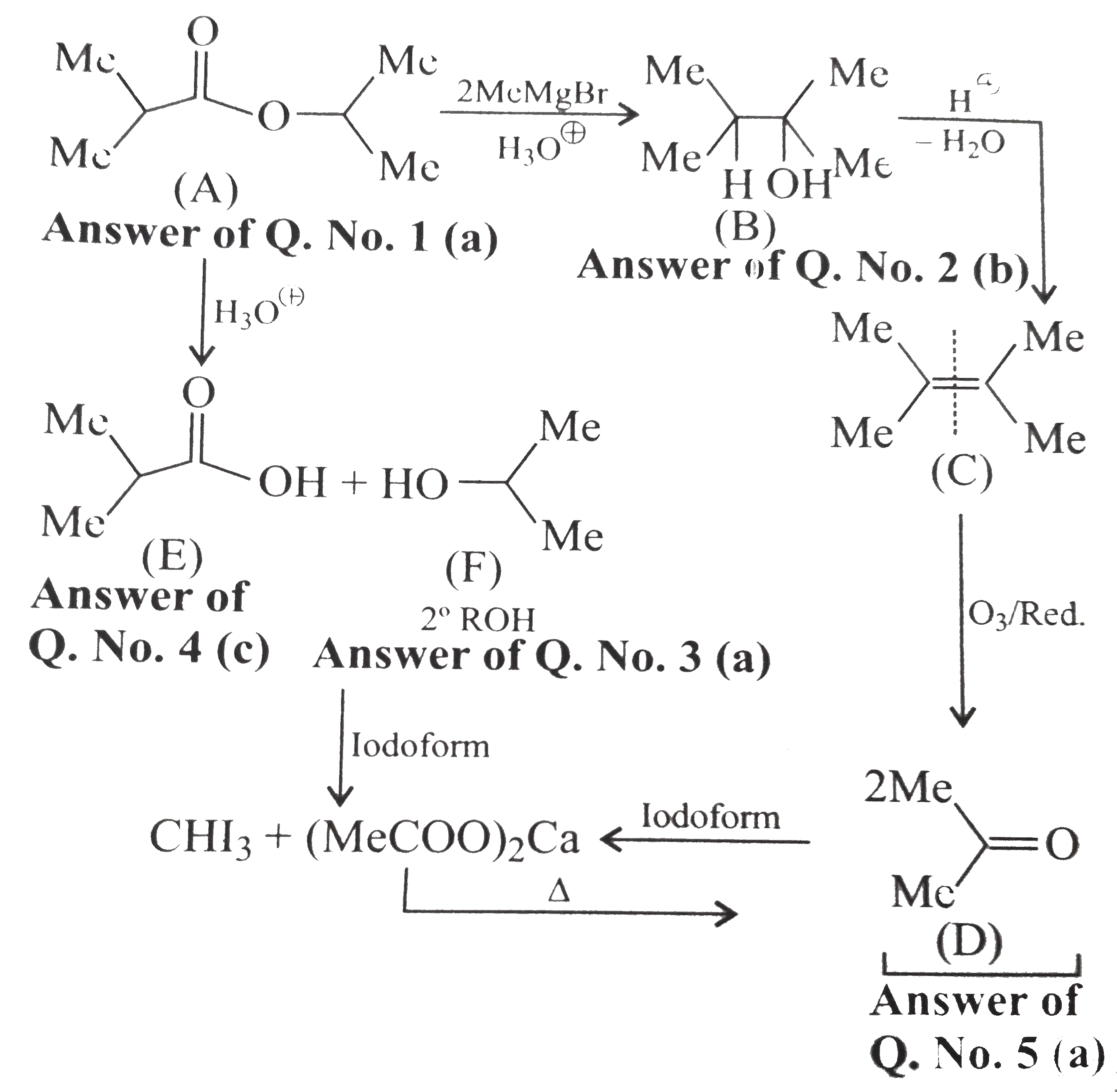
- Alcohol (B) is :
Text Solution
|
- Alcohol (F) is :
Text Solution
|
- Acid ( E) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound (D) is :
Text Solution
|
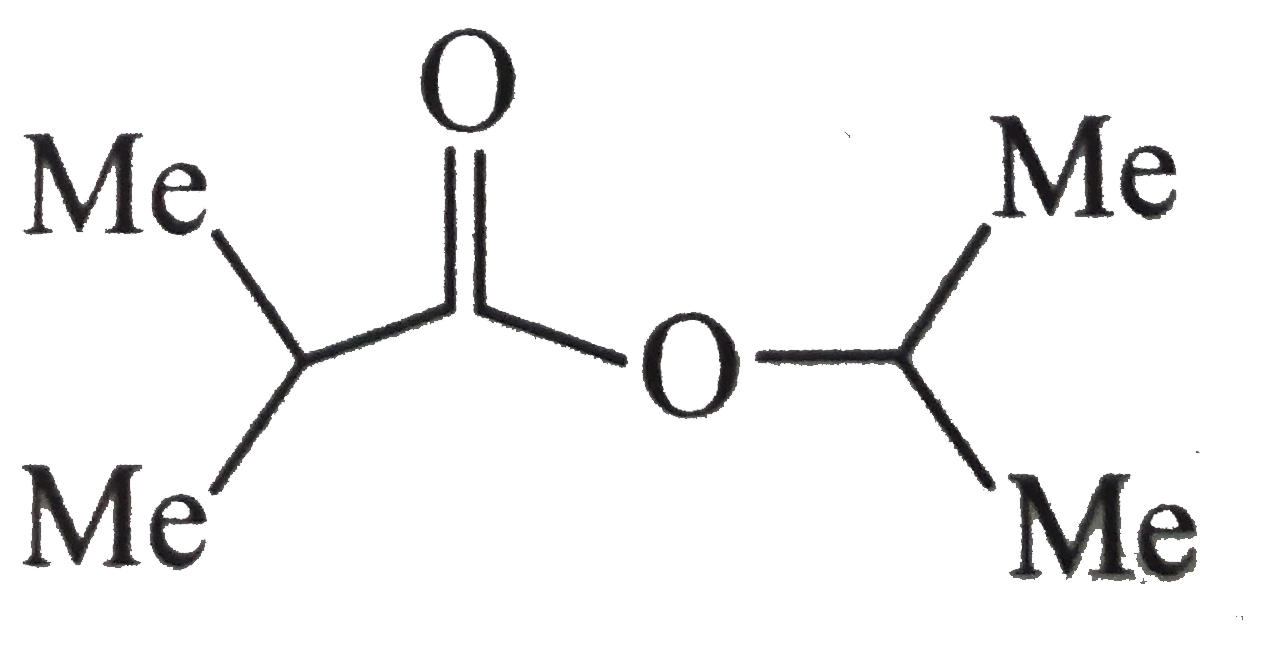
- Carboxylic acid (A) is:
Text Solution
|
- Carboxylic and (B) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound ( C) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound (D) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compounds ( C) and (D) can be distinguished by :
Text Solution
|
- Four isomeric optically active compounds overset (NaHCO3) rarr CO2 (g)...
Text Solution
|
- Four isomeric optically active compounds overset (NaHCO3) rarr CO2 (g)...
Text Solution
|
- Four isomeric optically active compounds overset (NaHCO3) rarr CO2 (g)...
Text Solution
|
- Four isomeric optically active compounds overset (NaHCO3) rarr CO2 (g)...
Text Solution
|
- Four isomeric optically active compounds overset (NaHCO3) rarr CO2 (g)...
Text Solution
|
- Write thermal decomposition reaction of Calcium carbonate.
Text Solution
|
- Identify (D) in the reaction (ii) Compound (D) is prepard by carbo...
Text Solution
|
- What is Royal Water and give its composition.
Text Solution
|
- Give the main properties of canal ray experiment.
Text Solution
|
- Compound (B) is :
Text Solution
|
- Compound ( C) is :
Text Solution
|
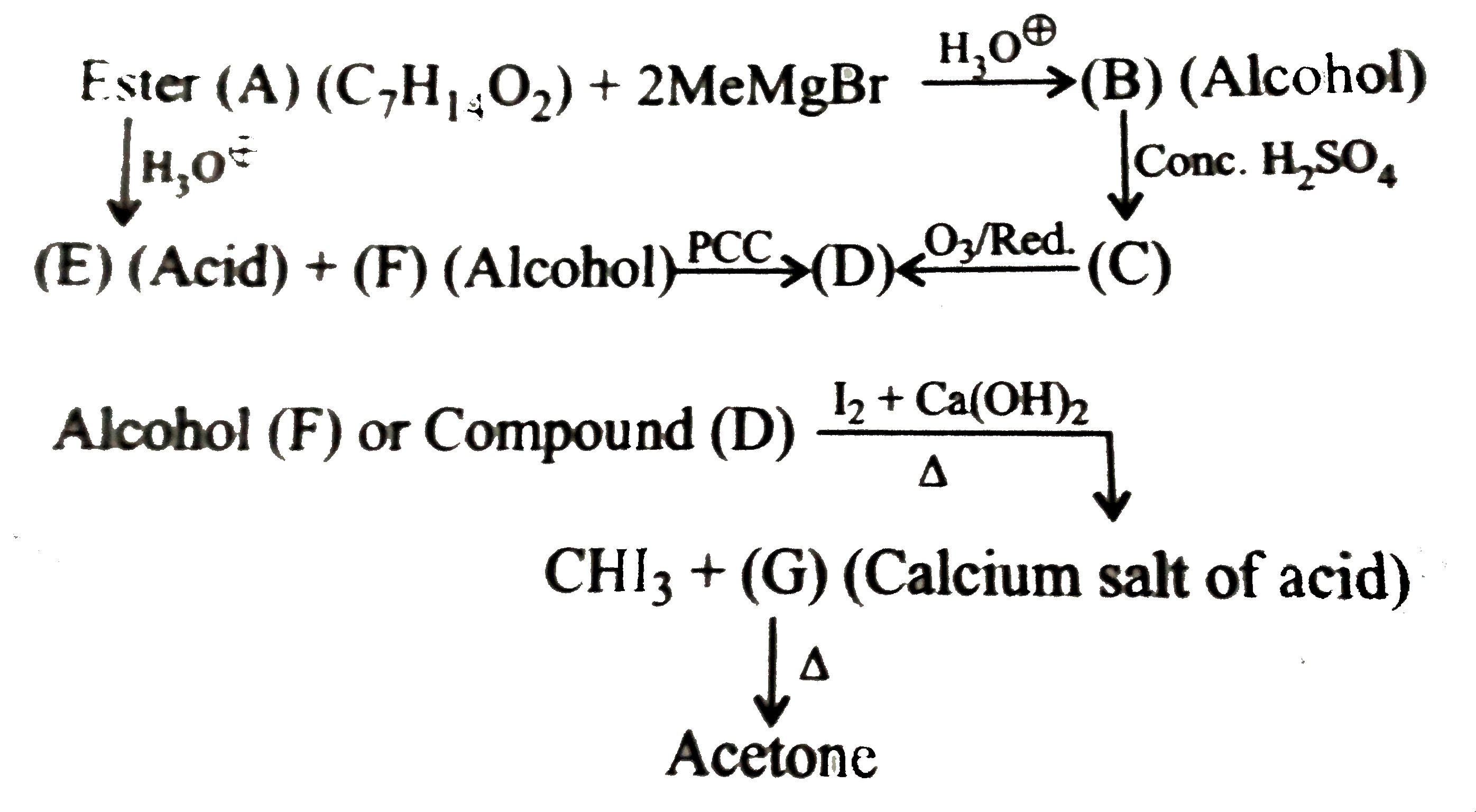
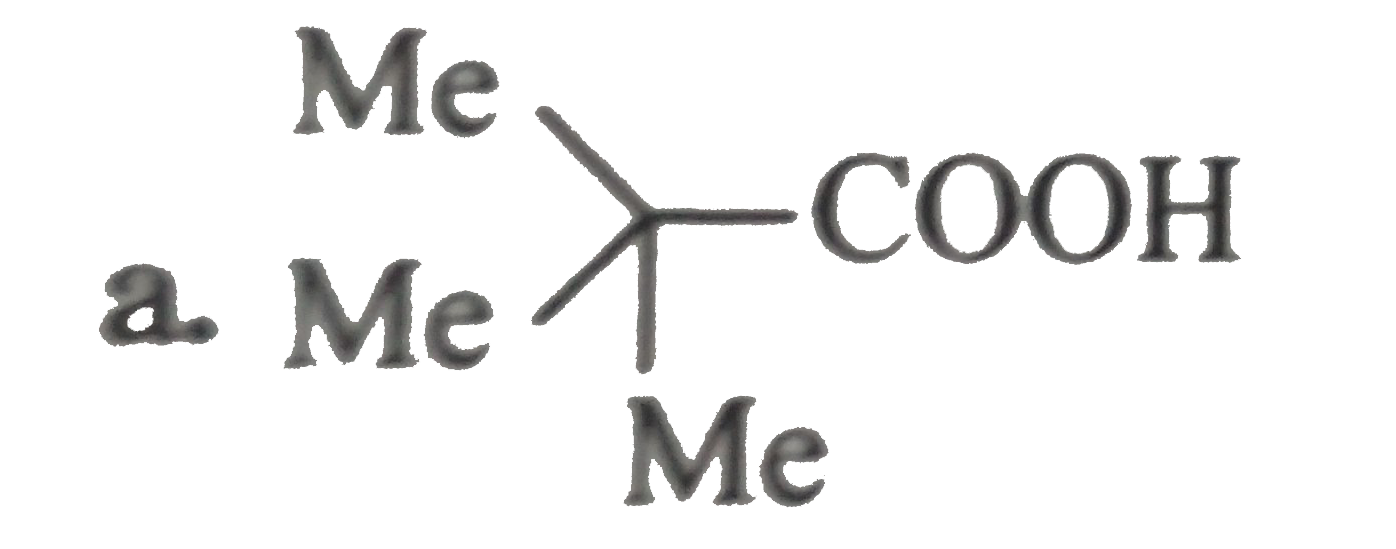

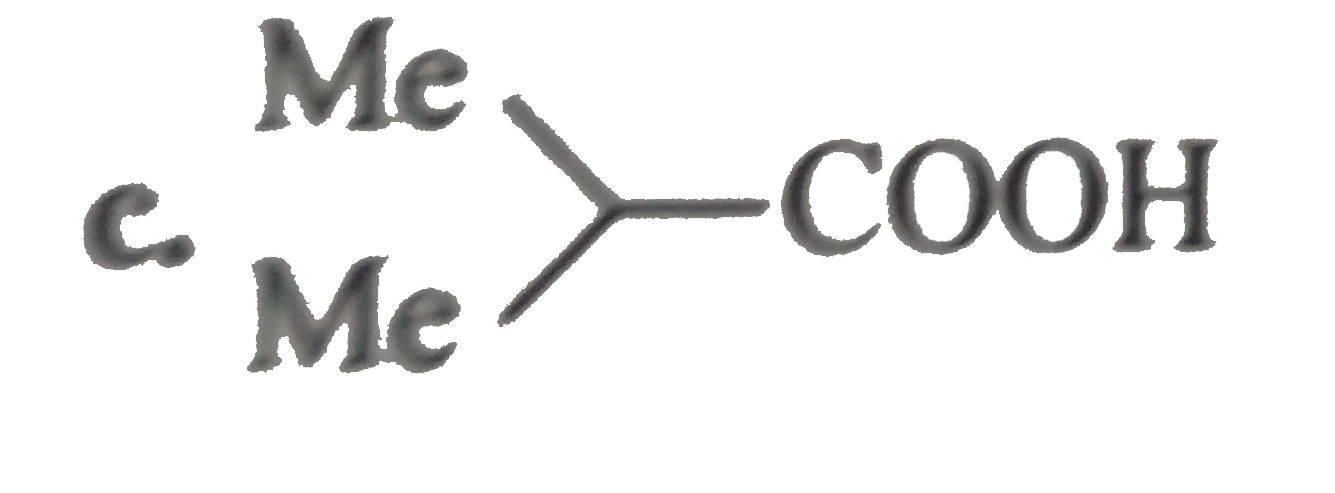
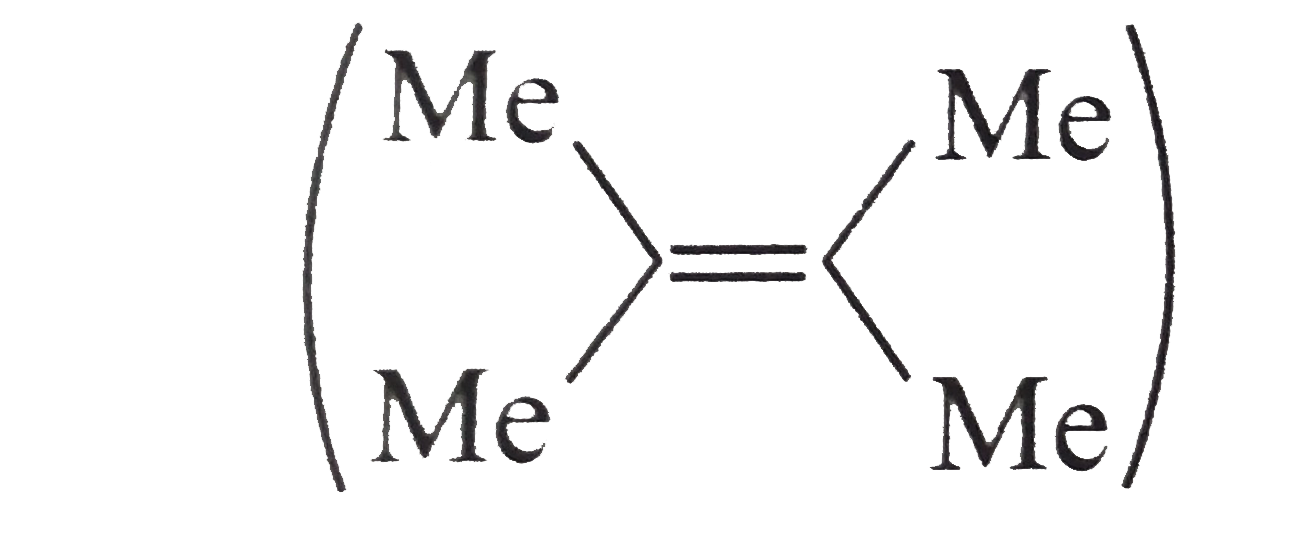
 .
.  .
.