Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PATHFINDER-ELECTROCHEMISTRY-QUESTION BANK
- What is the effect of temperature on the electrical conductance of an ...
Text Solution
|
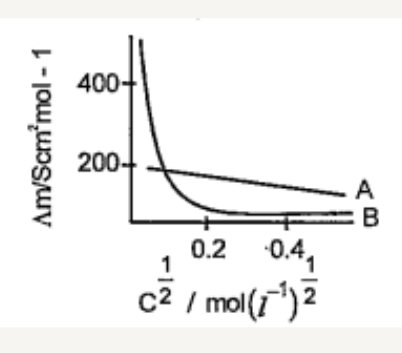
- The following curve is obtained with molar conductivity (Am)(y-axis) i...
Text Solution
|
- The following curve is obtained with molar conductivity (Am)(y-axis) i...
Text Solution
|
- If Zn^(2+) // Zn electrode is diluted 100 times then what will be the ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the role of ZnCl2 in dry cell?
Text Solution
|
- Why blocks of magnesium are often strapped to the steel hulls of ocean...
Text Solution
|
- Why rusting of iron is quicker in saline water than in ordinary water?...
Text Solution
|
- A current of one ampere is flowing through a wire. Calculate the numbe...
Text Solution
|
- The specific conductance of a 0.12 N solution of an electrolyte is 2.4...
Text Solution
|
- Two half cell reactions of an electrochemical cell are: MnO4^-(aq)+8...
Text Solution
|
- Dilution normally helps in increasing the electrical conductivity of a...
Text Solution
|
- On electrolysing CuSO4 solution. In presence of Pt the solution becom...
Text Solution
|
- 0.369 gm of copper was deposited an passing 0.750 A of current through...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment 0.40 F was passed through 400 ml of 1M solution of Na...
Text Solution
|
- The following chemical reaction is occuring in an electrochemical cell...
Text Solution
|
- The following chemical reaction is occuring in an electrochemical cell...
Text Solution
|
- The following chemical reaction is occuring in an electrochemical cell...
Text Solution
|
- The following chemical reaction is occuring in an electrochemical cell...
Text Solution
|
- The following chemical reaction is occuring in an electrochemical cell...
Text Solution
|
- At what p(H) will hydrogen electrode at 298K show an electrode potenti...
Text Solution
|