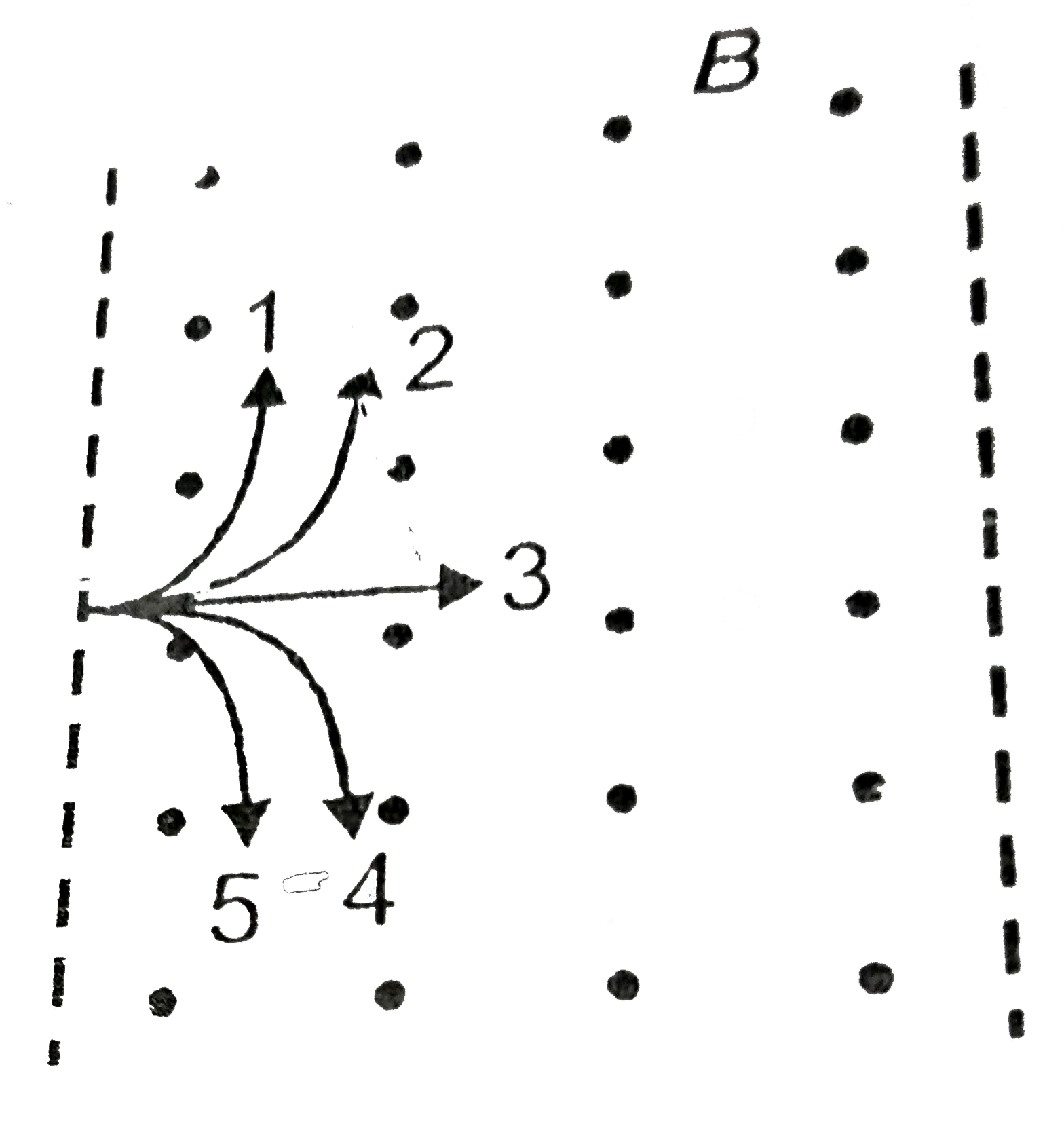
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOVING CHARGE AND MAGNESIUM
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise ILLUSTRATION|12 VideosMOVING CHARGE AND MAGNESIUM
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise TRY YOURSELF|12 VideosMOTION IN STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - J)|2 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section J (Aakash Challengers Questions)|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-MOVING CHARGE AND MAGNESIUM-SECTION D
- A proton, an electron, a neutron, an alpha-particle and an unknown par...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field produced around a straight line wire when current f...
Text Solution
|
- A : A point charge cannot exert force on itself. R : Coulomb force i...
Text Solution
|
- A: Net magnetic force expericneed by a current carrying loop in a unif...
Text Solution
|
- A: The trajectory of a charge when it is projected perpendicular to an...
Text Solution
|
- A: Like currents repel and unlike currents attract each other (in con...
Text Solution
|
- A: A magnetic dipole experiences maximum torque when it is placed norm...
Text Solution
|
- A: The relation between magnetic moment and angular momentum is true f...
Text Solution
|
- A: When currents vary with time, Newton's third law is valid only if m...
Text Solution
|
- A: In the expression for Lorentza force, vecF=q(vecvxxvecB+vecE). If o...
Text Solution
|
- A: Ampere circuital law is not independent of the Biot- Savart's law. ...
Text Solution
|
- A: The work done by magnetic field on a moving charge is zero. R: Th...
Text Solution
|
- A: In any magnetic field region the line integral ointvecB.vec(dl) alo...
Text Solution
|
- A: The magnetic field always accelerates a moving charge if the moving...
Text Solution
|
- A: The magnetic moment of a current carrying planar loop does depend o...
Text Solution
|
- A: magnetic field is produced by moving charges(s). R: The magnetic ...
Text Solution
|
- A: In the middle to high latitudes on a dark night an aurora or the cu...
Text Solution
|