Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TELUGU-NATURAL RESOURCES-CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER
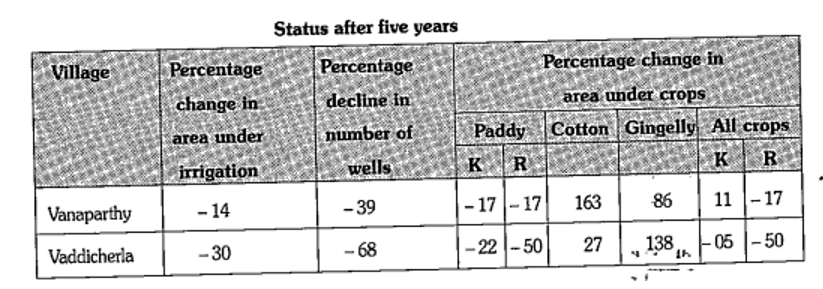
- K stands for Kharif while R stands for Rabi. Negative values indicate ...
Text Solution
|
- Percolation tanks helps to
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following practice is suitable to farmer with less water ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the fossil fuel reserves decrease more rapidly in India
Text Solution
|
- Huge amount of toxic chemicals leak into the surrounding ecosystem bec...
Text Solution
|
- Sustainable development means
Text Solution
|