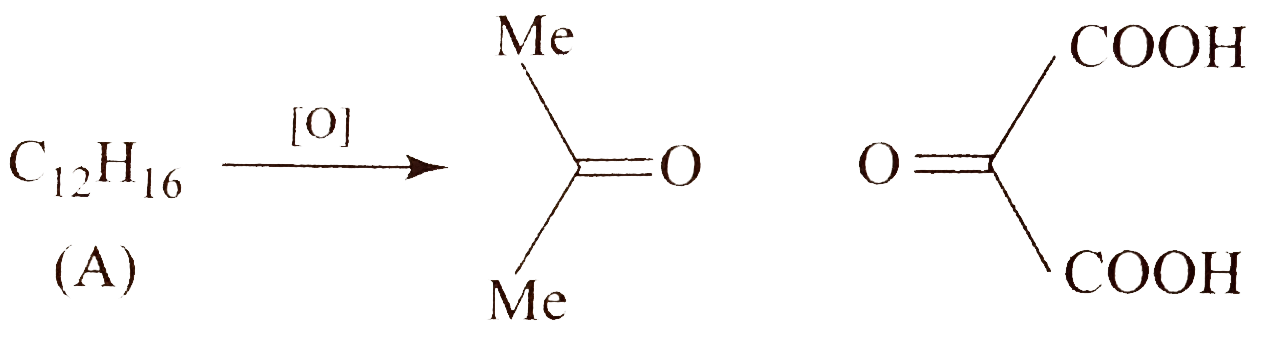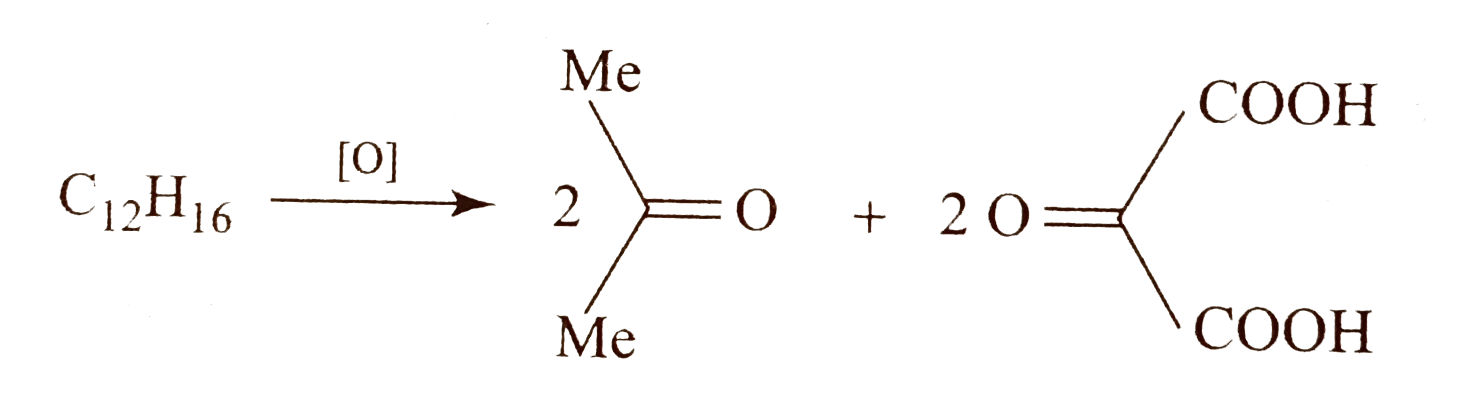Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise SOLVED Example|62 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISES|29 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALKENES AND ALKADIENES-Single correct Answer
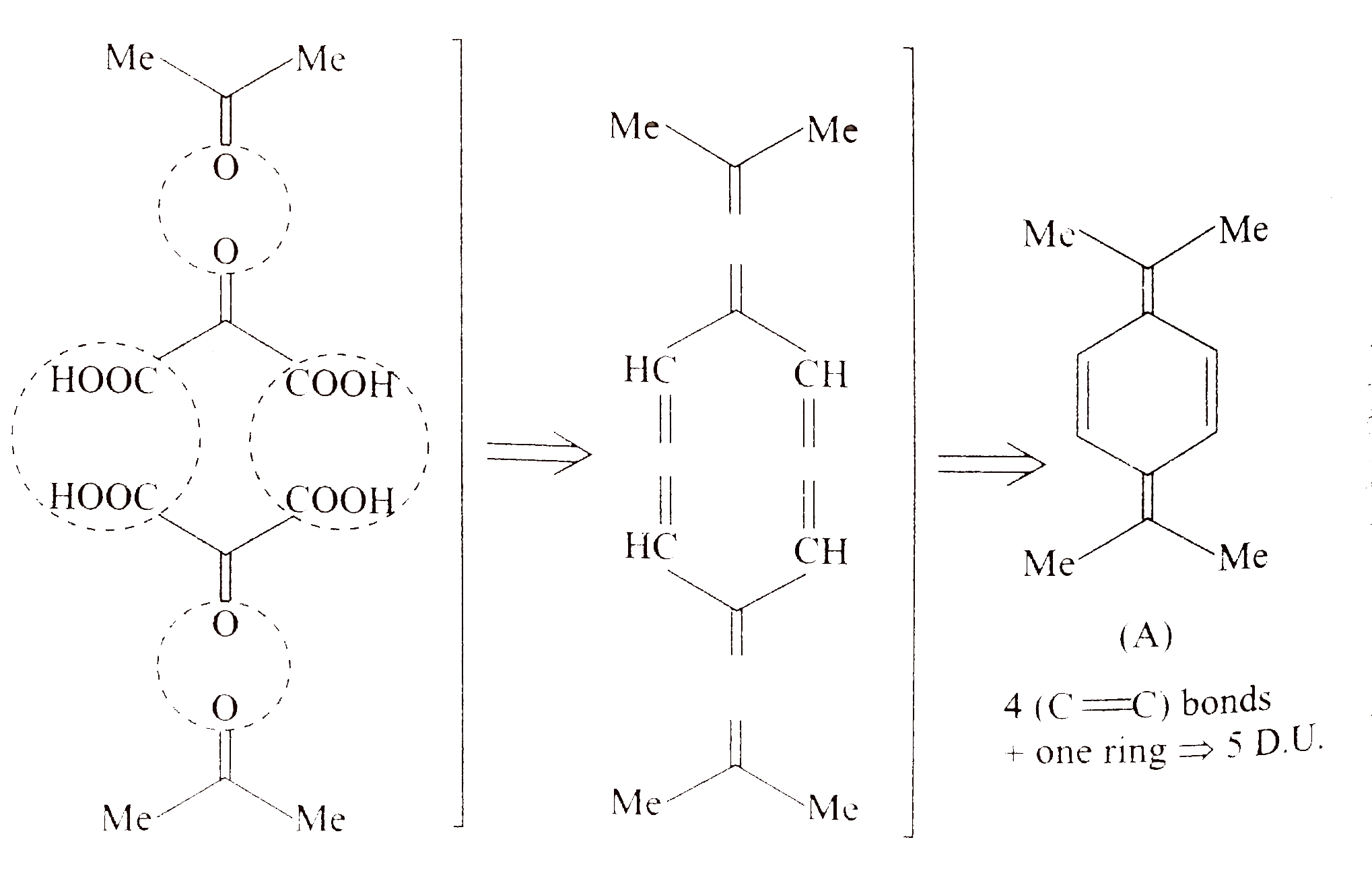
- Compound (A)(C(12)H(16)) on oxidation with acidic KMnO(4) solution giv...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will declourise alkaline KMnO(4)solution ?
Text Solution
|
- The compound 1, 2-butadiene has :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds does not dissolve in conc. H(2)SO(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- Baeyer's reagent is
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of with HBr gives
Text Solution
|
- In the compound, CH(2)=CH-CH(2)-CH(2)--C-=CH the C(2)-C(3) bond is the...
Text Solution
|
- When 1-butyne undergoes oxymercuraction with the help of HgSO(4)+H(2)S...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following alkenes will react faster with H(2) under ...
Text Solution
|
- Hydrogenation of the above compound in the presence of poisoned Pd cat...
Text Solution
|
- In the presence of peroxide, hydrogen chloride and hydrogen iodide do ...
Text Solution
|
- The nodal plane in the pi -bond of ethene is located in :
Text Solution
|
- 2 - Phenylpropene on acidic hydration , gives -
Text Solution
|
- 2-Hexyne gives cis -2- hexene on treatment with :
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)CH=CH(2)+NOClrarrP Identify the product.
Text Solution
|
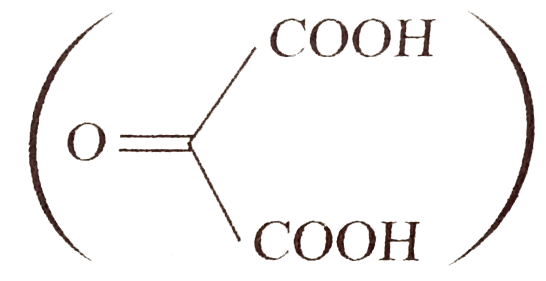 . Identify compound `(A)`.
. Identify compound `(A)`.