Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-OSCILLATIONS-Assignment (Section D) (ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS)
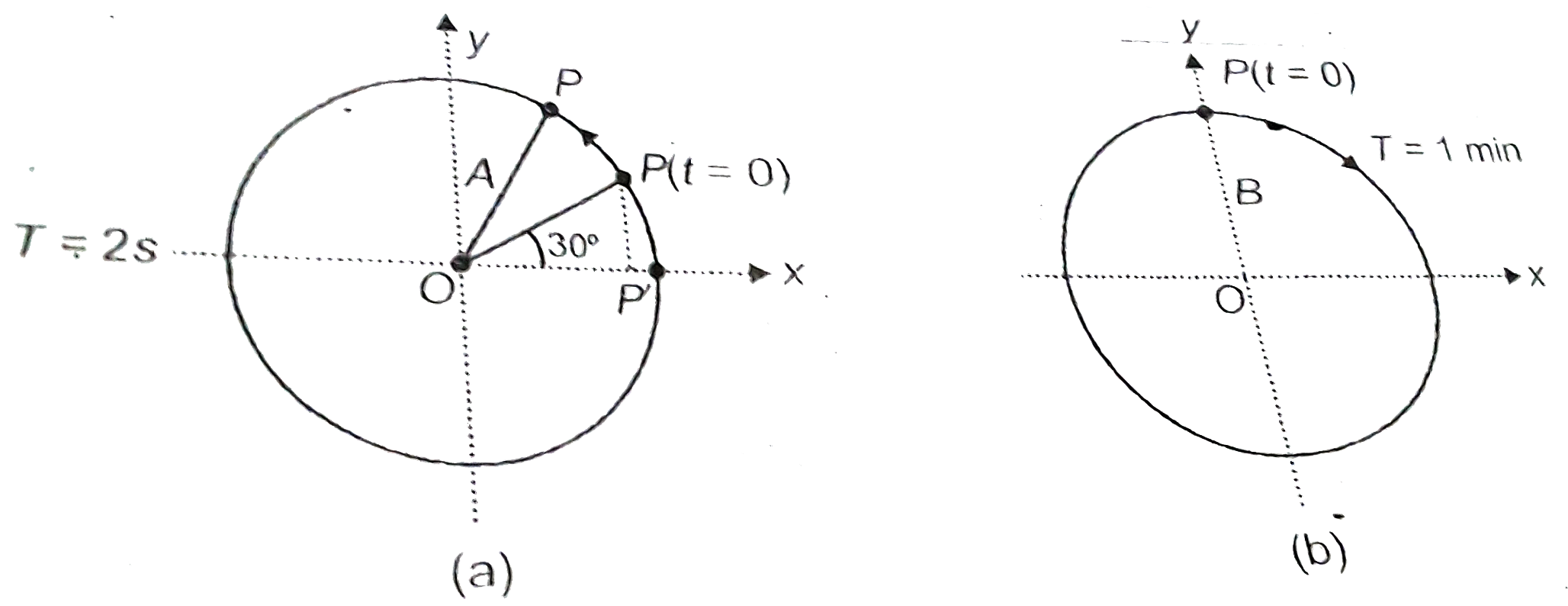
- Figure depicts two circular motions. The radius of the circle, the per...
Text Solution
|
- A: Simple harmonic motion is not a uniform motion. R: Simple harmoni...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: In simple harmonic motion the velocity is maximum when the ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The amplitude of an oscillation pendulum decreases gradual...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the velocity-displacement graph of a body executing shm.
Text Solution
|
- A: The phase difference between the two particles shown below is pi. (...
Text Solution
|
- Any periodic function can be expressed as a superposition of sine and ...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy of a particle executing SHM varies sinusoidally w...
Text Solution
|
- A: If a clock based on simple pendulum is taken to hill it will become...
Text Solution
|
- A: If a spring block system, oscillating in a vertical plane is made t...
Text Solution
|
- At resonance, the amplitude of forced oscillations is
Text Solution
|
- A: If length of a spring is halved, then its force constant becomes do...
Text Solution
|
- A: When soldier cross a bridge, they are asked to break steps. R: If...
Text Solution
|
- A: In SHM the change in velocity is not uniform. R: In SHM the accel...
Text Solution
|