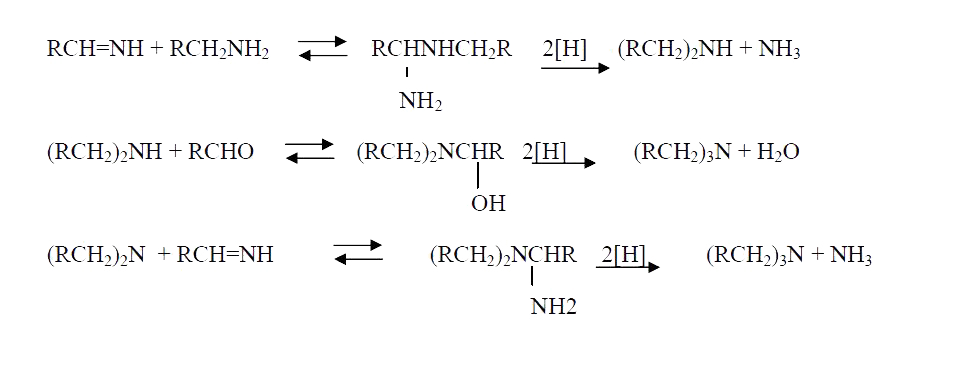
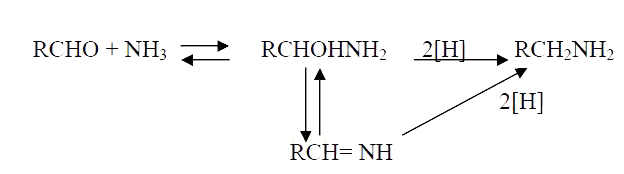A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CBSE MODEL PAPER-QUESTION BANK 2021-Multiple Choice Questions
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Red...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Red...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Red...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Red...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Som...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Som...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Som...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Som...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Som...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Industrially ...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Industrially ...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Industrially ...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Industrially ...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Industrially ...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Biopolymers ar...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Biopolymers ar...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Biopolymers ar...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Biopolymers ar...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer the question: Biopolymers ar...
Text Solution
|
- Read the passage given below and answer question: In the last 10 yea...
Text Solution
|