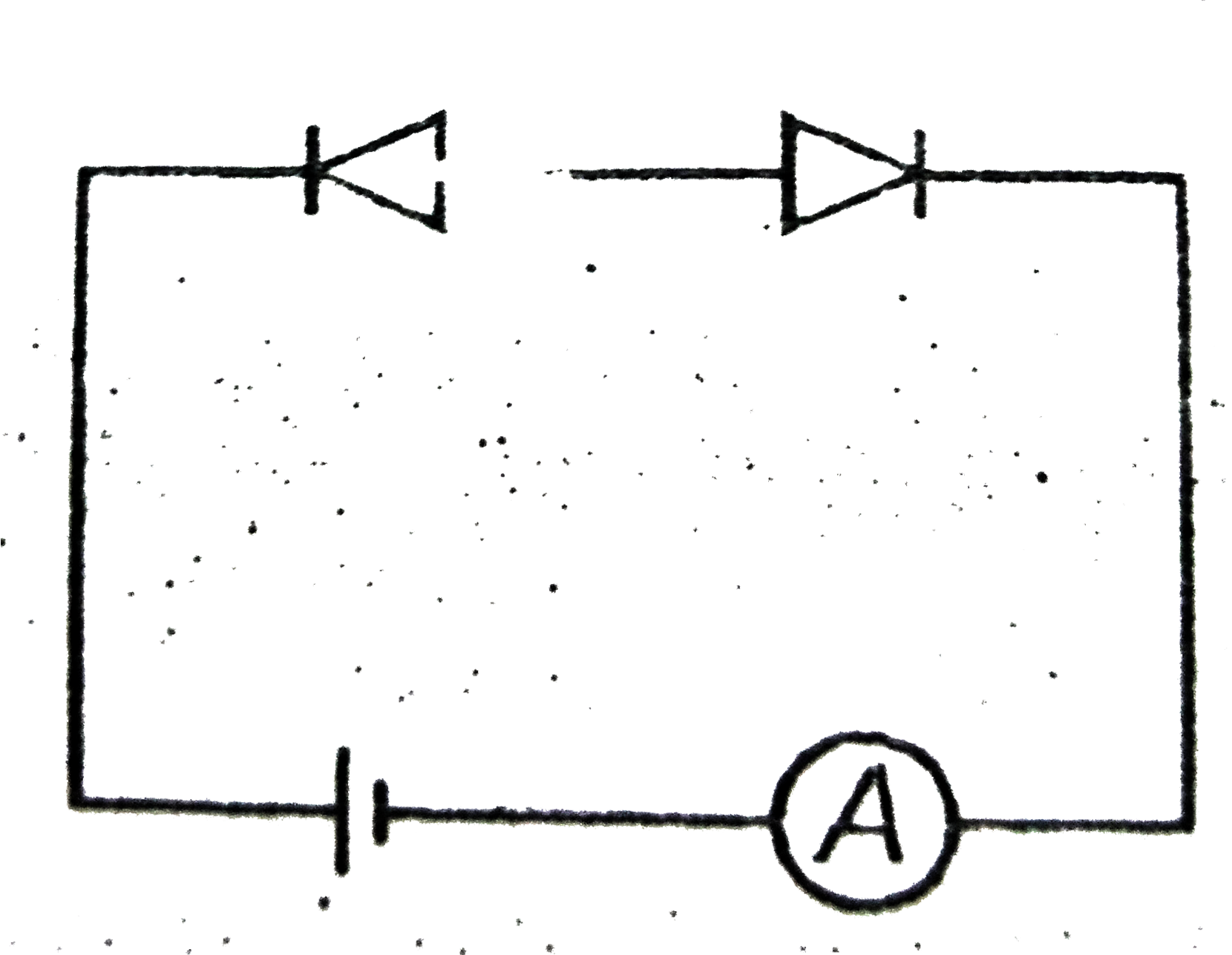
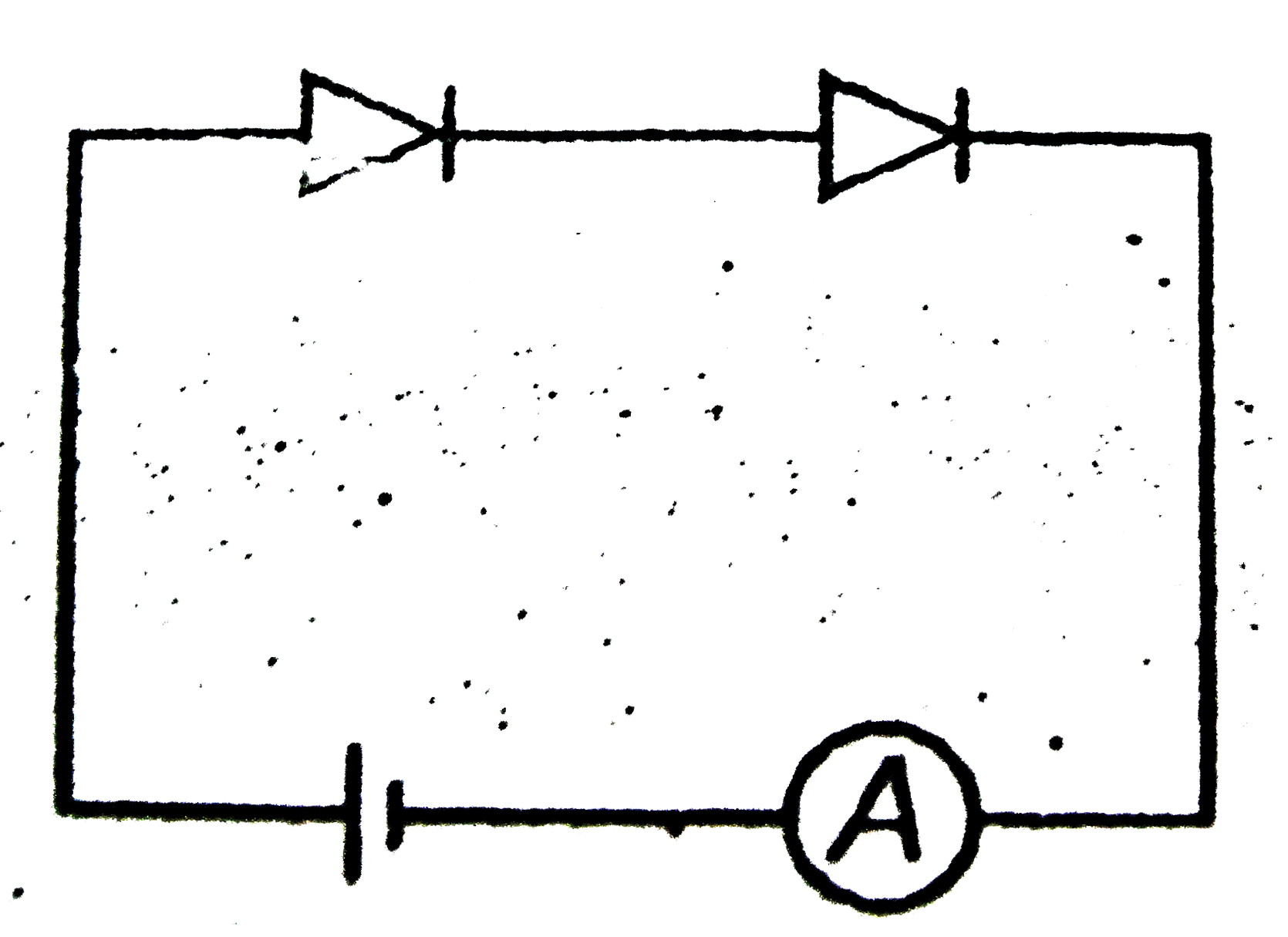
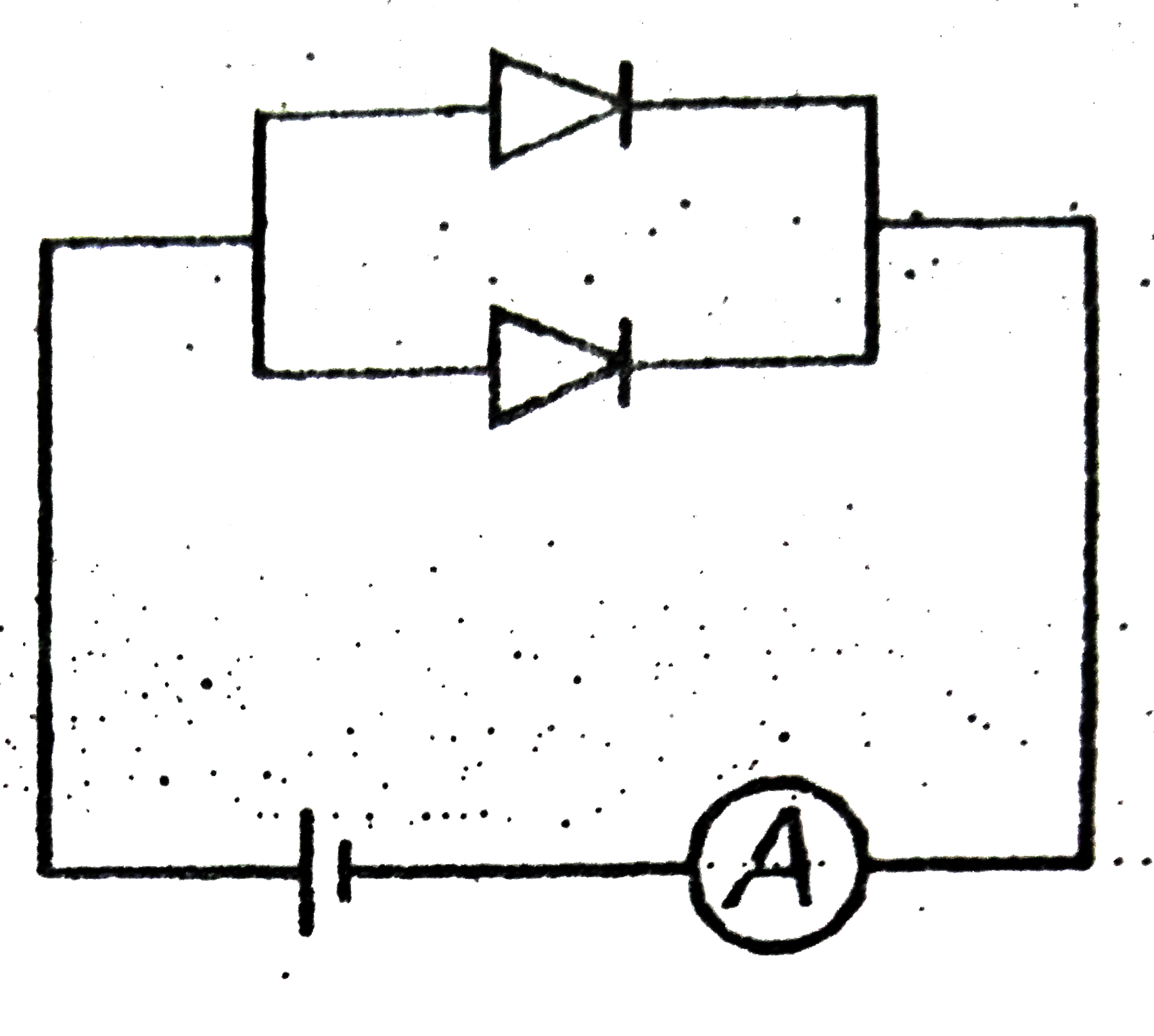
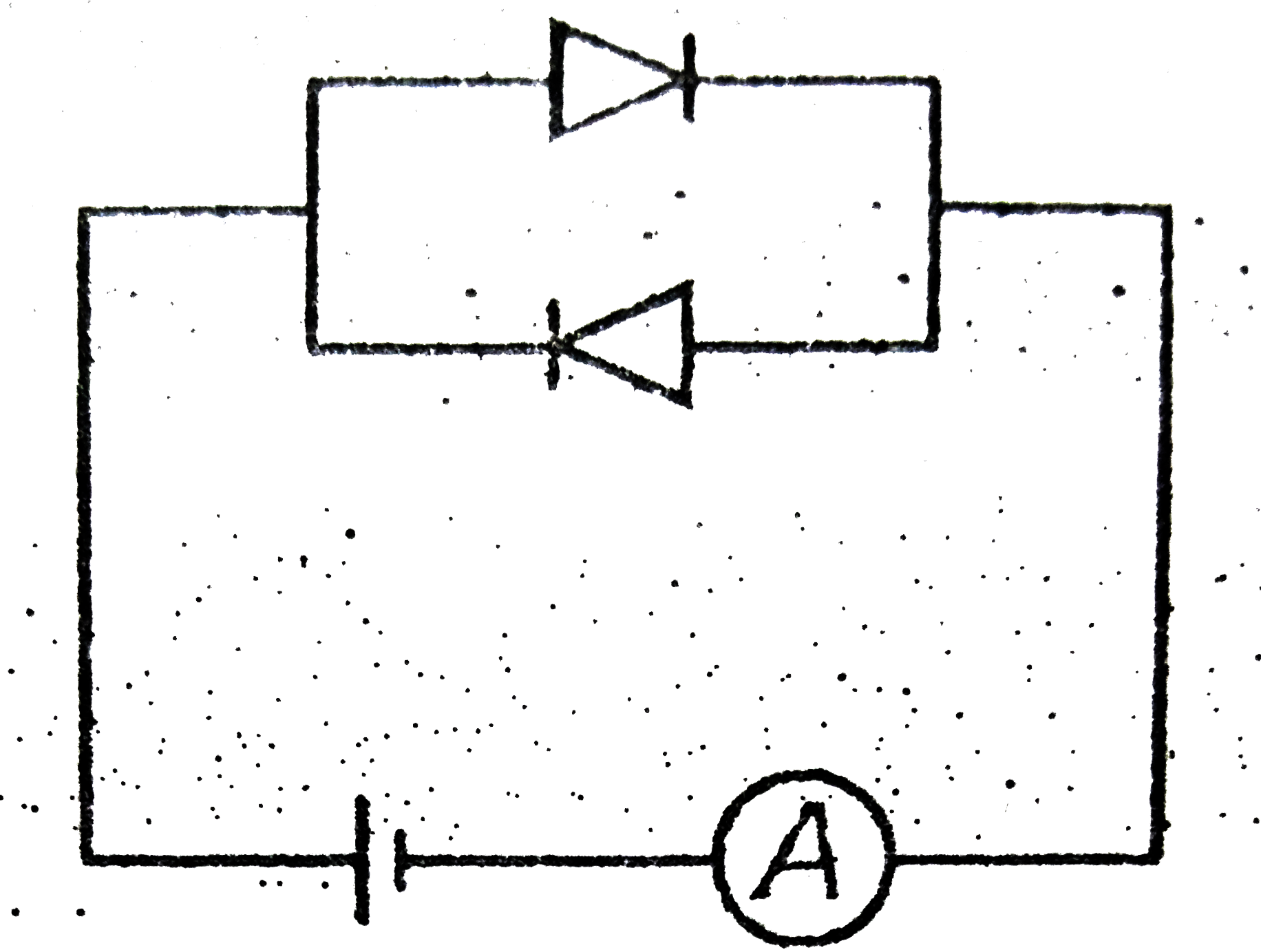
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section -B (Objective type question (one option is correct))|29 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (Section -C(Linked comprehension type question))|3 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try yourself|20 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS (MATERIAL, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRUITS )
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment SECTION - D (Assertion & reason type Question)|10 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|63 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS-Assignment (Section -A (Objective Type question (One option is correct))
- The mobility of free electrons is greater then that of free holes beca...
Text Solution
|
- Carbon , silicon and germanium have four valence electrons each . At r...
Text Solution
|
- Which circuit will not show current in ammeter ?
Text Solution
|
- A p-n photodiode is made of a material with a band gap of 2 e V. The m...
Text Solution
|
- Zener breakdown takes place if
Text Solution
|
- In the depletion region of an unbiased p-n junction diode there are
Text Solution
|
- Function of rectifier is
Text Solution
|
- In a p–n junction photo cell, the value of the photo electromotive for...
Text Solution
|
- Serious draw back of the semiconductor device is
Text Solution
|
- The reason of current flow in P-N junction forward biase is
Text Solution
|
- In the energy band diagram of a material shown below, the open circles...
Text Solution
|
- An oscillator is nothing but an amplifier with
Text Solution
|
- When a n-p-n transistor is used as an amplifier, then
Text Solution
|
- If l(1),l(2),l(3) are the lengths of the emitter, base and collector o...
Text Solution
|
- A common emitter amplifier gives an output of 3 V for an input of 0.01...
Text Solution
|
- In a common base amplifier the phase difference the input signal volta...
Text Solution
|
- In a common emitter amplifier the input signal is applied across
Text Solution
|
- The concentration of impurities in a transistor is
Text Solution
|
- In a transistor, the collector current is always · less then the emitt...
Text Solution
|
- The minimum potential difference between the base and emitter required...
Text Solution
|