Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section - A) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|62 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section - B) Objective Type Questions (One option is correct)|60 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|63 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section-D (Assertion and reason))|5 VideosTEST 1
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE|21 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-Illustration
- A square plate of side 'a' and mass 'm' is lying on a horizontal floor...
Text Solution
|
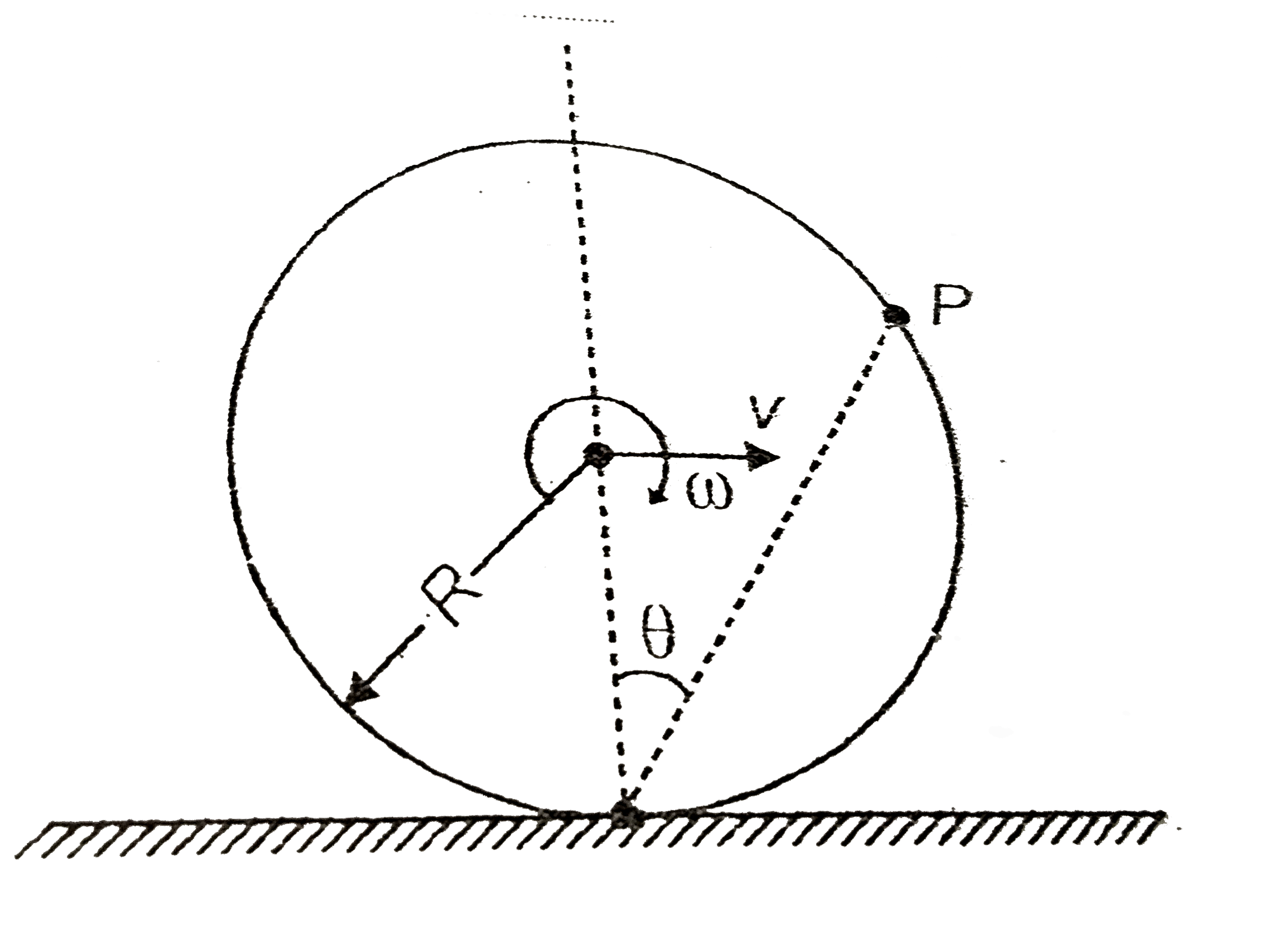
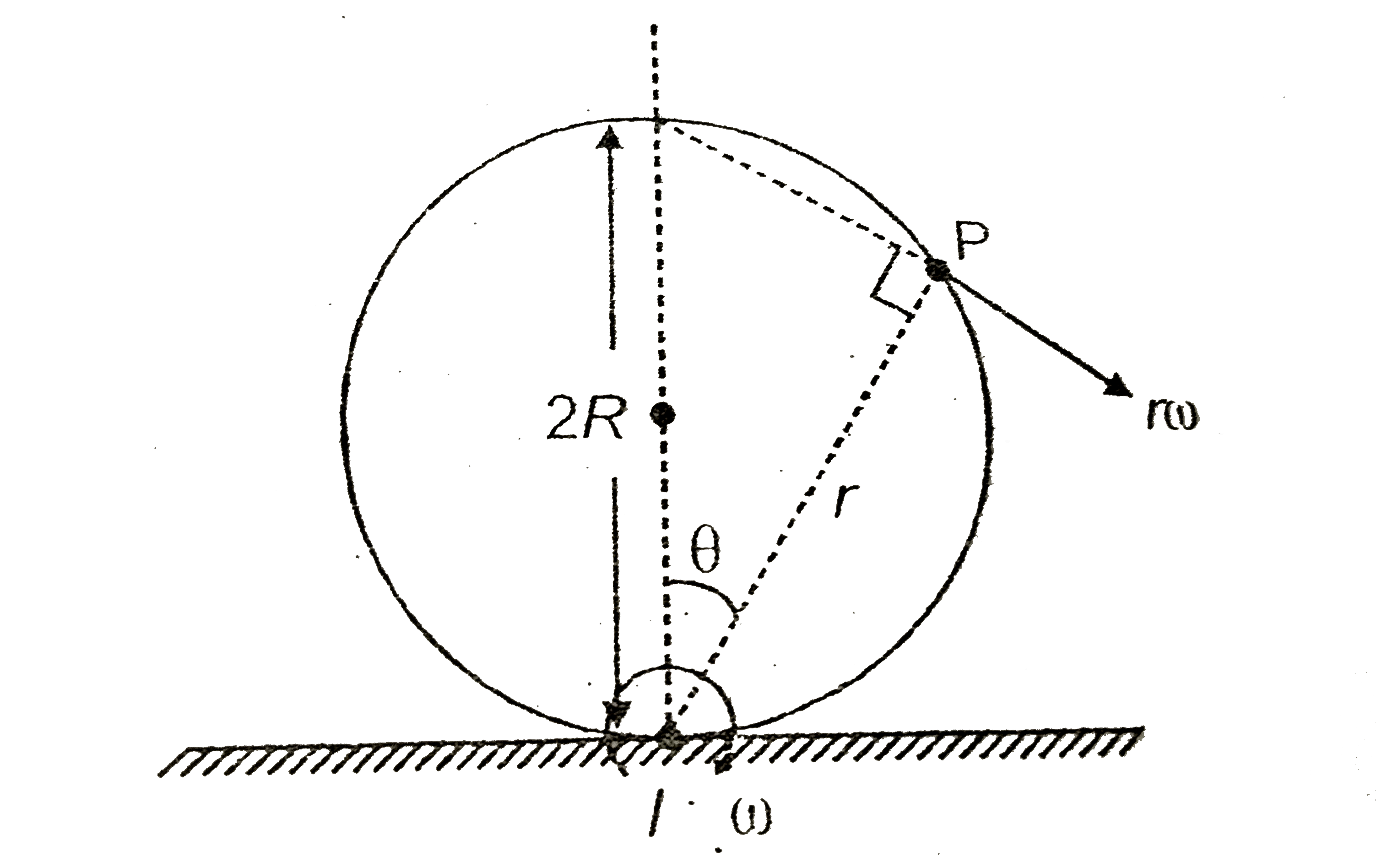
- The velocity of a point P on the surface of a pure rolling disc as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform round body of radius R and mass m and its moment of inertia...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a disc of mass m and radius R placed on a rough plank of mass...
Text Solution
|