Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section-A)|55 VideosWAVES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section-B)|35 VideosWAVES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION-D ( Assertion - Reason Type Questions ))|12 VideosWAVE OPTICS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section-J (Aakash Challengers question))|1 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - D)|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-WAVES-Try Yourself
- Explain the difference between the speed of a transverse wave travelli...
Text Solution
|
- A body executing shm completes 120 oscillations per minute. If the amp...
Text Solution
|
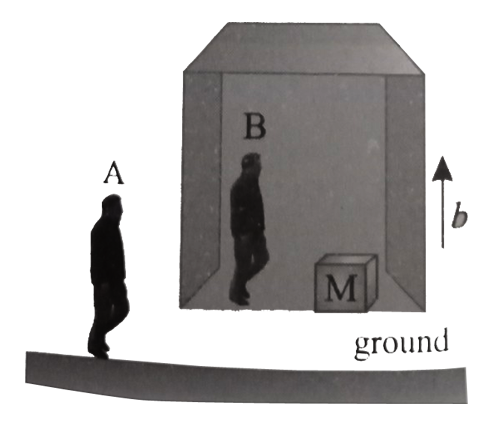
- A block of mass M is kept in elevator (lift) which starts moving upwar...
Text Solution
|
- A rope of length L and mass m hangs freely from the ceiling. The veloc...
Text Solution
|
- Find the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is double t...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why transver waves cannot be propagated through fluids?
Text Solution
|
- What is common in mechanical longitudinal and transverse waves?
Text Solution
|
- The frequency of a mechanical wave is 256 Hz. Calculate its wavelength...
Text Solution
|
- A mechanical wave has a velocity of 330 m/s. calculate its frequency i...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire 100 cm long has a mass of 10 gm. If the wire is under a t...
Text Solution
|
- What is the speed of a transverse wave in a rope of length 10 m and ma...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the speed of longitudinal sound wave in a liquid. The bulk m...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of longitudinal mechanical wave in a material is 4300 m/s. y...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound waves in air at 300K is 332 m/s. At what temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of sound in air at 20^(@)C is 340ms^(-1). Keeping the tem...
Text Solution
|
- Two waves represented by y(i)=3sin(200x-150t) and y(2)=3cos(200x-150t)...
Text Solution
|
- What is the phase difference between two waves of equal amplitude havi...
Text Solution
|
- A man fires a gun while standing between two parallel hills. If he hea...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a transverse wave travelling along a string is y(xt)=0...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a stationary wave is represented by y=2sin((2pix)/(3...
Text Solution
|