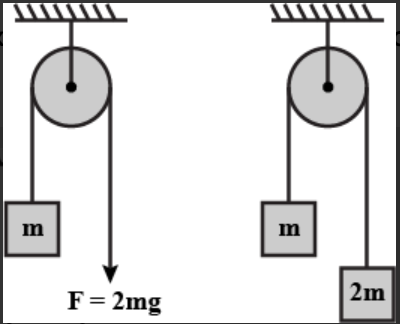
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
LAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -C) objective type questions (More than one options are correct)|21 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -D) Linked Comprehension Type Question|1 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -A)|50 VideosKINETIC THEORY
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE (ASSIGNMENT) SECTION - D Assertion - Reason Type Questions|10 VideosMAGNETISM AND MATTER
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ASSIGNMENT (SECTION D)|26 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-LAWS OF MOTION-ASSIGNMENT ( SECTION -B) objective type questions (one option is correct)
- For the system shown in figure , to be in equilibrium , determine mass...
Text Solution
|
- If two identical masses, attached by a light string passing over a lig...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitud of difference in accelerations of blocks of mass m in . B...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure the blocks A, B and C of mass m each , having accelerat...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a block of mass 2m sliding on a block of mass m. Find the...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical masses are attached by a light string that passes over a...
Text Solution
|
- A mass 2m lies on a fixed , smooth cylinder . An ideal string attached...
Text Solution
|
- A block is suspended by two light ropes r(1) and r(2) as shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m and M are connected by an inextensible light st...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 10 kg is suspended through two light spring balances a...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses M and 2M are connected to each other through a ...
Text Solution
|
- Three masses m(1) ,m(2) and m(3) are attached to a string -pulley syst...
Text Solution
|
- The block Q moves to the right with a constant velocity v(0) as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- The pull P is just sufficient to keep the 14 N block in equilibrium as...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m on a smooth horizontal surface is. Connected to a se...
Text Solution
|
- With what force must a man pull on the rope to hold the plank in posit...
Text Solution
|
- Blocks P and R starts from rest and moves to the right with accelera...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement , shown below pulleys are massless and frictionless...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in fig. m(1)=1kg, m(2)=2 kg. Pulleys are mass...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown m(1) = 1 kg , m(2) = 2 kg , pulley is ideal . At t...
Text Solution
|