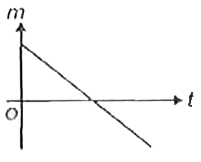
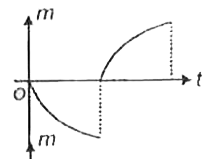
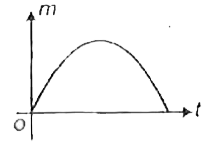
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A particle is projected at angle theta with horizontal from ground. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle is projected with a velocity at an angle with the hor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from the ground with velocity u at angle theta...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy particle is projected with a velocity at an acure angle with t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from ground at an angle theta with horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected at angle theta with horizontal from ground. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected at an angle theta with the horizontal . If ang...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected fro the ground with an initial speed v at an a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from the ground with an initial speed of 5 m s...
Text Solution
|