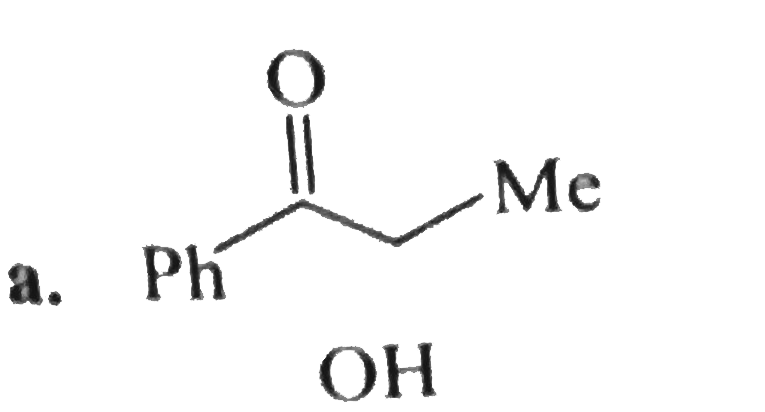
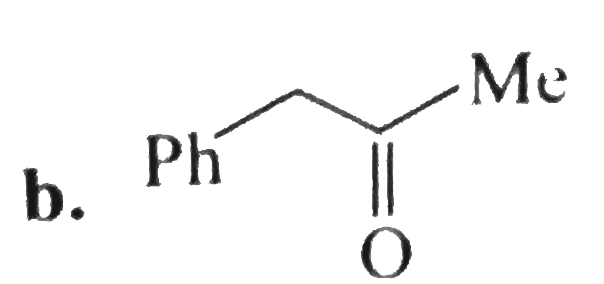
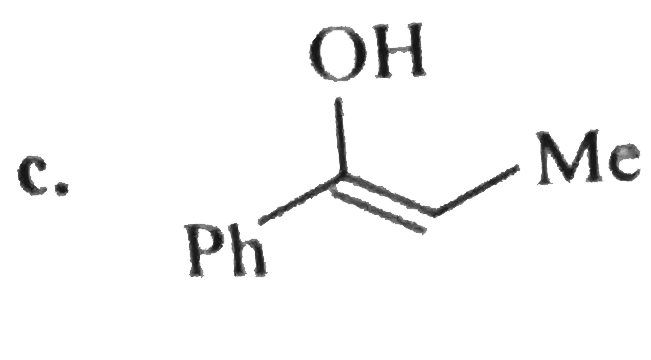
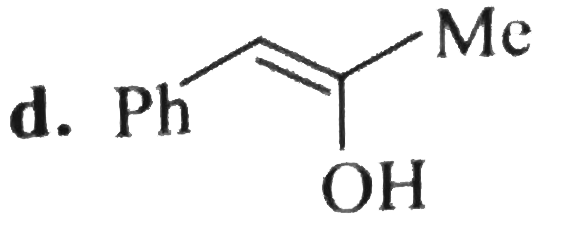
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
REDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|4 VideosREDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise (Assertion And Reasoning)|10 VideosQUALITATIVE INORGANIC SALT ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Viva Voce Questions And Part-C (Analysis Of Cations)|42 VideosSOLID STATE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Ex 1.2 (Objective)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-REDUCTION AND OXIDATION REACTION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS-Exercise Archives (Subjective)
- The appropriate reagent for the following transformation is
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following will most readily be dehydrated in acidic c...
Text Solution
|
- 1-Propanol and 2- propanol can be distinguished by:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (X) with molecular formula C(3)H(8)O is treated with acidifie...
Text Solution
|
- PhC-=CMeoverset(Hg^(2+)+H^(o+))to(A). The compound (A) is:
Text Solution
|
- The products of acid hydrolysis of P and Q can be distinguished by
Text Solution
|
- How will you convert butan -2-one to propanoic acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compound will give a yellow precipitate with io...
Text Solution
|
- Under Wolff-Kishner reduction conditions, the conversion which may be ...
Text Solution
|
- Fehling's solution 'A' consists of an aqueous solution of copper sulph...
Text Solution
|
- The yield of ketone is oxidised is more than the yield of aldeyde whe...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: Acetic acid does not undergo haloform test. and State...
Text Solution
|
- Give a chemical test to distinguish between methanol and ethanol.
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following with suitable equation wherever necessary : Sug...
Text Solution
|
- A ketone [A] which undergoes haloform reactions gives compound [B] on ...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons: iodoform is obtained by the reaction of acetone with h...
Text Solution
|
- When t-butanol and n-butanol are separately treated with a few drops o...
Text Solution
|
- A compund X(C8H10O) upon treatment with alkaline solution of iodine gi...
Text Solution
|
- Identify (A), (B), and (C ) and give their strucyures.
Text Solution
|
- An alkene (A) C(16)H(16) on ozonolysis gives only one product (B) (C(8...
Text Solution
|