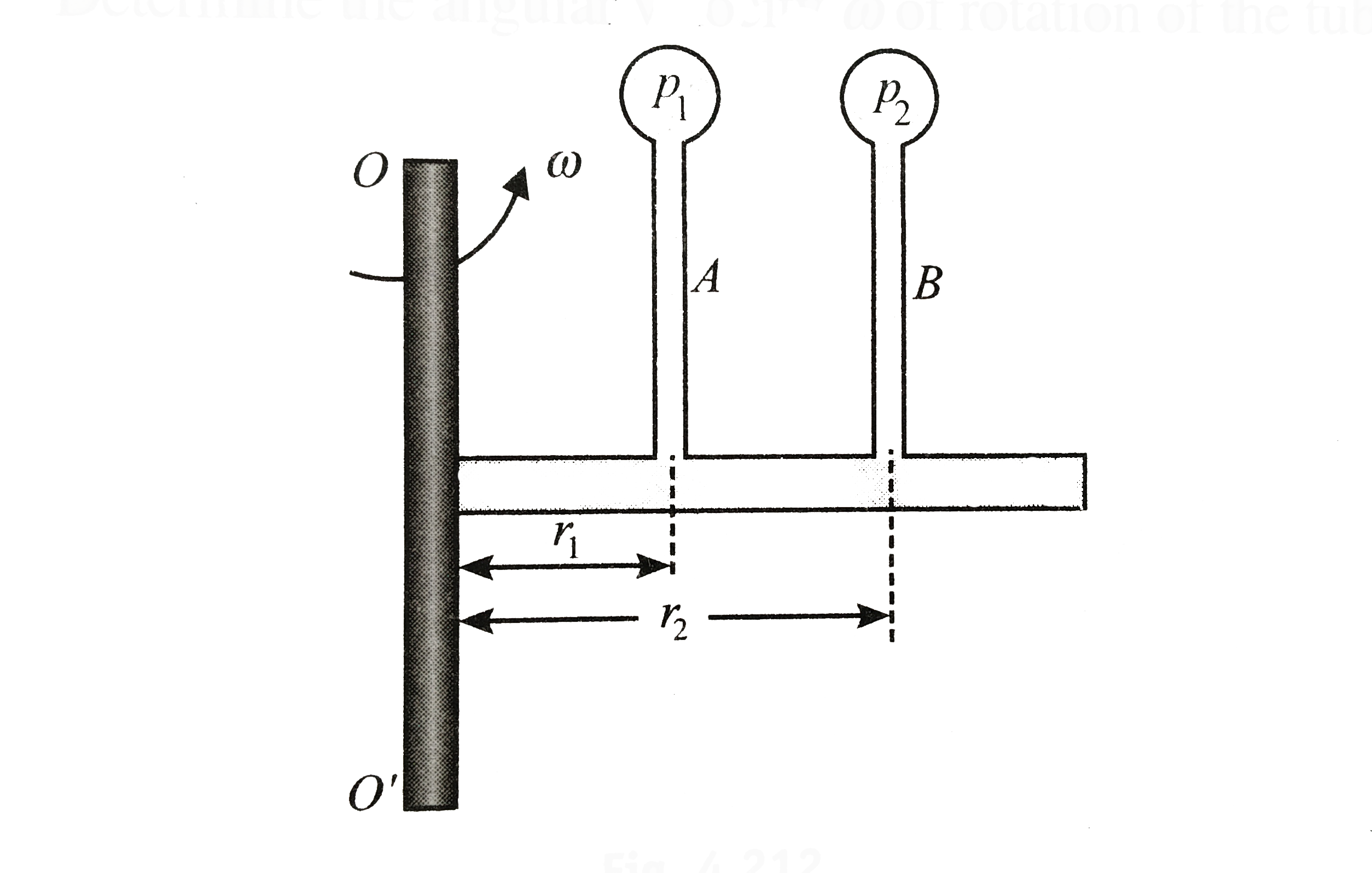
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A tube filled with water and closed at both ends uniformly rotates in ...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal tube of length I closed at both ends contains an ideal ga...
Text Solution
|
- A U-tube rotates with angular velocity omega about the vertical axis A...
Text Solution
|
- A tube filled with water and closed at both ends uniformly rotates in ...
Text Solution
|
- A tube of length 'L' is filled completely with an in compressiblem liq...
Text Solution
|
- Length of a horizontal arm of U-tube is L and ends of both the vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A closed tube filled with water is rotating uniformly in a horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- L लम्बाई की एक नली को एक असंपीड्य द्रव से पूरा भरकर इसे दोनों सिरों स...
Text Solution
|
- L लम्बाई की एक नलिका M द्रव्यमान के असंपीड्य द्रव से पूर्णतया भरी है द...
Text Solution
|