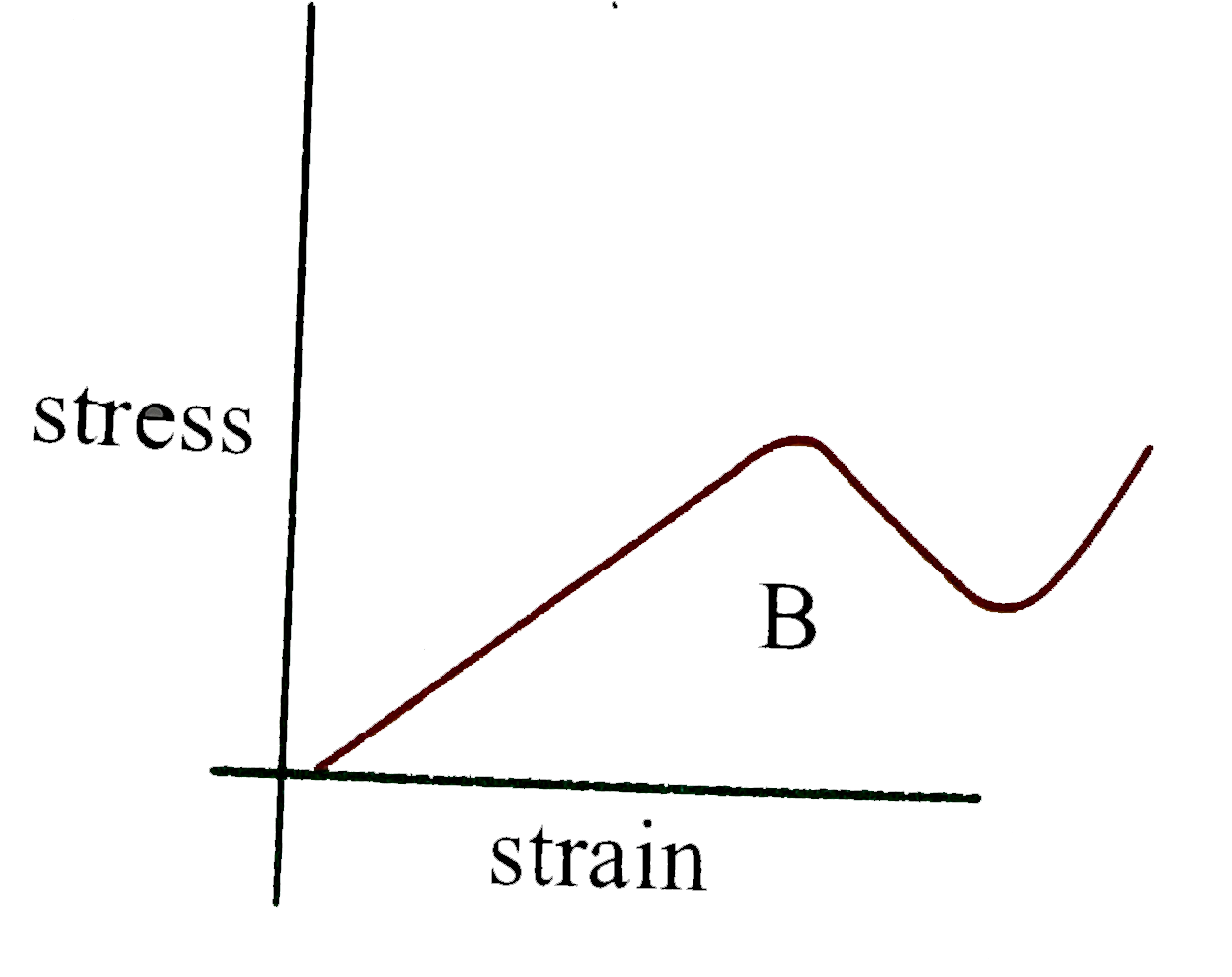
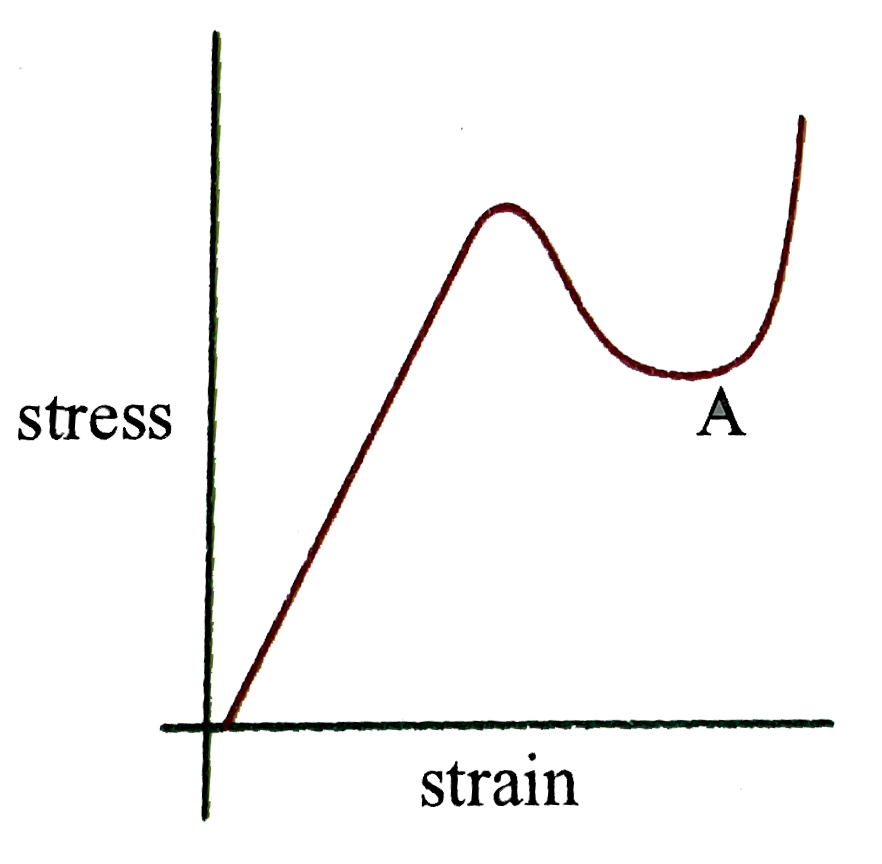A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - B)|15 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - C)|2 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|32 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise SECTION - J|9 VideosMock test 03
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXAMPLE|44 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-Assignment (SECTION - A)
- What is the Young's modulus for a perfect rigid body?
Text Solution
|
- The breaking stress of aluminium is 7.5 xx 10^7 Nm^(-2) Find the great...
Text Solution
|
- The stress- strain graphs for materials A and B are as shown. Choose t...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire of diameter 2 mm has a breaking strength of 4xx10^(5)N. W...
Text Solution
|
- Find the greatest length of copper wire, that can hang without breakin...
Text Solution
|
- A wire 2 m in length suspended vertically stretches by. 10 mm when mas...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L and cross-sectional area A is made of a material of...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball contracts in volume by 0.01% when subjected to a norm...
Text Solution
|
- What is the percentage increase in length of a wire of diameter 2.5 mm...
Text Solution
|
- Two exactly similar wires of steel and copper are stretched by equal f...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following graphs represents stress-strain variation for...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod has a radius 10 mm and a length of 1.0 m. A force stretch...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of equal length and cross sectional area suspended as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- When a wire is stretched to double its length, then
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct alternative (s)
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length l and cross-sectional area A is made of a mat...
Text Solution
|
- The Poisson's ratio of a material is 0.5. If a force is applied to a w...
Text Solution
|
- The load versus extension graph for four wires of same material is sh...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylindrical rod of length L, cross-section area A and Young'...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a wire of length L and weight w is attached rigidly to a po...
Text Solution
|