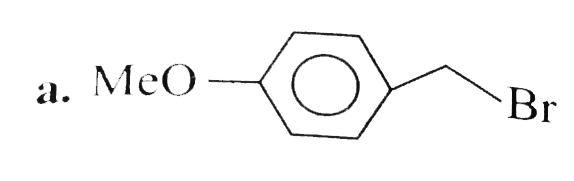
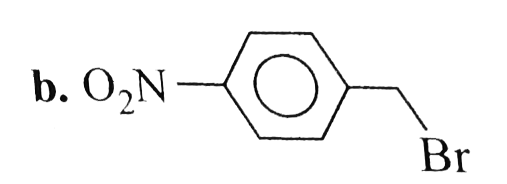
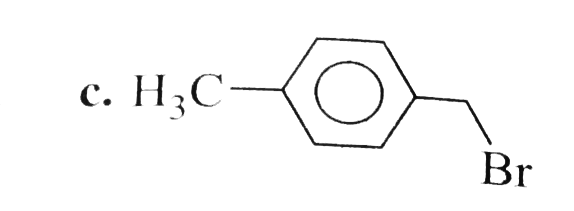
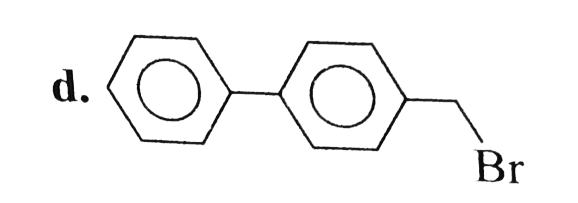
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Assertion-Resoning Type|1 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Assertion-Resoning|11 VideosAROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Single Correct Answer Type|28 VideosAPPENDIX INORGANIC VOLUME 2
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type|179 VideosBIOMOLECULES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-AROMATIC COMPOUNDS AND ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES -Exercises Single Correct
- Which of the folliwng is the order of the rate of reaction of C(6)H(6)...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the folliwng is the correct order of the order of the rate of...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will give SN^(2) mechanism?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds gives SN^(1), SN^(2) and SN^(2) mecha...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the folliwning ether wil always give SN^(2) mechanism in acid...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the follwoign ether will always give SN^(2) mechanism in acid...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following substrates will gave racemised product?
Text Solution
|
- The energy of activation is lowest for which reaction?
Text Solution
|
- Isopentane on monochlorination gives....isomers and out of them .........
Text Solution
|
- Propane on dichlorinatin gives......isomers and out of them .....are o...
Text Solution
|
- A solution of (+)2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly i...
Text Solution
|
- The number of isomers for the compounds with molecular formula C(2)B...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing basic order of the following compounds is: i. NH(3)...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing nucleophilic order of the following compounds is: i...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing nucleophilic order of the following compounds is: i...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing basic order of the following is: i. F^(o-), ii. Cl^(o...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing nucleophillic order fo the following compounds is: i...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing leaving group order of the following is: i. F^(o-), i...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing basic order of the following is: i. overset(o-)(C)H(...
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing nucleophilic oder of the following compounds is: i. o...
Text Solution
|