Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TELUGU-AREA AND PERIMETER-EXERCISE - 6
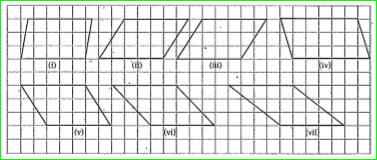
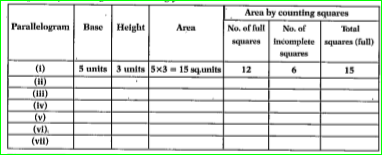
- Carefully study the following parallelograms. i) find the area of each...
Text Solution
|
- A path 2.5 m wide is running around a square field whose side is 45m. ...
Text Solution
|
- The central hall of a school is 18m long and 12.5m wide. A carpet is t...
Text Solution
|
- The length of the side of a grassy square plot is 80m. two walking pat...
Text Solution
|
- A verandah 2m wide is constructed all around the room of dimensions 8m...
Text Solution
|
- The length of a rectangular park is 700m and its breadth is 300m. two ...
Text Solution
|