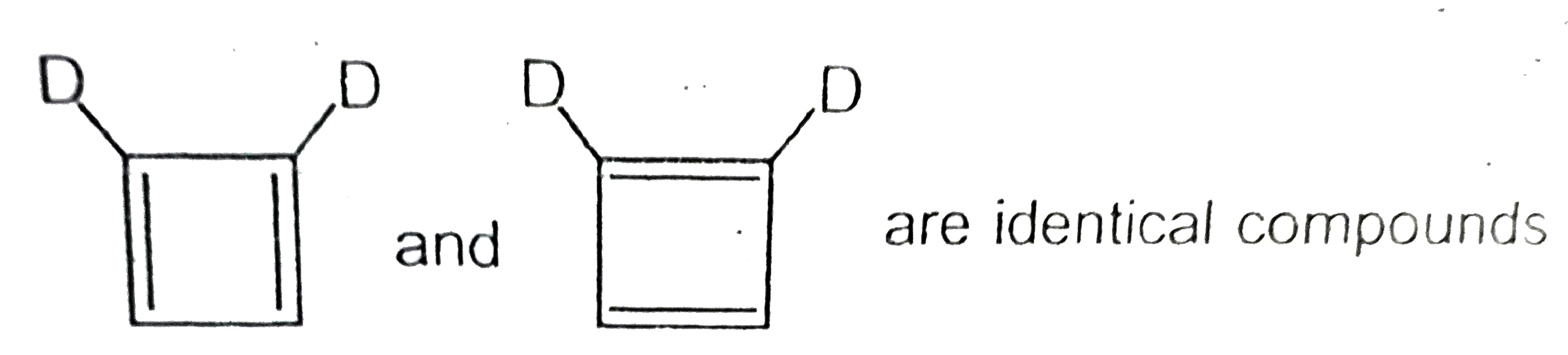
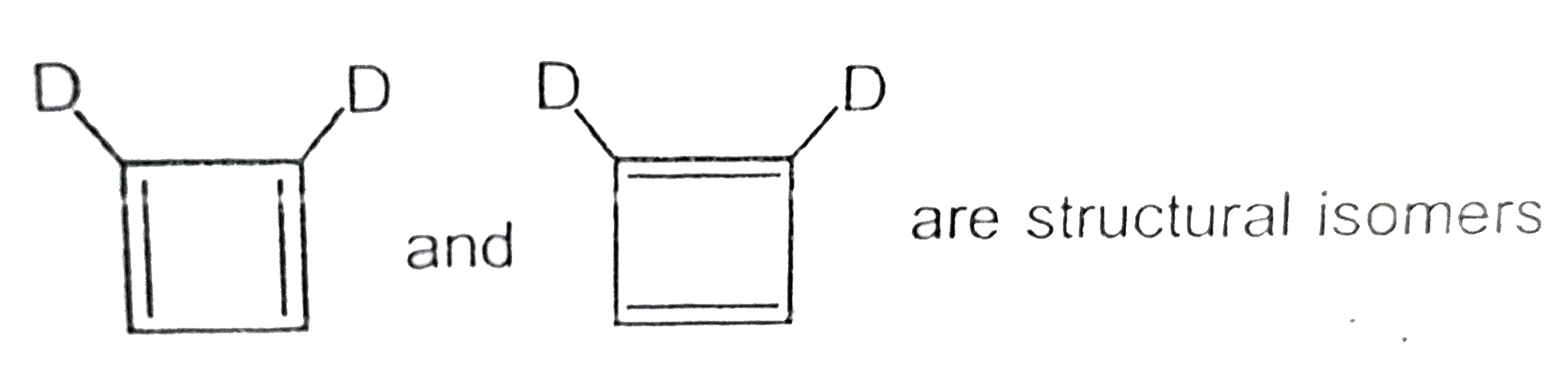
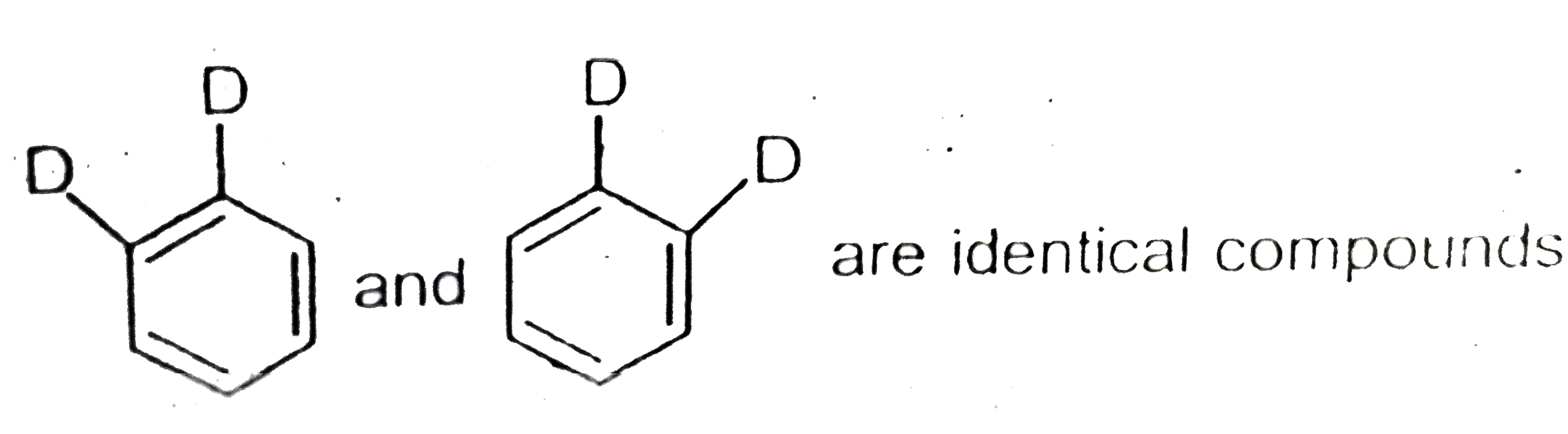
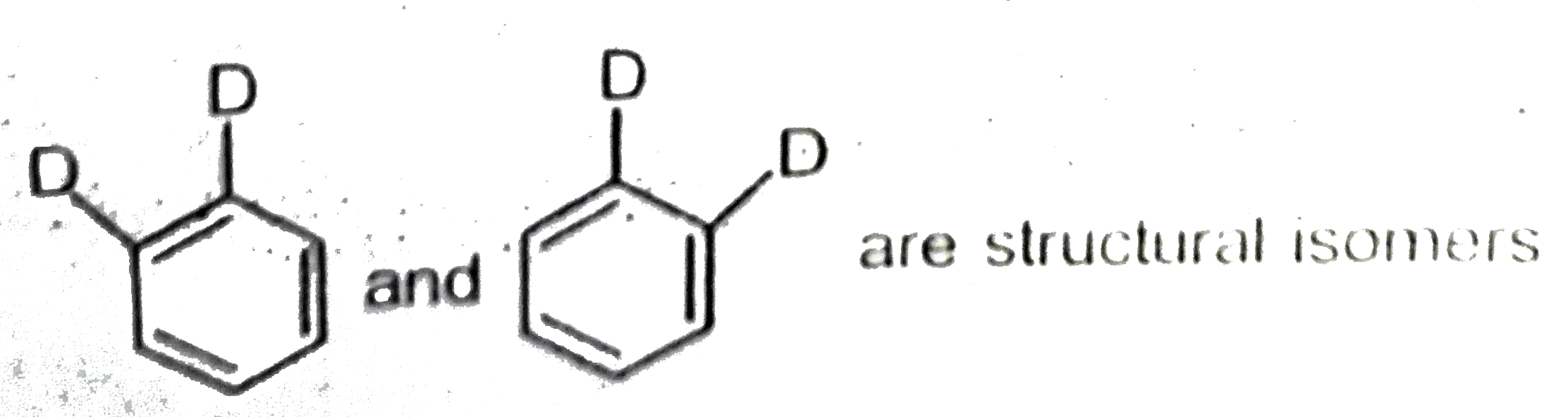
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise TRY YOURSELF|28 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION-I SUBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment(Section-D)(Assertion - Reason Type Questions)|15 VideosPOLYMERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION-D)|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES-SECTION-J AAKASH CHALLENGERS QUESTIONS
- Which of the following hydocarbon can be readily deprotonated by NaOEt...
Text Solution
|
- Pick out the correct statements about the barrier of rotation about th...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the given species in the increasing acidic strength: (a)I I...
Text Solution
|
- Order of basicity of the following species is
Text Solution
|
- The correct statbility order of the following resonance structure is
Text Solution
|
- Correct statements among the following is/are
Text Solution
|
- Species in which all C-C bonds are not equal is/are
Text Solution
|
- Most stable carbocation among the following is
Text Solution
|
- For which of the following compound tautomerization reaction is very ...
Text Solution
|
- Compare acidic strength of
Text Solution
|