Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Illustration|7 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise TRY YOURSELF|69 VideosKINETIC THEORY
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE (ASSIGNMENT) SECTION - D Assertion - Reason Type Questions|10 VideosMAGNETISM AND MATTER
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION D)|26 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-LAWS OF MOTION-Assignment (SECTION-D) (Assertion-Reason Type Questions)
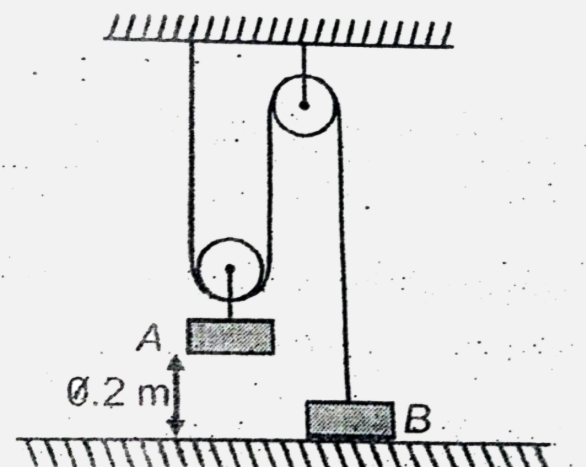
- In the arrangment shown in figure , the mass of the body A is 4 m and ...
Text Solution
|
- A : Due to inertia an object is unable to change by itself its state o...
Text Solution
|
- A : Acceleration of an object in uniform motion is zero. R : No forc...
Text Solution
|
- A : Newton's second law of motion gives the measurement of force. R ...
Text Solution
|
- A : According to Newton's third law of motion for every action, there ...
Text Solution
|
- A : Inertia depends on the mass of an object. R : Greater the mass, ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In the case of free fall of the lift, the man will feel ...
Text Solution
|
- A : Static friction force is a self adjusting force. R : The interat...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The value of dynamic friction is less than the limiting fr...
Text Solution
|
- A : During horizontal circular turn of a car, the centripetal force re...
Text Solution
|
- A : A person on a frictionless surface can get away from it by blowing...
Text Solution
|
- A : It is difficult to move a cycle along a road with its brakes on. ...
Text Solution
|
- A : It makes easier to walk on slippery muddy road if we throw some sa...
Text Solution
|
- A : Banking of roads reduces the wear and tear of the tyres of automob...
Text Solution
|
- A : The centripetal and centrifugal forces never cancel each other. ...
Text Solution
|
- A : Work done by friction can increase the kinetic energy of the body...
Text Solution
|