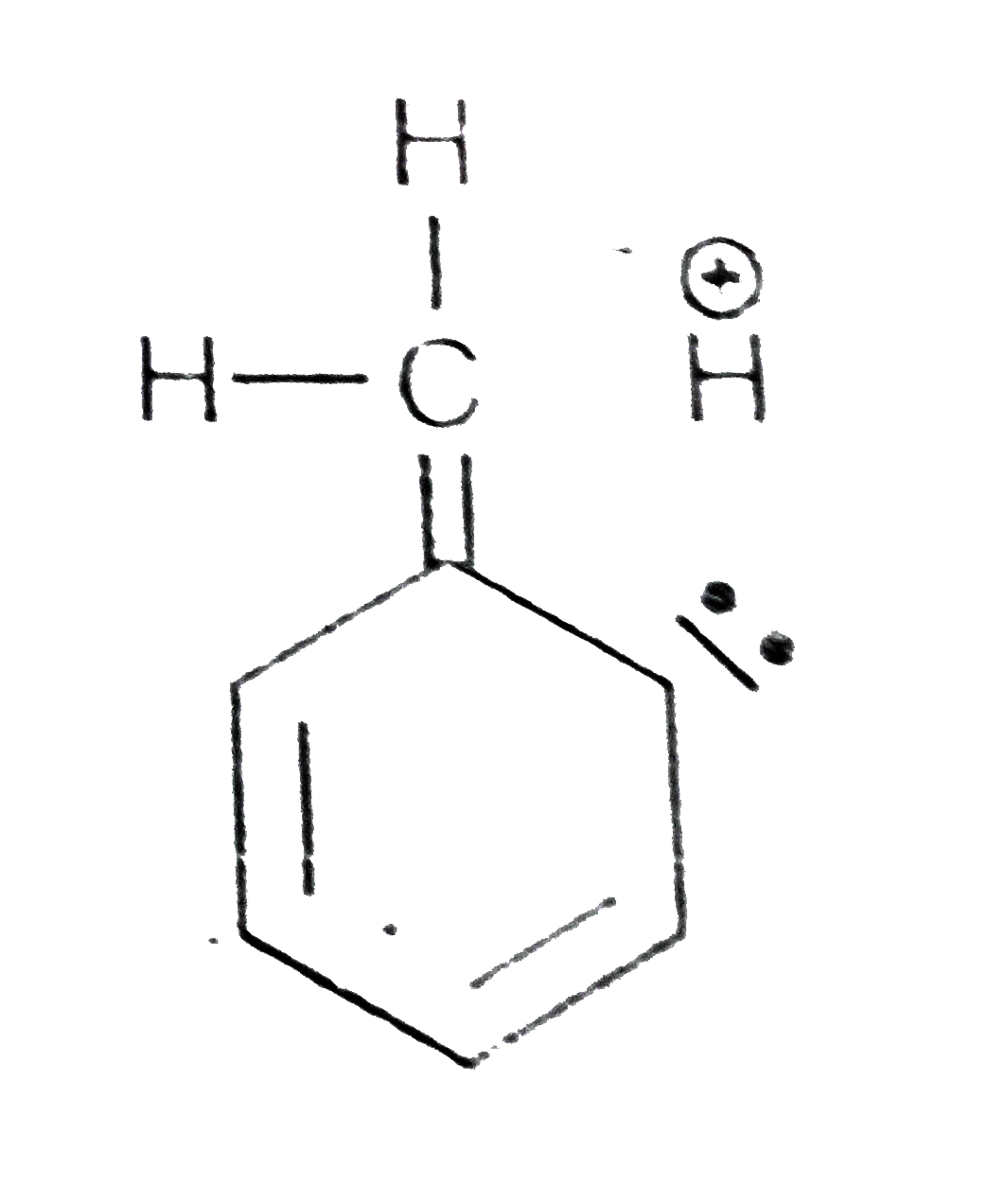
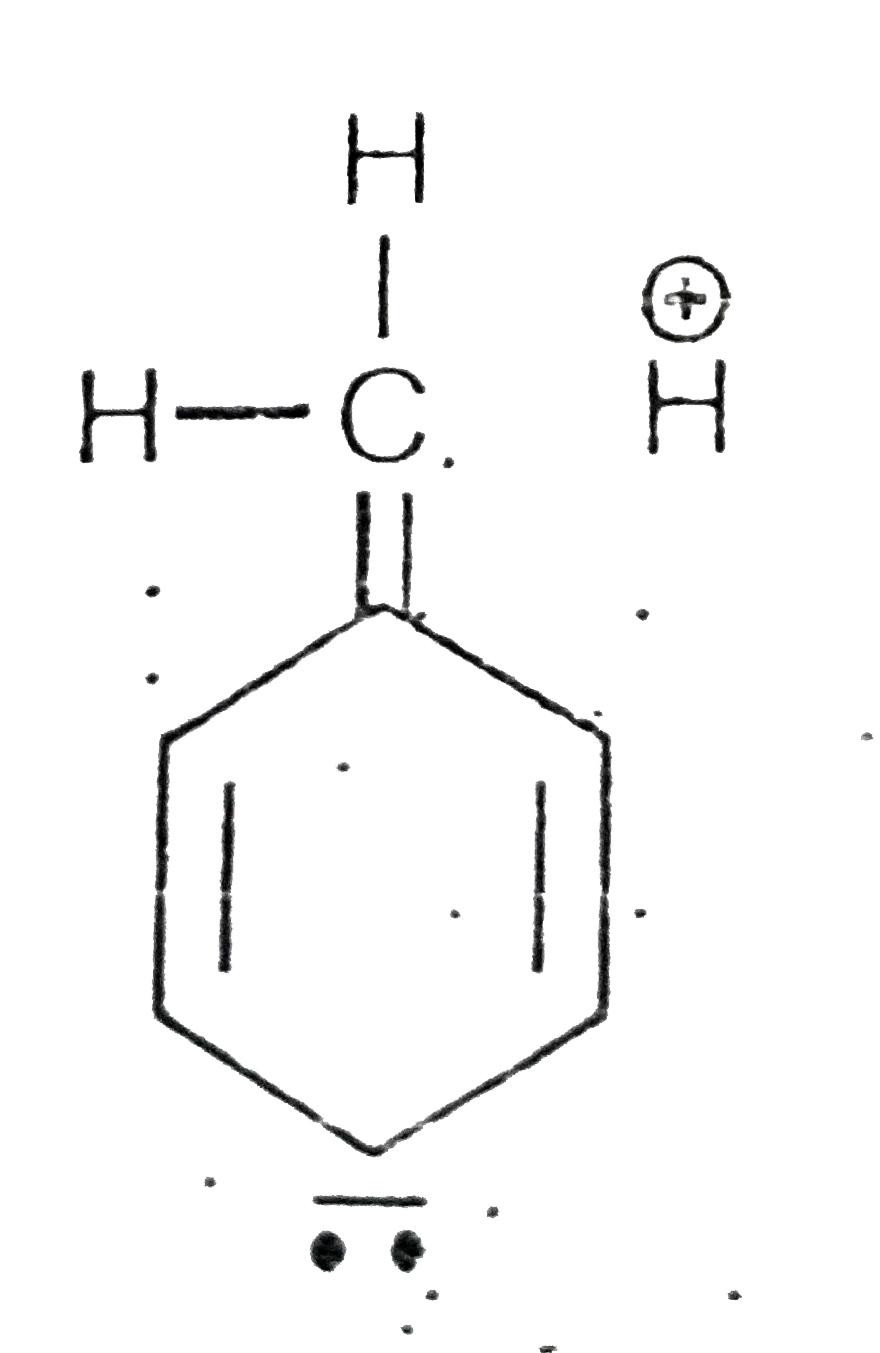
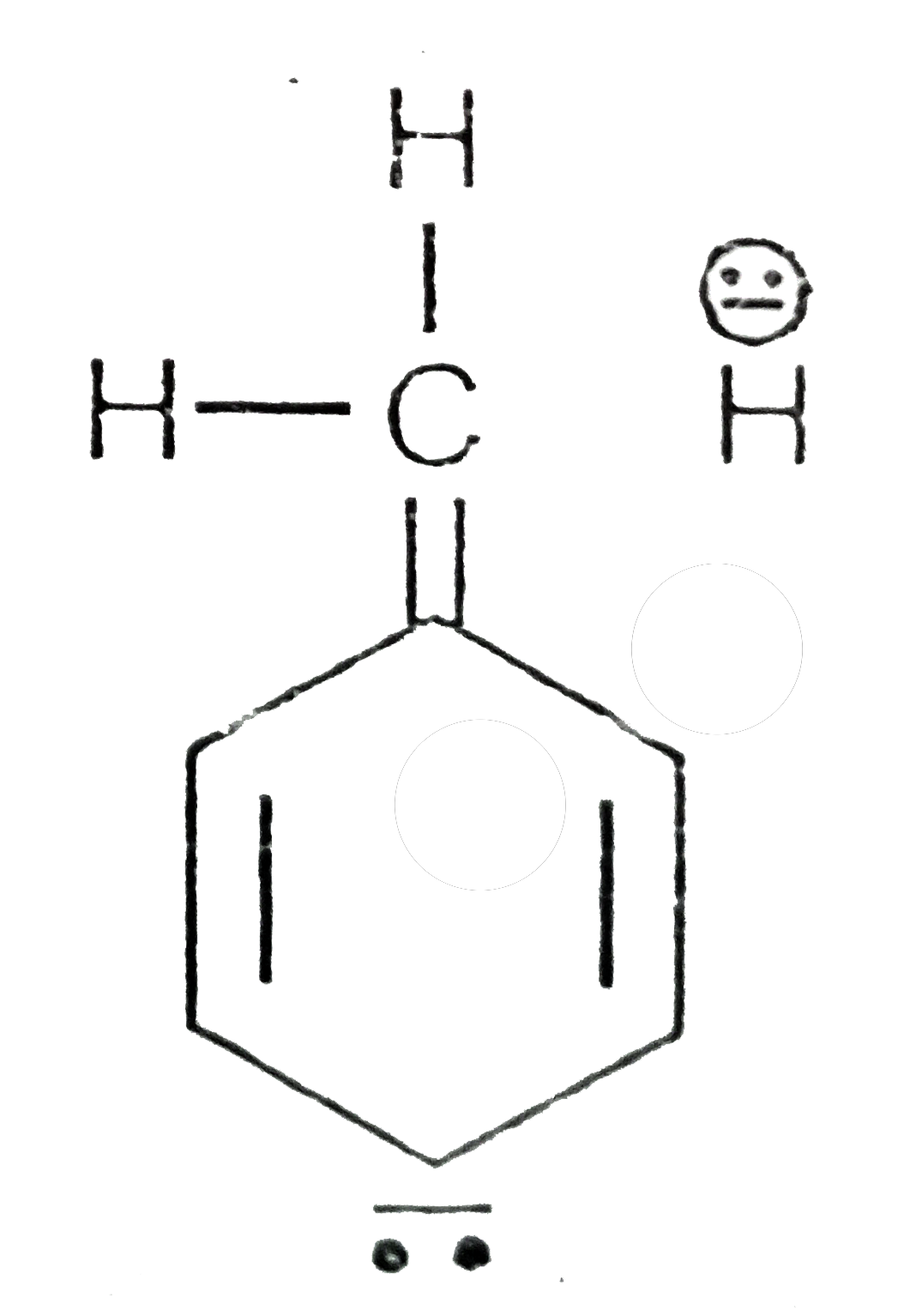
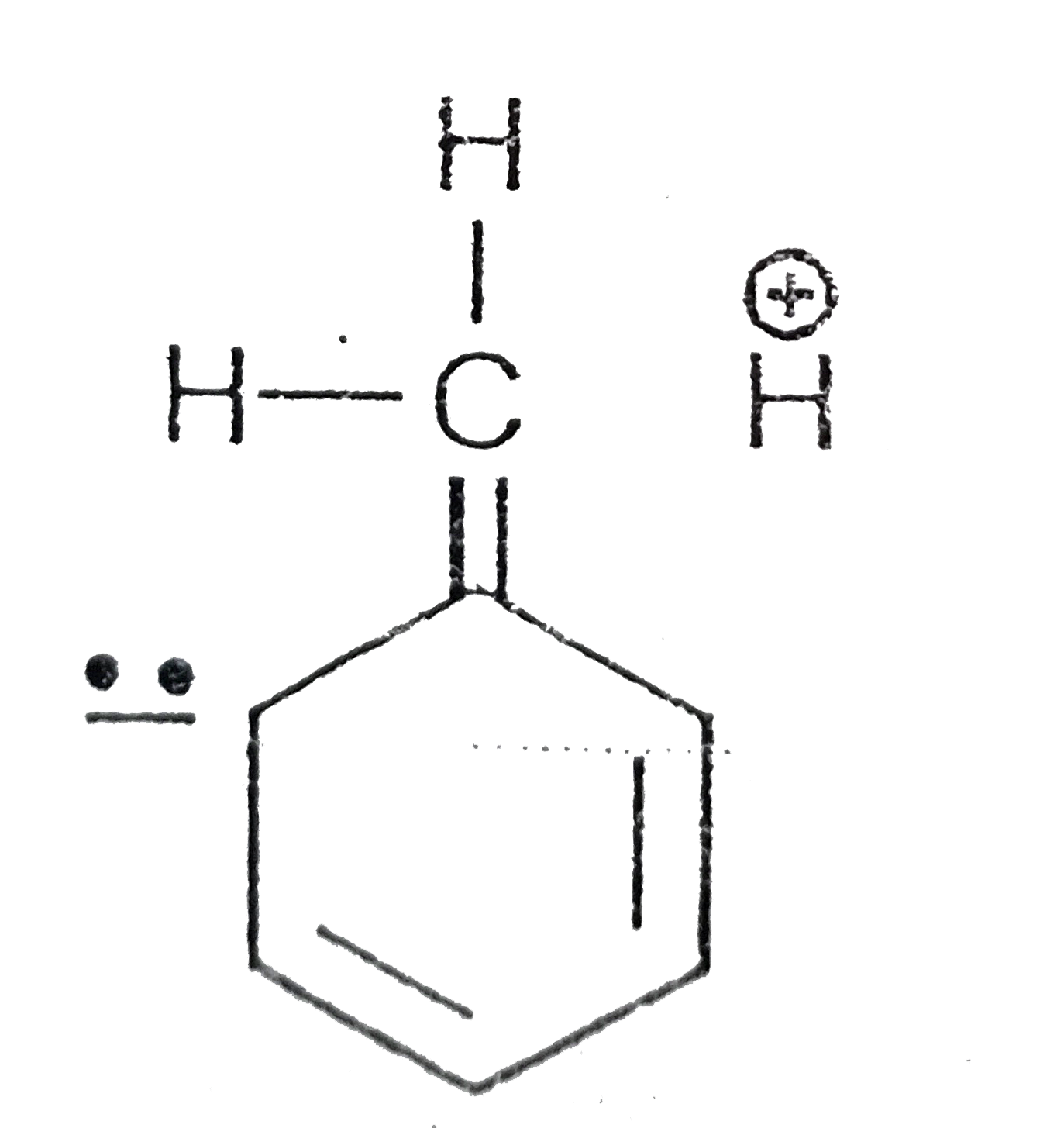
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION-E ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS|14 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION-F MATRIX-MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS|4 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION-C OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION (MORE THAN ONE OPTIONS ARE CORRECT)|18 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment(Section-D)(Assertion - Reason Type Questions)|15 VideosPOLYMERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)|13 Videos
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES-SECTION-D LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS
- Tautomerism, stricity defined could be used to describe the reversible...
Text Solution
|
- Names of organic compounds are under the latest guide line of IUPAC. I...
Text Solution
|
- Names of organic compounds are under the latest guide line of IUPAC IU...
Text Solution
|
- Weak Acid does not dissociate completely into its ions. It is in equil...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is having most acidic alpha-Hydrogen?
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation is defined as No bond resonance. The concept of hyper...
Text Solution
|
- Hyperconjugation is defined as No bond resonance. The concept of hyper...
Text Solution
|