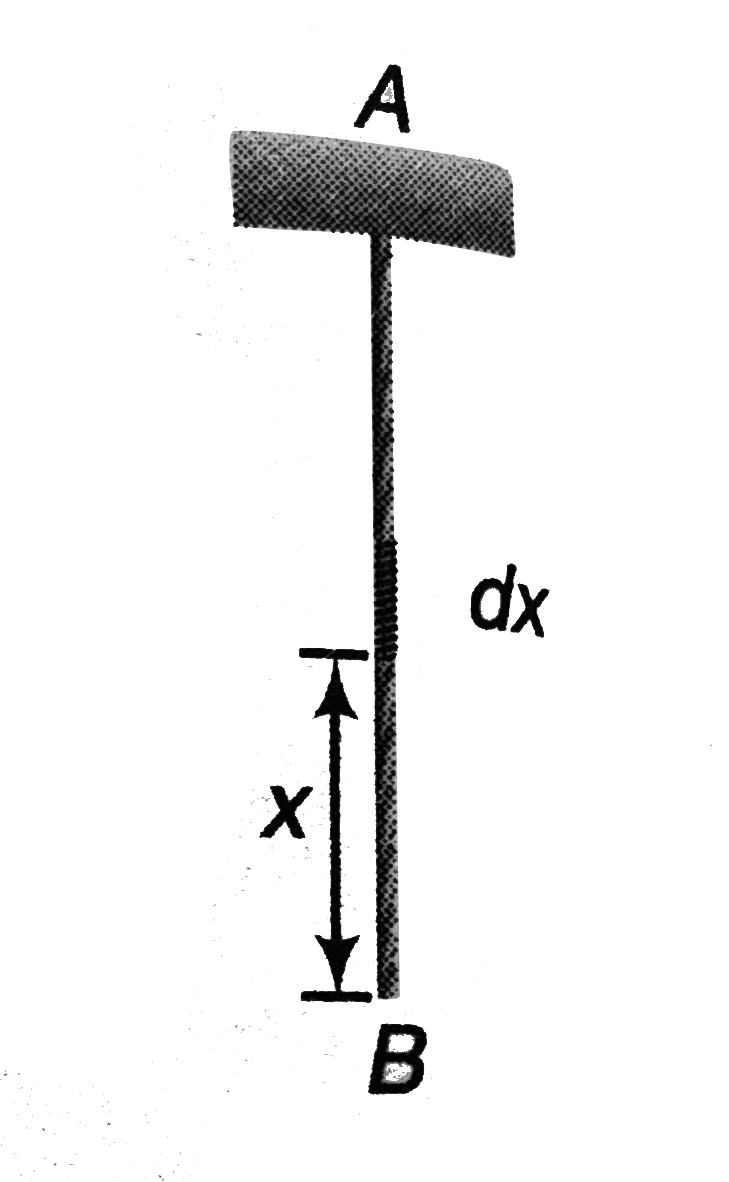
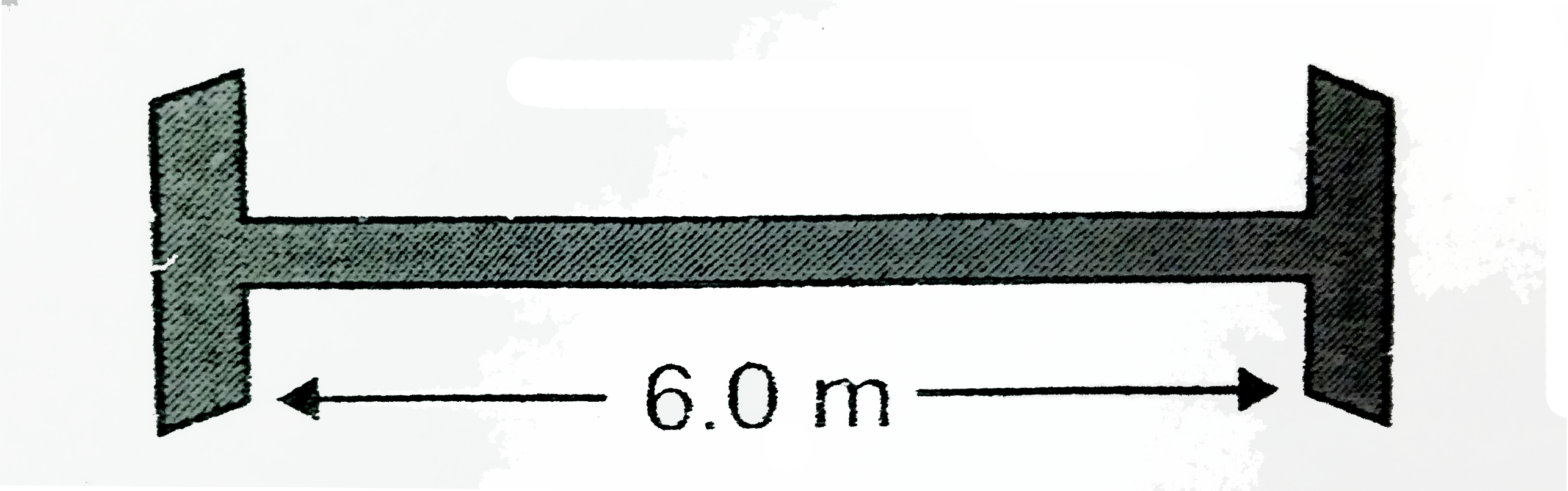Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|32 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - A)|31 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION - J|9 VideosMock test 03
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXAMPLE|44 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-Assignment(Section-D)
- A steel rod of length 6.0 m and diameter 20 mm is fixed between two ri...
Text Solution
|
- According to Hooke's law of elasticity if stress is increased, the rat...
Text Solution
|
- A: Strain is a dimensionless quantity, R: Strain is internal force pe...
Text Solution
|
- A: Diamond is more elastic than rubber. R: When same deforming force ...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: Young's modulus for a perfectly plastic body is zero St...
Text Solution
|
- Statement-1: The bridges are declared unsafe after a long use. Stat...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Spring balances show incorrect readings after using for a l...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion Modulus of elasticity does not depend upon the dimensions of...
Text Solution
|
- The adiabatic elasticity of a gas is equal to
Text Solution
|
- A beam of metal supported at the two ends is loaded at the centre. The...
Text Solution
|
- A:To minimise the depression in a beam. It is designed as "I" shape g...
Text Solution
|
- A:Iron is more elastic than copper R:Under a given deforming force Iro...
Text Solution
|
- A: Lateral strain is directly proportional to the longitudinal strain ...
Text Solution
|
- Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which,...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: With increase of temperature, elastic property of a substan...
Text Solution
|