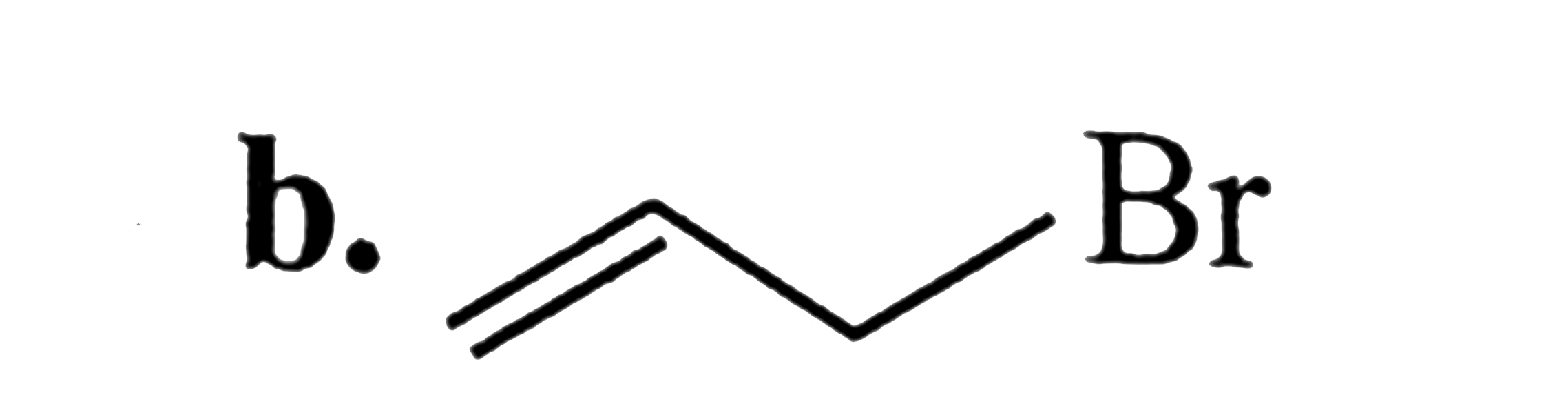
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Linked Compreshension Type|11 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|32 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Concept Application|4 VideosAPPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type|179 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES -Exercises Linked Compreshension
- In the conversion of (C) to (E) , (E) is Bu - NH(2). This reaction is ...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (G) is:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (H) is:
Text Solution
|
- The compounds (I) and (J) are respectively:
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is wrong about the hydrolysis of R - overset(o+)(N) -...
Text Solution
|
- Compound (B) is:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (C) is:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (E) is:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (F) is:
Text Solution
|
- SN reaction is given by these compounds, which have a nuclophilic gr...
Text Solution
|
- SN reaction is given by these compounds, which have a nuclophilic gr...
Text Solution
|
- SN reaction is given by these compounds, which have a nuclophilic gr...
Text Solution
|
- SN^(2) reaction is a bimolecular reaction which takes places by the fo...
Text Solution
|
- SN^(2) reaction is a bimolecular reaction which takes places by the fo...
Text Solution
|
- SN^(2) reaction is a bimolecular reaction which takes places by the fo...
Text Solution
|
- SN^(2) reaction is a bimolecular reaction which takes places by the fo...
Text Solution
|
- IsoprophI bromide was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under t...
Text Solution
|
- IsoprophI bromide was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under t...
Text Solution
|
- IsoprophI bromide was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under t...
Text Solution
|
- IsoprophI bromide was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under t...
Text Solution
|