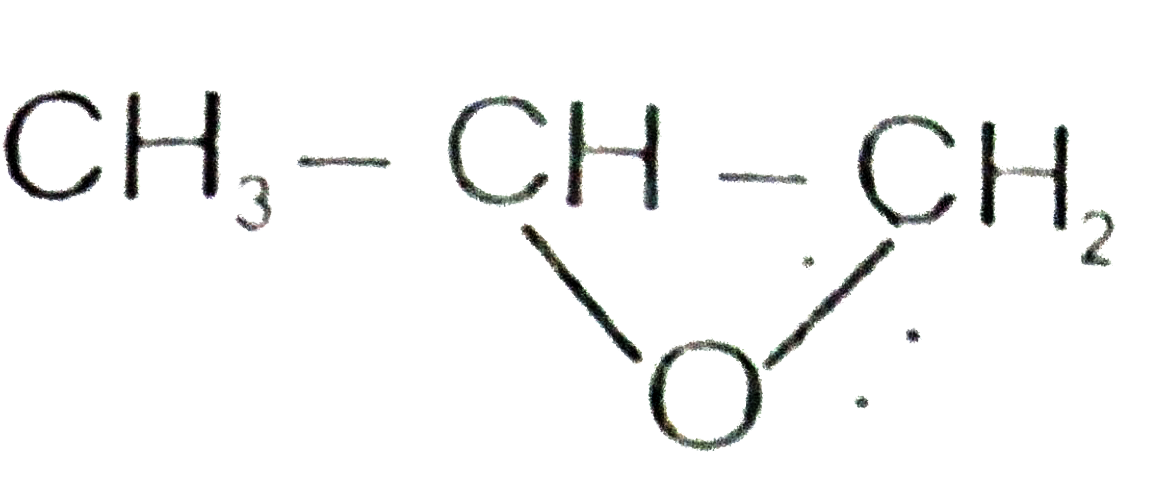A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- CH(3)CH= CH(2) overset(H//H(2)O)(to) major product is
Text Solution
|
- In the following hydration CH(3)-overset(CH(3))overset(|)(CH)-CH = ...
Text Solution
|
- The major product formed in the reaction CH(3)CH = CH - overset(O)over...
Text Solution
|
- In the reaction given below, the product would be : CH(3)-CH=CH-CH(3)o...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)-overset(CH(2)CH(3))overset(|)(CH)CH=CHCH(3)overset(H(3)O^(+))rar...
Text Solution
|
- In the following reaction H(3)C-underset(CH(3))underset(|)overset(CH(3...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)underset(CH(3))underset(|)overset(CH(3))overset(|)C-CH=CH(2)overs...
Text Solution
|
- In the following reaction H(3)C-underset(CH(3))underset(|)overset(CH(3...
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)CH= CH(2) overset(H//H(2)O)(to) major product is
Text Solution
|