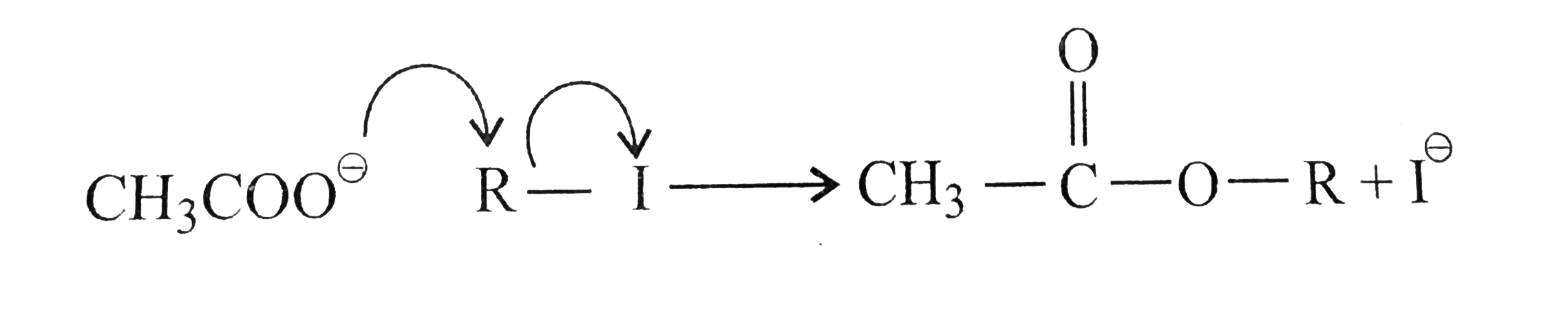
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Subjective Type|5 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Subjective|17 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Solved Examples|21 VideosAPPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type|179 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES -Solved Problems
- Give the order of reactivity towards SN^(2) reaction of the followig: ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the order of reactivity towards SN^(1) reaction of the followig: ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the order of SN^(-1) of SN^(-1) and SN^(2) displacement of haloge...
Text Solution
|
- Give the order of reactivity towards E2 dehydrohalo-genation of the fo...
Text Solution
|
- Give the order of reactivity towards SN^(-1) solvoloysis of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- Give the order of reactivityh towards SN^(1) reaction of the following...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Outline the preparationof the following compounds using a nucliphileic...
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each of the following paris will react faster in SN^...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the folliwing compounds in increasing order of SN^(-1) reactiv...
Text Solution
|
- Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of...
Text Solution
|
- Predict all order of reactivity of the following compounds in dehydroh...
Text Solution
|
- Explain : a. Vinyl chloride is unreactive in nucliphillic 4- subsitu...
Text Solution
|
- The nucliphilic substituation of primary alkyl chlorides wityh sodium ...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the folliwing halides in order of increasing SN^(2) and SN^(1...
Text Solution
|
- Predicrt the order of reactivity of the following compounds in SN^(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in S(n^(1))...
Text Solution
|
- Identify all the possible alkenes that would be formed on the dehydroh...
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
 But in alkyl chloride `(C-Cl)` is a strong bond and is difficult to break. But in teh presence of `Nal, (R-Cl)` is converted to `(R-1)` (Finkelstein reaction) and in `(R-1)`, the `(C-I)` bond is weak which can be easily cleaved, So `SN^(2)` reaction is cataysed in the presence of `Nal `R - Cl + Nal rarr R-1 + NaCl`
But in alkyl chloride `(C-Cl)` is a strong bond and is difficult to break. But in teh presence of `Nal, (R-Cl)` is converted to `(R-1)` (Finkelstein reaction) and in `(R-1)`, the `(C-I)` bond is weak which can be easily cleaved, So `SN^(2)` reaction is cataysed in the presence of `Nal `R - Cl + Nal rarr R-1 + NaCl`