Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration|4 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section - A) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|62 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section-D (Assertion and reason))|5 VideosTEST 1
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE|21 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-Try Yourself
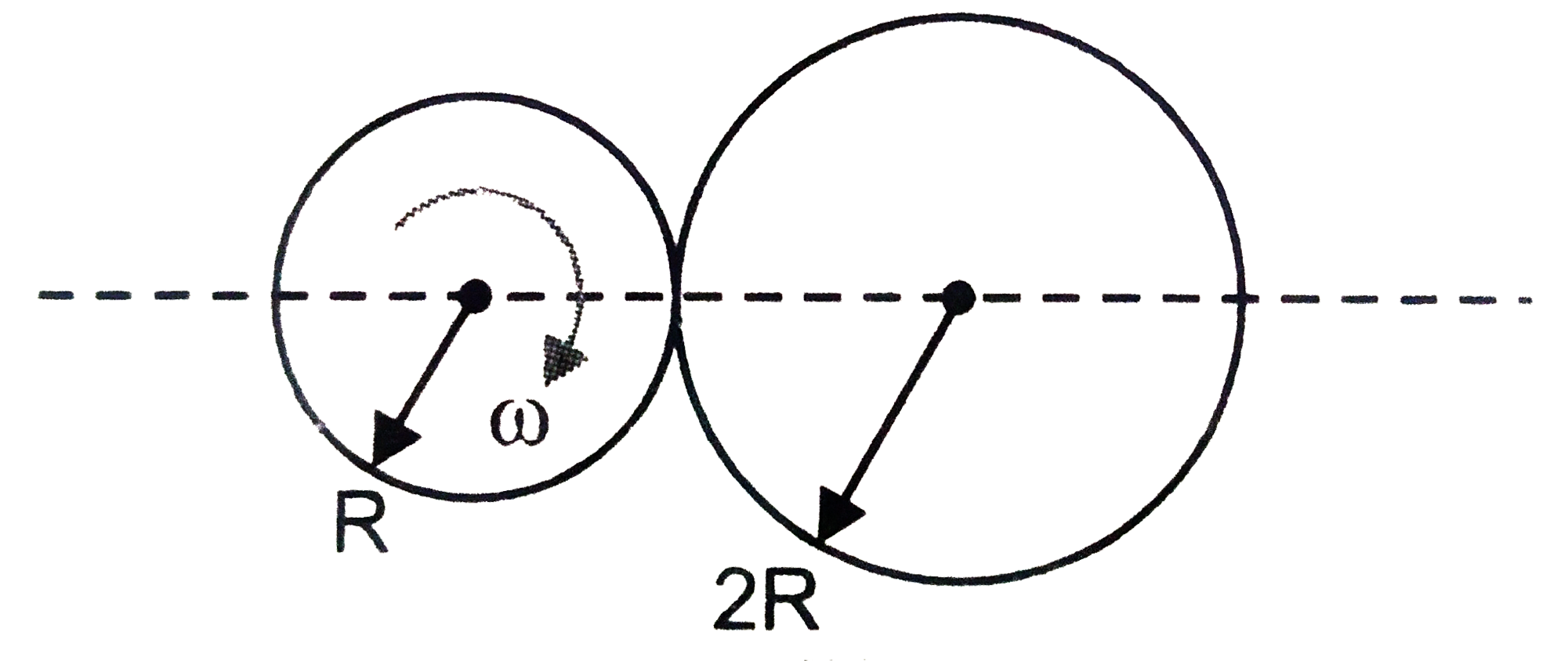
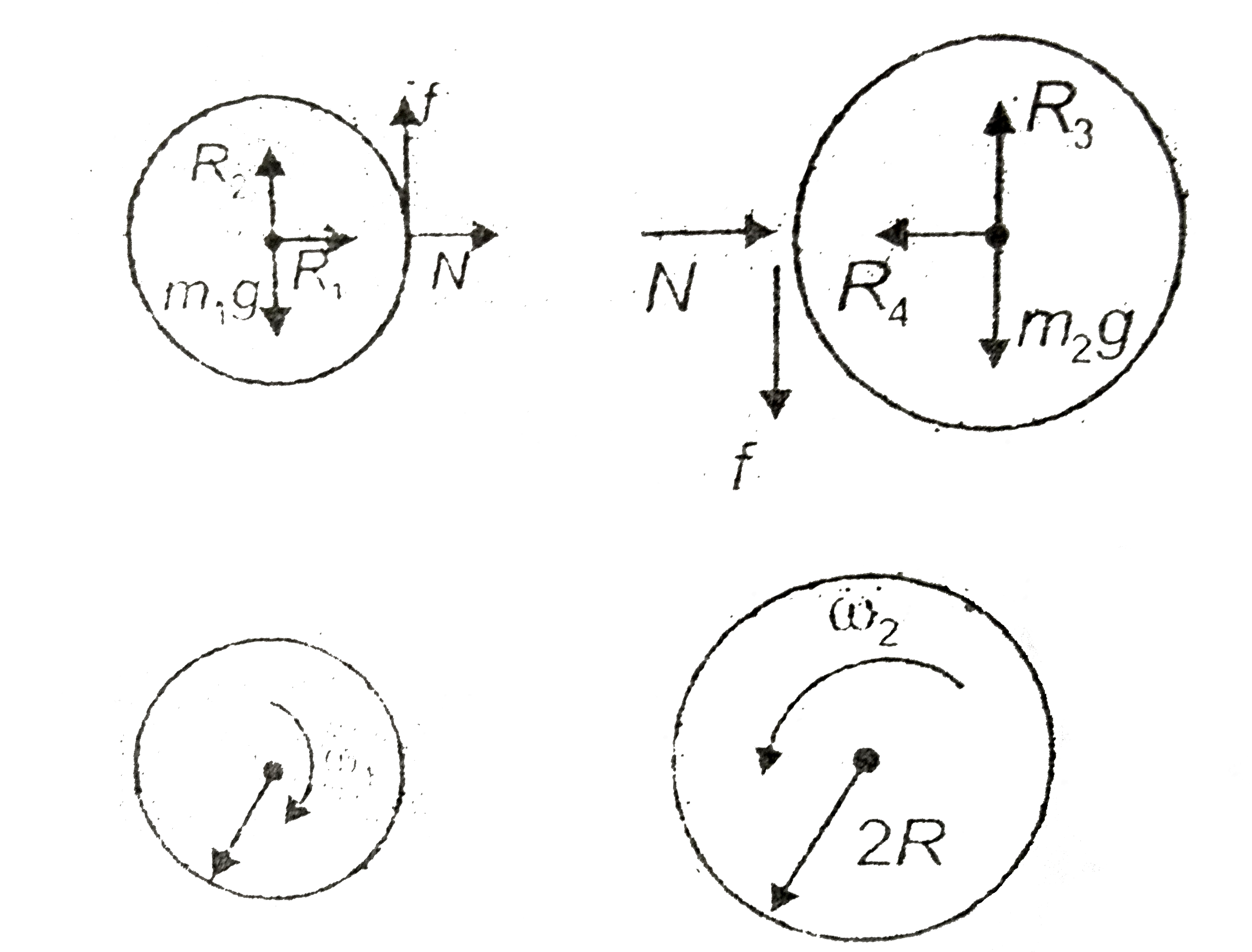
- Two discs of radii R and 2R are pressed against each other. Initially,...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses 1kg and 3kg are lying in xy plane at (0,0) and (2...
Text Solution
|
- Three point masses of 1kg, 2kg and 3kg lie at (0,0), (1,2), (3,-1) res...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles of masses m,m and 4kg are kept at a verticals of trian...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles having their masses in the ratio 1 : 3 : 5 are kept at...
Text Solution
|
- Centre of mass of the system lies inside disc or square plate and why ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of equal mass are moving along the same line with the sa...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of equal mass are moving along the same straight line wi...
Text Solution
|
- A shell following a parabolic path explodes somewhere in its flight. T...
Text Solution
|
- All the particles are situated at a distance R from the origin. The di...
Text Solution
|
- Will the velocity and acceleration of centre of mass change if particl...
Text Solution
|
- vecA=(3hati+2hatj-6hatk) and vecB=(hati-2hatj+hatk), find the scalar p...
Text Solution
|
- vecA=(hati-2hatj+6hatk) and vecB=(hati-2hatj+hatk), find the cross pro...
Text Solution
|
- Find a unit vector in the direction of vector vecA=(hati-2hatj+hatk)
Text Solution
|
- Find a vector perpendicular to vector vecA=(hati+2hatj-3hatk) as well ...
Text Solution
|
- The angular displacement of a particle is 24 rad in 10 seconds. Calcul...
Text Solution
|
- The angular velocity of a rigid body is 24 rad s^(-1), Calculate the t...
Text Solution
|
- The angular velocity of circular disc of radius 2cm is 20 rad s^(-1). ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the angular velocity of a particle lying on the axis of rotati...
Text Solution
|
- What is the angular acceleration of a particle moving with constant an...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel is rotating with an angular velocity of 3 rad s^(-1). If the a...
Text Solution
|