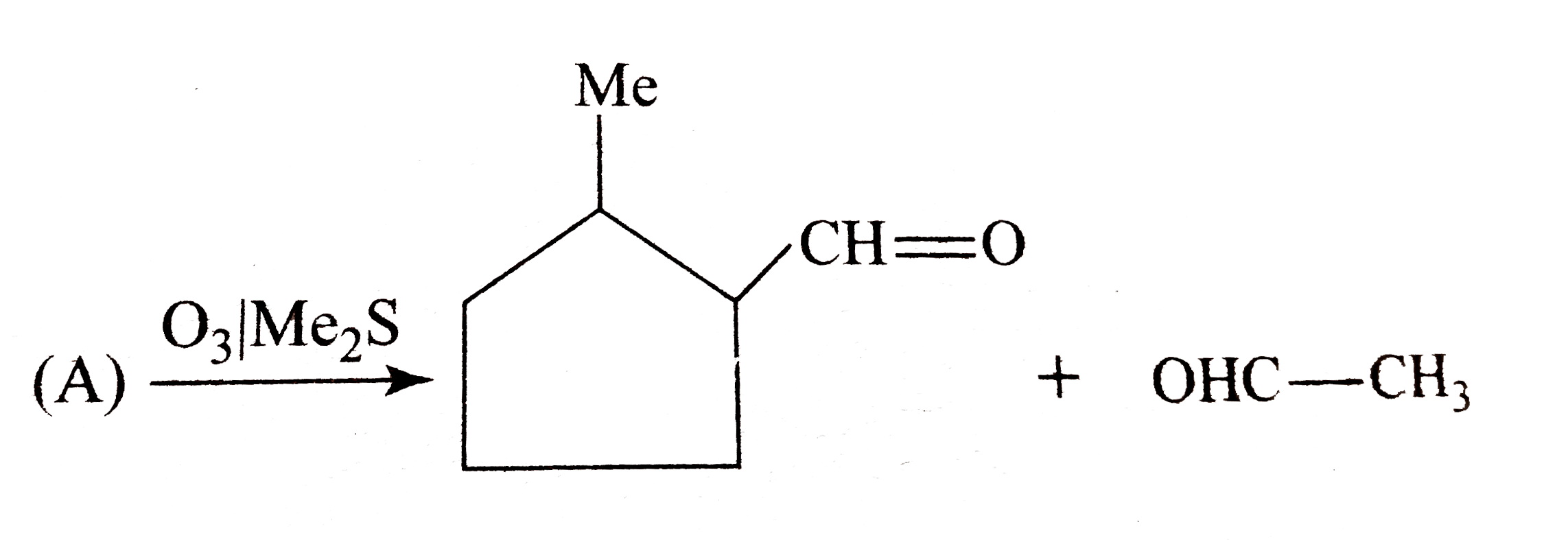
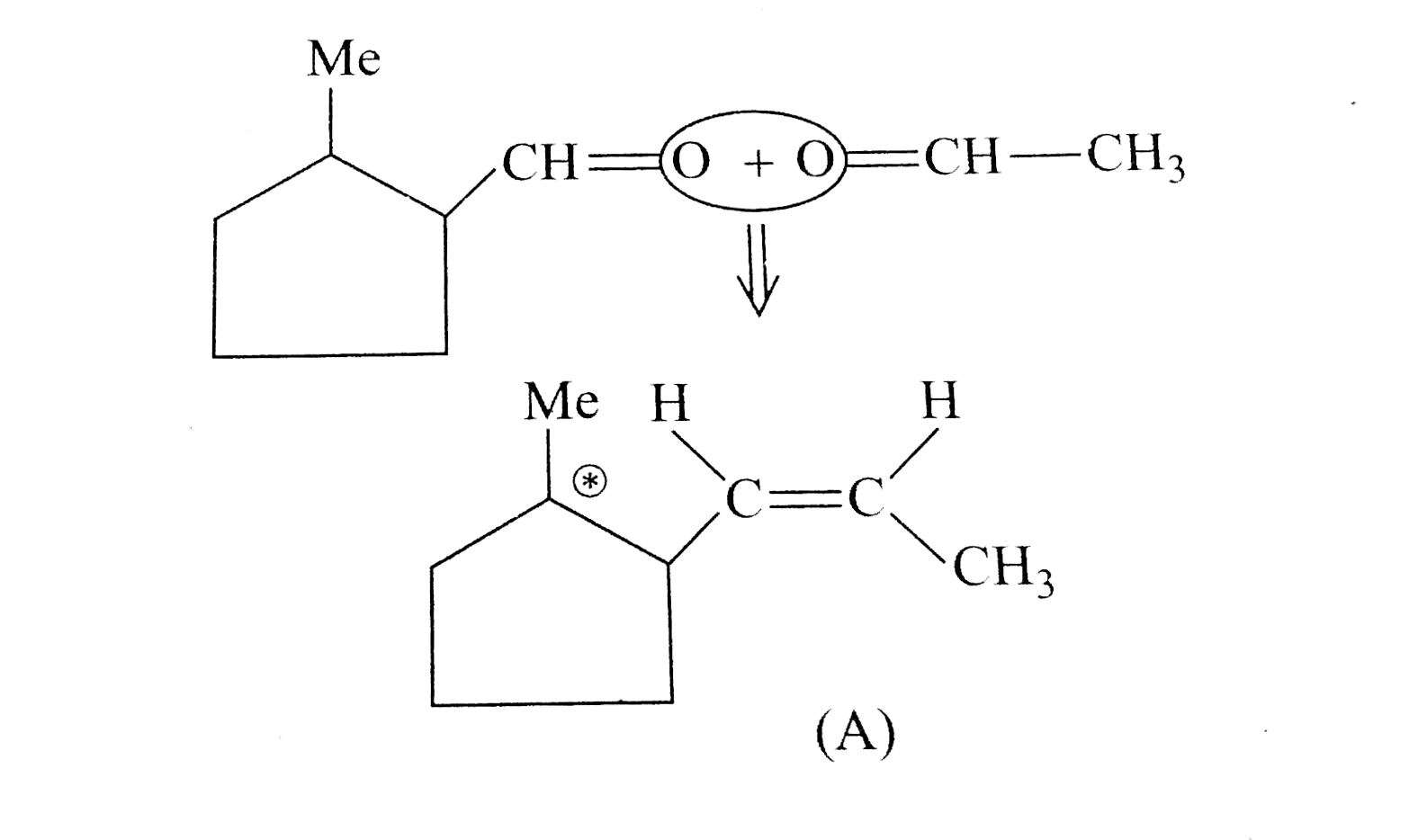
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives(ASSERTION-REASIOING)|4 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Fill in the Blanks|3 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|41 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ALKENES AND ALKADIENES-Single Correct Answer Type
- Which reagent cannot be used for the above conversion ?
Text Solution
|
- Which one is the most easily dehydrated ?
Text Solution
|
- The number of geometrical isomers of (A) can be :
Text Solution
|
- Meso- and racemic -2,3-dibromobutane on reaction with Nal in acetone g...
Text Solution
|
- The racemic -2,3-dibromopentane on reaction with KI in acetone give ...
Text Solution
|
- (A) is 2,3-dibromobutan -1,4-dioc acid. Which stereochemical reacta...
Text Solution
|
- (A) and (B) are :
Text Solution
|
- (A),(B),and (C) are:
Text Solution
|
- (A)overset((i)BD(3)//THF)underset((ii)CH(3)COOH)larrPenten eoverset((i...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A) are :
Text Solution
|
- Which is the wrong statement about oxymercuration - demercuration ?
Text Solution
|
- (A), (B), and (C) are :
Text Solution
|
- Which is the wrong statement ?
Text Solution
|
- Which statement(s) is/are correct ? i. In oxymercuration and demercu...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following alcohols in the decreasing order of dehydratio...
Text Solution
|
- (A) is :
Text Solution
|
- A is :
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is true ? i. The product is ii. The product is ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the product
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|